Facultad de Ingeniería, Universidad Autónoma de Baja California (UABC), 21280 Mexicali, Mexico
Sustainability 2017, 9(8), 1304; https://doi.org/10.3390/su9081304 - 28 Jul 2017
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 5391
Abstract
Despite the fact that the implementation of ISO 50001 has helped organizations to successfully accomplish energy saving policies, there is still a significant disparity in the number of companies certificated under ISO 50001 compared with other standards such as ISO 14001. Considering the
[...] Read more.
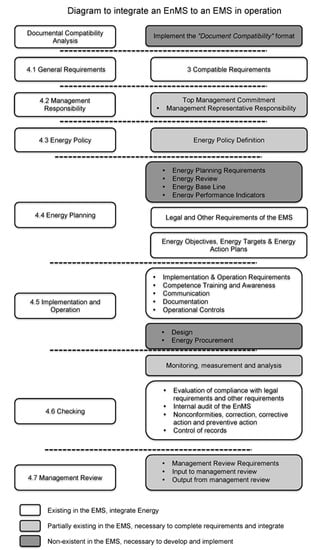
Despite the fact that the implementation of ISO 50001 has helped organizations to successfully accomplish energy saving policies, there is still a significant disparity in the number of companies certificated under ISO 50001 compared with other standards such as ISO 14001. Considering the compatibilities between both standards, a potential sector is identified for the integration of ISO 50001 in organizations that operate under ISO 14001 systems. The cost and time associated with the development and implementation of the Energy Management System are identified as being amongst the most important obstacles, restricting the number of companies that are inclined to this energy certification. As an attempt to overcome this limitation, in this work, both standards were analyzed in detail and their coincidences identified and organized to propose a novel methodology that allows companies to naturally integrate an Energy Management System based on ISO 50001 into an ISO 14001 already in operation. The results provide evidence of a strong compatibility among the energy and environmental management systems, allowing enterprises to integrate the former with minimum investment and resources. In order to validate the proposed methodology and to demonstrate the agreement between both programs, these procedures were applied in a manufacturing company of the automotive sector, considered as a high energy consumer according to the classification made by the National Commission for the Efficient Use of Energy in Mexico.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Energy Policy and Policy Implications—Good Examples and Critical Reflections)
▼
Show Figures