Sustainability 2019, 11(18), 5036; https://doi.org/10.3390/su11185036 - 14 Sep 2019
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 4507
Abstract
Energy-efficient manufacturing is an important aspect of sustainable development in current society. The rapid development of sensing technologies can collect real-time production data from shop floors, which provides more opportunities for making energy saving decisions about manufacturing systems. In this paper, a digital
[...] Read more.
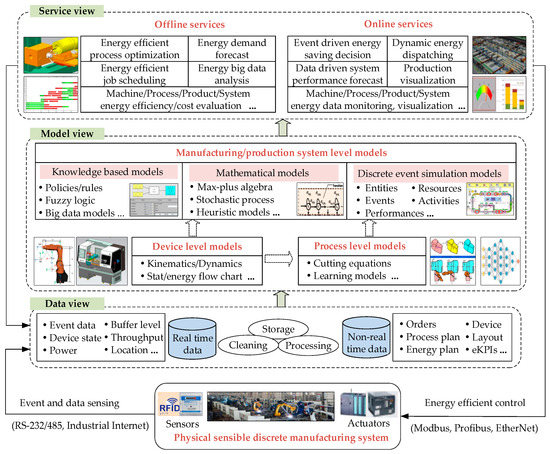
Energy-efficient manufacturing is an important aspect of sustainable development in current society. The rapid development of sensing technologies can collect real-time production data from shop floors, which provides more opportunities for making energy saving decisions about manufacturing systems. In this paper, a digital twin-based bidirectional operation framework is proposed to realize energy-efficient manufacturing systems. The data view, model view, and service view of a digital twin manufacturing system are formulated to describe the physical systems in virtual space, to perform simulation analysis, to make decisions, and to control the physical systems for various energy-saving purposes. For online energy-saving decisions about machines in serial manufacturing systems, an event-driven estimation method of an energy-saving window based on Max-plus Algebra is presented to put the target machine to sleep, considering real-time production data of a system segment. A practical, simplified automotive production line is used to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method by simulation experiments. Our method has no restriction on machine failure mode and predefined parameters for energy-saving decision of machines. The proposed approach has potential use in synchronous and asynchronous manufacturing systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Industry 4.0 for SMEs - Smart Manufacturing and Logistics for SMEs)
►
Show Figures