Viruses 2021, 13(4), 595; https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040595 - 31 Mar 2021
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3269
Abstract
Echoviruses (E) are a diverse group of viruses responsible for various pathological conditions in humans including aseptic meningitis, myocarditis, and acute flaccid paralysis. The detection and identification of echovirus genotypes in clinical samples is challenging due to its high genetic diversity. Here, we
[...] Read more.
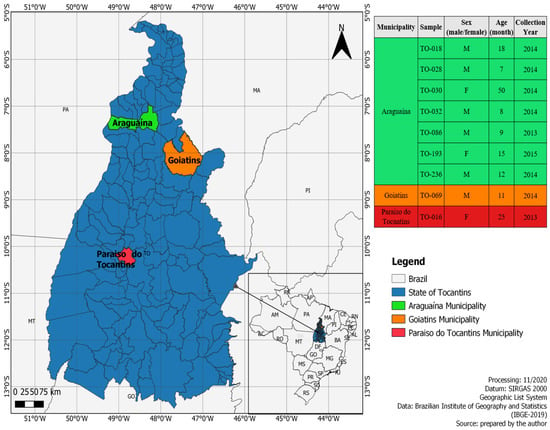
Echoviruses (E) are a diverse group of viruses responsible for various pathological conditions in humans including aseptic meningitis, myocarditis, and acute flaccid paralysis. The detection and identification of echovirus genotypes in clinical samples is challenging due to its high genetic diversity. Here, we report the complete genome sequences of nine echoviruses, obtained by next-generation sequencing of 238 fecal samples from individuals with gastroenteritis in regions of Brazil. Detected viruses were classified into six genotypes: Three E1 sequences (BRA/TO-028, BRA/TO-069 and BRA/TO-236), one E3 (BRA/TO-018), one E11 (BRA/TO-086), one E20 (BRA/TO-016), two E29 (BRA/TO-030 and BRA/TO-193), and one E30 sequence (BRA/TO-032). Phylogenetic analysis indicated that the echoviruses E1 and E29 circulating in Brazil are divergent from strains circulating worldwide. The genotype diversity identified in our study may under-represent the total echovirus diversity in Brazil because of the small sample size and the restricted geographical distribution covered by the survey.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Enteroviruses 2021)
►
Show Figures