- Review
Applications of Large Language Models in Glaucoma: A Scoping Review
- Giovanni Rubegni,
- Alessandra Cartocci and
- Gian Marco Tosi
- + 6 authors
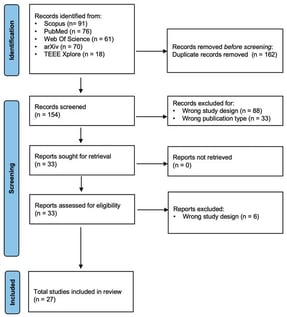
Background: Large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs) have recently been applied to ophthalmology for patient education, diagnosis, and surgical decision support. Their ability to generate, interpret, and synthesize medical information positions them as promising assistive tools in glaucoma care. This scoping review aims to consolidate current evidence on the applications of LLMs and VLMSs in glaucoma, summarizing their tasks, inputs, performance metrics, and limitations to guide future clinical and research developments. Methods: A systematic search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, arXiv, and IEEE Xplore from 2014 to July 2025. Eligible studies included original research and research letters employing LLMs or VLMs/MM-LLMs in any glaucoma-related application, including diagnostic reasoning, image interpretation, patient education, or surgical decision support. Screening and full-text review were independently performed by two reviewers following PRISMA-ScR methodology, with discrepancies resolved by consensus. Results: In total, 316 records were identified across five databases, with 27 studies meeting the inclusion criteria. The selected studies focused on three main domains: patient education (n = 11), diagnosis and risk prediction (n = 10), and surgical management (n = 6). Conclusions: Current LLMs serve best as assistive rather than autonomous tools in glaucoma care. They demonstrate strong potential in patient communication and text-based clinical decision support but remain constrained by variable accuracy, limited multimodal integration, and a lack of ophthalmology-specific fine-tuning. Future research should focus on developing domain-trained and retrieval-augmented LLMs, enhancing multimodal (text-image) fusion, ensuring readability adaptation for patients, and establishing ethical and regulatory frameworks for clinical implementation.
9 February 2026