Molecules 2021, 26(10), 2867; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102867 - 12 May 2021
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 5465
Abstract
Aldose reductase (AR, ALR2), the first enzyme of the polyol pathway, is implicated in the pathophysiology of diabetic complications. Aldose reductase inhibitors (ARIs) thus present a promising therapeutic approach to treat a wide array of diabetic complications. Moreover, a therapeutic potential of ARIs
[...] Read more.
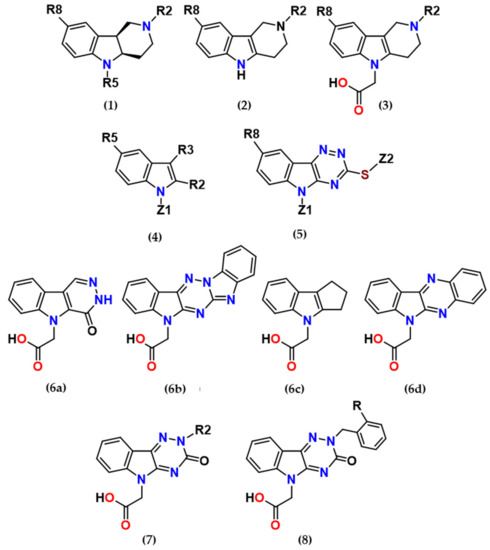
Aldose reductase (AR, ALR2), the first enzyme of the polyol pathway, is implicated in the pathophysiology of diabetic complications. Aldose reductase inhibitors (ARIs) thus present a promising therapeutic approach to treat a wide array of diabetic complications. Moreover, a therapeutic potential of ARIs in the treatment of chronic inflammation-related pathologies and several genetic metabolic disorders has been recently indicated. Substituted indoles are an interesting group of compounds with a plethora of biological activities. This article reviews a series of indole-based bifunctional aldose reductase inhibitors/antioxidants (ARIs/AOs) developed during recent years. Experimental results obtained in in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo models of diabetic complications are presented. Structure–activity relationships with respect to carboxymethyl pharmacophore regioisomerization and core scaffold modification are discussed along with the criteria of ‘drug-likeness”. Novel promising structures of putative multifunctional ARIs/AOs are designed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Designed Multiple Ligands in Drug Design and Development)
►
Show Figures