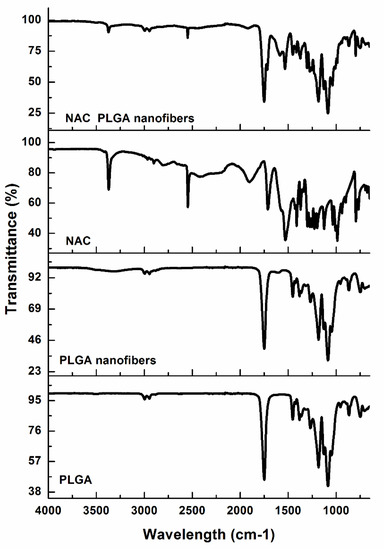
Pharmaceutics 2020, 12(10), 940; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100940 - 30 Sep 2020
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2920
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Cancer treatment has been greatly improved by the combined use of targeted therapies and novel biotechnological methods. Regarding the former, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) has a preferential accumulation within cancer tumors, thus having lower toxicity on healthy cells. PLD has been implemented in
[...] Read more.
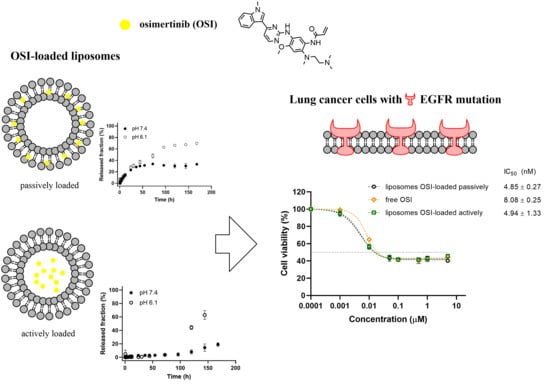
Cancer treatment has been greatly improved by the combined use of targeted therapies and novel biotechnological methods. Regarding the former, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) has a preferential accumulation within cancer tumors, thus having lower toxicity on healthy cells. PLD has been implemented in the targeted treatment of sarcoma, ovarian, breast, and lung cancer. In comparison with conventional doxorubicin, PLD has lower cardiotoxicity and hematotoxicity; however, PLD can induce mucositis and palmo-plantar erythrodysesthesia (PPE, hand-foot syndrome), which limits its use. Therapeutical apheresis is a clinically proven solution against early PLD toxicity without hindering the efficacy of the treatment. The present review summarizes the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of PLD and the beneficial effects of extracorporeal apheresis on the incidence of PPE during chemoradiotherapy in cancer patients.
Full article