Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(6), 5490; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065490 - 13 Mar 2023
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 2476
Abstract
Dogs are highly valued companions and work animals that are susceptible to many life-threatening conditions such as canine leishmaniosis (CanL). Plasma-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs), exploited extensively in biomarker discovery, constitute a mostly untapped resource in veterinary sciences. Thus, the definition of proteins associated
[...] Read more.
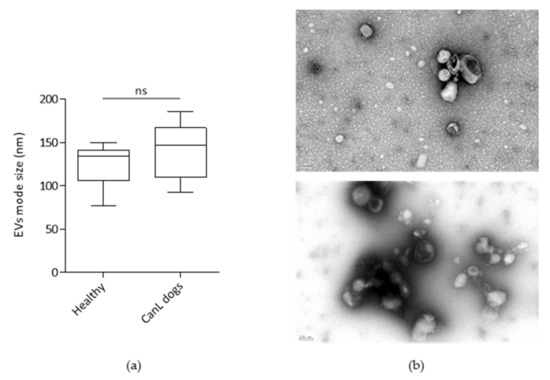
Dogs are highly valued companions and work animals that are susceptible to many life-threatening conditions such as canine leishmaniosis (CanL). Plasma-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs), exploited extensively in biomarker discovery, constitute a mostly untapped resource in veterinary sciences. Thus, the definition of proteins associated with plasma EVs recovered from healthy and diseased dogs with a relevant pathogen would be important for biomarker development. For this, we recovered, using size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), EVs from 19 healthy and 20 CanL dogs’ plasma and performed proteomic analysis by LC-MS/MS to define their core proteomic composition and search for CanL-associated alterations. EVs-specific markers were identified in all preparations and also non-EVs proteins. Some EVs markers such as CD82 were specific to the healthy animals, while others, such as the Integrin beta 3 were identified in most samples. The EVs-enriched preparations allowed the identification of 529 canine proteins that were identified in both groups, while 465 and 154 were only identified in healthy or CanL samples, respectively. A GO enrichment analysis revealed few CanL-specific terms. Leishmania spp. protein identifications were also found, although with only one unique peptide. Ultimately, CanL-associated proteins of interest were identified and a core proteome was revealed that will be available for intra- and inter-species comparisons.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Extracellular Vesicles and Nanoparticles)
►
Show Figures