Forests 2019, 10(4), 300; https://doi.org/10.3390/f10040300 - 1 Apr 2019
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 3384
Abstract
The retention forestry approach is considered as one of the potentially effective tools for sustainable forest management for conservation of biodiversity in managed temperate and boreal forests. Retention of old-growth forest structures (e.g., very large old living trees) in forest stands during clear-cutting
[...] Read more.
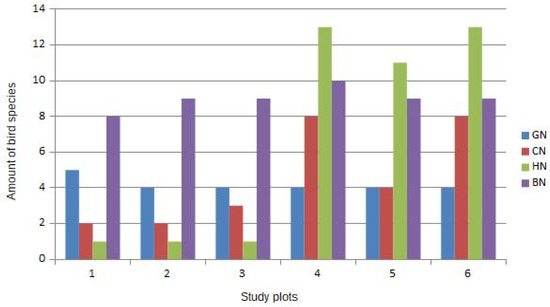
The retention forestry approach is considered as one of the potentially effective tools for sustainable forest management for conservation of biodiversity in managed temperate and boreal forests. Retention of old-growth forest structures (e.g., very large old living trees) in forest stands during clear-cutting provides maintenance of key habitats for many old-growth forest interior-species. Most of ecological studies on green tree retention (GTR) consequences for biodiversity have been focused on birds. However, the long-term studies of GTR impacts on forest birds are very poor. In this paper, we focused on assessment of the long-term consequences of leaving legacy oak trees on the cut areas for bird diversity 18–22 years after clear-cutting in managed temperate European hardwood floodplain forests. Results based on bird counting using mapping of bird nesting territories revealed a key importance of legacy oak trees for maintaining bird diversity in the study area. These results are widely applicable for managed temperate hardwood forests with serious dominance of oak (Quercus sp.) in forest stands. Legacy oak trees in this habitat type are keystone structures for bird diversity. Retention approach focused on these trees is potentially an important conservation tool for preserving forest bird diversity and other associated species in temperate hardwood forests managed by clear-cutting.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effects of Forest Management Practices on Forest Biodiversity)
►
Show Figures