Sensors 2022, 22(15), 5925; https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155925 - 8 Aug 2022
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3995
Abstract
In this paper, we proposed an accurate and robust method for absolute pose estimation with UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) using RANSAC (random sample consensus). Because the artificial 3D control points with high accuracy are time-consuming and the small point set may lead low
[...] Read more.
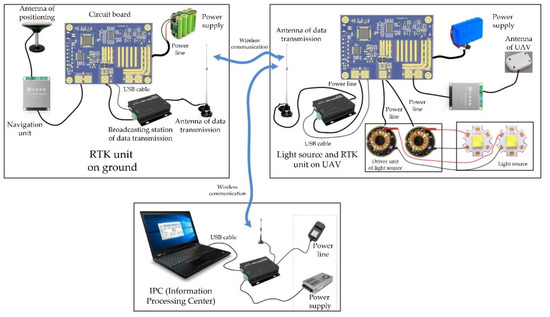
In this paper, we proposed an accurate and robust method for absolute pose estimation with UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) using RANSAC (random sample consensus). Because the artificial 3D control points with high accuracy are time-consuming and the small point set may lead low measuring accuracy, we designed a customized UAV to efficiently obtain mass 3D points. A light source was mounted on the UAV and used as a 3D point. The position of the 3D point was given by RTK (real-time kinematic) mounted on the UAV, and the position of the corresponding 2D point was given by feature extraction. The 2D–3D point correspondences exhibited some outliers because of the failure of feature extraction, the error of RTK, and wrong matches. Hence, RANSAC was used to remove the outliers and obtain the coarse pose. Then, we proposed a method to refine the coarse pose, whose procedure was formulated as the optimization of a cost function about the reprojection error based on the error transferring model and gradient descent to refine it. Before that, normalization was given for all the valid 2D–3D point correspondences to improve the estimation accuracy. In addition, we manufactured a prototype of a UAV with RTK and light source to obtain mass 2D–3D point correspondences for real images. Lastly, we provided a thorough test using synthetic data and real images, compared with several state-of-the-art perspective-n-point solvers. Experimental results showed that, even with a high outlier ratio, our proposed method had better performance in terms of numerical stability, noise sensitivity, and computational speed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue 3D Object and Scene Detection, Reconstruction, Segmentation Based on Advanced Sensing Technology)
►
Show Figures