Molecules 2017, 22(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010011 - 23 Dec 2016
Cited by 40 | Viewed by 7792
Abstract
Psidium is a genus of tropical bushes belonging to the Myrtaceae family distributed in Central and South America. The polar extract of Psidium friedrichsthalianum Nied. was partitioned with ethyl ether, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol, and the total phenolic content and antioxidant activity
[...] Read more.
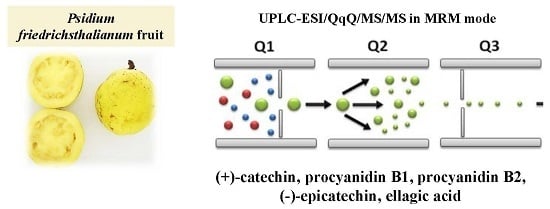
Psidium is a genus of tropical bushes belonging to the Myrtaceae family distributed in Central and South America. The polar extract of Psidium friedrichsthalianum Nied. was partitioned with ethyl ether, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol, and the total phenolic content and antioxidant activity were measured by Folin-Ciocalteu and ABTS assays, respectively. The ethyl acetate fraction exhibited both the highest phenolic content and antioxidant activity. Due to the complexity of this fraction, an analytical method for the comprehensive profiling of phenolic compounds was done by UPLC-ESI/QqQ in MRM (multiple reaction monitoring) mode. In this targeted analysis, 22 phenolic compounds were identified, among which several hydroxybenzoic, phenylacetic, and hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives were found. This is the first time that (+)-catechin, procyanidin B1, procyanidin B2, and (−)-epicatechin have been reported as constituents of sour guava. A fractionation by exclusion size, C18-column chromatography, and preparative RRLC (rapid resolution liquid chromatography) allowed us to confirm the presence of ellagic acid and isomeric procyanidins B, well-known bioactive compounds. The content of phenolic compounds in this fruit shows its potential for the development of functional foods.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Flavonoids: From Structure to Health Issues)
►
Show Figures