Journal Description
Uro
Uro
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of urology and andrology, including oncology, endourology, sexual dysfunction, fertility, and infertility, published quarterly online by MDPI. The Italian Society of Andrology (SIA) is affiliated to Uro, and its members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 23.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 9.2 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Uro is a companion journal of JCM.
Latest Articles
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for High-Risk Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Uro 2026, 6(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro6010006 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) is increasingly used for localized prostate cancer (PCa), but evidence supporting its use in high-risk PCa (HRPC) remains limited. Standard management continues to favor conventional or moderately hypofractionated radiotherapy combined with long-course androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). This
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) is increasingly used for localized prostate cancer (PCa), but evidence supporting its use in high-risk PCa (HRPC) remains limited. Standard management continues to favor conventional or moderately hypofractionated radiotherapy combined with long-course androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). This systematic review aimed to synthesize current data on SBRT biochemical outcomes, toxicity, and technical aspects in localized HRPC. Methods: A systematic PubMed search was conducted on 1 May 2024, following PRISMA 2020 guidelines (PROSPERO ID CRD420251235649). Studies reporting biochemical control (BC) for HRPC treated definitively with SBRT, with or without ADT, were included. Studies not meeting these criteria or including ≤10 HRPC patients were excluded. Risk of bias was assessed through qualitative appraisal of study methodology. Substantial heterogeneity across study design, SBRT schedules, cohort composition, and ADT integration precluded a meta-analysis; data were synthesized descriptively. Results: Thirty studies contributed biochemical control data after prostate SBRT for 1354 patients meeting inclusion criteria. SBRT was delivered using diverse platforms and dose-fractionation schemes, frequently in combination with ADT. Across studies, BC was generally favorable, though follow-up duration varied widely. Toxicity profiles were acceptable, with most reports describing predominantly grade 1–2 events and low rates of severe toxicity. Marked variability was observed in target volume definition, focal-boost strategies, urethra-sparing techniques, and the use of rectal spacers. Conclusions: Although current evidence is heterogeneous and largely derived from non-randomized studies, BC and toxicity outcomes are consistently promising, supporting SBRT as a potentially effective strategy for localized HRPC. Randomized prospective trials are needed to confirm these findings and refine optimal SBRT regimens and the role of ADT. This review received no funding.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Updated Analysis: Blue-Light Transurethral Resection and Biopsy of Bladder Cancer with Hexaminolevulinate in a Single UK Centre
by
Anushree Kucheria, Elaina Gubbay, Aoife Meabh Linzell, Irfan Kar, Mohammad Alomari, Kimberley Chan, Christine Gan and Nikhil Vasdev
Uro 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro6010005 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the diagnostic yield of blue-light cystoscopy (BLC) compared with white-light cystoscopy (WLC) in detecting carcinoma in situ (CIS) and muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC), and to assess recurrence-free survival (RFS) following BLC-HAL resection. Patients and Methods: We retrospectively analysed 238 patients
[...] Read more.
Objective: To evaluate the diagnostic yield of blue-light cystoscopy (BLC) compared with white-light cystoscopy (WLC) in detecting carcinoma in situ (CIS) and muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC), and to assess recurrence-free survival (RFS) following BLC-HAL resection. Patients and Methods: We retrospectively analysed 238 patients undergoing BLC-HAL between July 2017 and July 2024. Seventy-two underwent primary BLC at initial resection, and 166 underwent BLC re-resection following WLC. Endpoints were CIS detection, tumour upstaging, and recurrence-free survival at 12 and 24 months using Kaplan–Meier analysis. Results: Overall, malignancy was confirmed in 113/238 patients (47%). Detection was higher in the secondary arm (55%) compared with the primary arm (29%). In the primary arm, CIS was detected in 19% and MIBC in 24%. In the secondary arm, CIS increased from 18% on WLC to 38% with BLC (p = 0.001), with 26% detected only under blue light; 10% were upstaged to MIBC (p = 0.022). Over one-third of patients were reclassified into a higher EAU NMIBC risk group. Kaplan–Meier analysis showed 12- and 24-month RFS of 71% (95% CI: 36–92%) and 67% (95% CI: 35–88%) in the primary arm, and 62% (95% CI: 49–74%) and 63% (95% CI: 43–79%) in the secondary arm. Median RFS was not reached within 24 months. Conclusions: BLC significantly enhances CIS detection and identifies MIBC and higher-risk disease not seen on WLC, directly influencing patient management. Despite improved detection, recurrence-free survival remains modest, consistent with high-risk NMIBC, supporting guideline recommendations for routine use of BLC at TURBT, particularly in suspected CIS and high-grade disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Clinical Management of Urologic Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Role of Nutraceuticals and Phytotherapy in Andrological Diseases: Tips and Tricks for Everyday Clinical Practice
by
Andrea Abramo, Tommaso Ceccato, Simone Botti, Daniele Mattevi, Nicola Mondaini, Luca Gallelli, Truls E. Bjerklund Johansen, Michele Rizzo, Giovanni Liguori, Alessandro Zucchi, Alessandro Palmieri, Luca Boeri and Tommaso Cai
Uro 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro6010004 - 30 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Interest in the use of nutraceuticals and phytotherapy for the management of andrological diseases has increased markedly in recent years. In particular, growing attention has been directed toward the treatment of patients affected by erectile dysfunction (ED), male infertility, chronic prostatitis/chronic
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Interest in the use of nutraceuticals and phytotherapy for the management of andrological diseases has increased markedly in recent years. In particular, growing attention has been directed toward the treatment of patients affected by erectile dysfunction (ED), male infertility, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), and induratio penis plastica (IPP). However, several areas of uncertainty remain. This narrative review aims to examine the role of nutraceuticals and phytotherapeutic agents in the management of andrological disorders. Methods: A narrative review was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane CENTRAL, and EMBASE to identify relevant studies published over the past 25 years. Only articles published in English and involving adult populations were included in the analysis. Results: Nutraceuticals and phytotherapeutic compounds have been extensively investigated in the current literature, and certain formulations—particularly specific combinations—have been evaluated in high-quality studies. Conversely, other compounds lack sufficient scientific evidence and therefore should not be recommended in routine clinical practice. In the management of ED, the following compounds, administered either alone or in combination, have demonstrated clinically significant effects: Panax ginseng, Tribulus terrestris, L-arginine, and Withania somnifera. L-carnitine, combined with micronutrients, antioxidants, and various traditional herbal supplements, appears to be an effective therapeutic option for male infertility and subfertility. Pollen extracts play an important role in the management of CP/CPPS, while carnitine, coenzyme Q10, silymarin, bromelain, and curcumin show promising potential in the treatment of IPP. Conclusions: Nutraceuticals and phytotherapeutic agents may provide favorable outcomes in the management of andrological diseases. Although current evidence is encouraging, larger prospective studies employing standardized protocols and treatment schedules are required to confirm long-term efficacy and to optimize therapeutic strategies.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Differences in Quality of Life Related to Lower Urinary Tract, Bowel and Sexual Function After Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy in Patients with and Without Nerve-Sparing
by
Danae Merentitis, Julia Neuenschwander, Beat Foerster, Hubert John, Lucas M. Bachmann, Nicolas S. Bodmer and Jure Tornic
Uro 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro6010003 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The objective of this study is to compare nerve-sparing (NS) and non-nerve-sparing (NNS) robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) techniques used to treat localized prostate cancer. Numerous studies have evaluated the impact of NS techniques on patient-reported outcomes. However, there are unaddressed methodological
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The objective of this study is to compare nerve-sparing (NS) and non-nerve-sparing (NNS) robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) techniques used to treat localized prostate cancer. Numerous studies have evaluated the impact of NS techniques on patient-reported outcomes. However, there are unaddressed methodological issues making interpretation of results difficult. Therefore, we performed a comparison of the two techniques, accounting for methodological threats, including patient selection and confounding. Methods: We sampled 120 patients with similar disease burden who underwent RARP by the same surgeon, either with NS (n = 84) or NNS (n = 36) and assessed changes in lower urinary tract (LUT) function and bother, and bowel function/bother using the Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC) questionnaire and the six-item International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-6) survey at 6 weeks and 12 months postoperatively. Multivariable linear regression models were used to adjust for differences in age, preoperative PSA levels, pathological tumor stage and Gleason-score of patients receiving either NS or NNS. Results: At 6 weeks postoperatively, the NNS group had a significantly larger decrease in LUT function compared to the NS group (−17.42; 95% Confidence Interval (CI): −31.31, −3.53; p = 0.0145). At 12 months, both groups recovered substantially, and no group differences were observed (p > 0.9). No significant differences were observed between the NS and NNS groups for the EPIC bowel subscores, whereas the IIEF-6 showed borderline significance at 12 months. Conclusions: The results suggest a small impact of NS vs. NNS RARP on important patient-reported outcomes when controlling for tumor biology, surgeon skill, and patient characteristics. These results need to be confirmed by larger studies using similar sampling strategies and design considerations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Clinical Management of Urologic Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Effect of Preoperative Pelvic Floor Muscle Training on Erectile Dysfunction After Radical Prostatectomy—A Systematic Review
by
Vahid Mehrnoush, Dhruv Lalkiya, Nilanga Aki Bandara, Fatemeh Darsareh, Emmanuelle Rousseau, Sara Paziraei, Omar AbdelAziz, Waleed Shabana and Walid Shahrour
Uro 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro6010002 - 29 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: The societal effects of prostate cancer are profound. Prostate surgeries remain one of the main treatment modalities in the care of prostate cancer, and one of the common complications associated with this procedure is postoperative erectile dysfunction (ED). ED can have
[...] Read more.
Background: The societal effects of prostate cancer are profound. Prostate surgeries remain one of the main treatment modalities in the care of prostate cancer, and one of the common complications associated with this procedure is postoperative erectile dysfunction (ED). ED can have a significant negative impact on men’s quality of life. The included articles from the last systematic review on effect of pre-operative pelvic floor muscle training (PPFMT) on ED after radical prostatectomy (RP) showed mixed findings but recommended the need for better exercise regime to witness better outcome. Therefore, this systematic review aims to provide further evidence from 2018 to understand the impact of PPFMT on postoperative ED and provide latest insights for future research. Methods: A systematic search was conducted on Medline, Embase, CINAHL, and Google Scholar from 2018 to June 2025, with the assistance of a subject-expert librarian. The inclusion criteria include articles which examine the effect of PPFMT on ED post prostatectomy from 2018 to June 2025 and have a minimum of two comparative groups (control vs. case). In addition, non-English articles were excluded from the study. The included articles were further assessed by two independent reviewers using Covidence, and disagreements were resolved by another independent reviewer. Results: A total of 344 articles were located and after removing duplicates, 250 articles remained. Following the abstract and title screening, nine articles were assessed for eligibility. Upon full-text review, three studies (two randomized control trials (RCTs) and one non-RCT) were ultimately included. The two RCTs showed no significant impact of PPFMT on post-operative ED. On the other hand, the non-RCT reported a significant difference in the post-operative ED rate in the case (5%) vs. control (48.6%) group. PPFMT was defined as ten pre-operative physiotherapy sessions in ten consecutive working days using anal biofeedback. Conclusions: The current study, since 2018, reveals mixed findings on the effect of PPFMT on postoperative ED. However, upon reviewing the evidence on the positive role of PPFMT in other fields (e.g., gynecology, general surgery), we noticed that the included studies may be lacking some major components like knowledge assessment, subjective and objective assessment, along with characteristics of sessions (number, duration, intensity, interval to surgery, and biofeedback) that play a crucial role in the effectiveness of the PPFMT in strengthening the pelvic floor muscle and improving the outcomes. Further research with robust designs is warranted.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Clinical, Translational, and Basic Research and Novel Therapy on Functional Bladder Diseases and Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunctions)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prostate Cancer Health Information on Google Using the Quality Evaluation Scoring Tool (Quest): A Cross-Sectional, Multilingual Analysis
by
Nikola Jeker, Matthias Walter and Christian Wetterauer
Uro 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro6010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The internet is a major source of health information, including prostate cancer, but the quality of such content is inconsistent and may influence patient decision-making. This study aimed to evaluate the quality of online prostate cancer information by language, location, and
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The internet is a major source of health information, including prostate cancer, but the quality of such content is inconsistent and may influence patient decision-making. This study aimed to evaluate the quality of online prostate cancer information by language, location, and user mode (“Logged off” vs. “Anonymous”) using the Google search engine. Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional, observational study between 5 and 11 December 2022, evaluating Google search results for prostate cancer information across three European cities (Basel, Munich, and Paris) and three languages (English, German, and French) in both “Logged off” and “Anonymous” user modes. A total of 900 websites (450 per mode) were retrieved and classified as: (1) university, (2) hospital, (3) governmental/medical societies, (4) industrial/commercial/NGOs, or (5) other. Website quality was assessed using the validated QUEST, which evaluates authorship, attribution, conflicts of interest, currency, and evidence. Inclusion rates and QUEST scores were compared across languages, locations, and categories using Kruskal-Wallis tests with multiple comparison adjustments. A total of 900 websites (450 per mode) were retrieved in English, German, and French from searches conducted in Basel, Munich, and Paris. Websites were classified as: (1) university, (2) hospital, (3) governmental/medical societies, (4) industrial/commercial/NGOs, or (5) other. Quality was assessed using the QUEST, which evaluates authorship, attribution, conflicts of interest, currency, and evidence. Inclusion rates and QUEST scores were compared across languages, locations, and categories using Kruskal-Wallis tests with multiple comparison adjustments. Results: Inclusion rates were high for both modes (Logged off: 86%; Anonymous: 85%). Location-based differences were significant for Basel (p = 0.04) and Paris (p = 0.02), while language-based differences were not significant. In “Logged off” mode, Category 1 achieved the highest median QUEST score (18.3), followed by 3 (17.8), while Category 2 scored lowest (14.2). Differences were significant (χ2 = 50, p < 0.001), particularly between Categories 2 vs. 3 and 2 vs. 4 (p < 0.001). Similar patterns were observed in the “Anonymous” mode. Conclusions: Online prostate cancer information varies substantially in quality. French-language sites, despite high inclusion rates, were of lower quality, while English and German content more frequently met high-quality standards. University websites were the most reliable, hospital websites the least. Language, location, and site type influence the accessibility and reliability of online prostate cancer information.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Crossroads of Cancer Regulation: Discussing the Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Bladder Cancer Stem Cells
by
Alexandros Georgiou, Dimitrios Triantis, Maria Goulielmaki and Vassilis Zoumpourlis
Uro 2025, 5(4), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5040022 - 11 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Despite substantial progress in the field of bladder cancer management, the disease continues to represent an important health issue characterized by increased recurrence and progression rates. This is largely attributed to cancer stem cells (CSCs), a unique cell subpopulation capable of self-renewal, differentiation
[...] Read more.
Despite substantial progress in the field of bladder cancer management, the disease continues to represent an important health issue characterized by increased recurrence and progression rates. This is largely attributed to cancer stem cells (CSCs), a unique cell subpopulation capable of self-renewal, differentiation and resistance to conventional anti-cancer therapies. At the same time, our understanding of cancer biology has been revolutionized by the identification of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), a heterogeneous group of RNA molecules that do not translate into proteins yet function as pivotal regulators of gene expression. Emerging evidence demonstrates that ncRNAs modulate key hallmarks of CSCs, including self-renewal, epithelial–mesenchymal transition and drug resistance. This review investigates the intricate interplay between ncRNAs and the core signaling pathways that underlie bladder CSC biology. Unravelling the nexus between CSCs and ncRNAs is crucial for developing novel diagnostic biomarkers, better prognostic tools and innovative therapeutic strategies for patients with bladder cancer.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Dissecting the Development of the Evaluation and Management of Pediatric Diurnal Enuresis
by
Alicia DuPont, Caroline Little, Veronica Vuong, Rachael Martino, Zia Flaminio, Heather Ferrill and Benjamin Brooks
Uro 2025, 5(4), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5040021 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Diurnal enuresis can significantly affect a child’s biopsychosocial well-being; however, there is a lack of diagnostic and management algorithms on the diagnosis. The purpose of this literature review is to dissect the development of the evaluation and management of diurnal enuresis. A total
[...] Read more.
Diurnal enuresis can significantly affect a child’s biopsychosocial well-being; however, there is a lack of diagnostic and management algorithms on the diagnosis. The purpose of this literature review is to dissect the development of the evaluation and management of diurnal enuresis. A total of 44 articles published from January 1900 to December 2024 were chosen through literature searches in PubMed, Science Direct, Embase, and Google scholar. Search terms were “Diurnal Enuresis” or “Daytime Incontinence” as Mesh terms, and subsequent terms included “pediatrics”, “urinary bladder, overactive”, and “therapeutics”. Inclusion criteria included studies involving pediatric study subjects aged 5–18 years old with a specific diagnosis of diurnal enuresis, exclusion criteria were studies before 1900 and involving night-time wetting diagnoses. A consensus among the literature and the American Academy of Family Physicians recommends a stepwise diagnostic evaluation, including history taking followed by a focused physical exam, for diurnal enuresis has proven to be the most effective. Regarding treatment, biofeedback was shown to improve symptoms in 74% of cases in one study by Wiener, while pharmacological treatment via Mirabegron (beta 3 agonist) showed a 70% improvement in one study by Fryer, but older drugs such as oxybutynin (anticholinergics) are still preferred. A multidisciplinary approach with TENS therapy, behavioral modification, biofeedback, and pharmacology can enhance effectiveness, improve reliability, and provide more successful results while minimizing the impact of diurnal enuresis on a child’s well-being. Further research is needed to optimize pharmacologic management strategies and improve adherence to increase the likelihood of reaching treatment goals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Clinical, Translational, and Basic Research and Novel Therapy on Functional Bladder Diseases and Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunctions)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Omitting the Second Bladder Resection: A 3-Year Prospective Pilot Study
by
Juliusz Jan Szczesniewski, Carlos Tellez-Fouz, Francisco Javier Diaz-Goizueta, Ana García-Tello, David Esteban Diaz-Perez and Luis Llanes-Gonzalez
Uro 2025, 5(4), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5040020 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The study aimed to find out if the patients without a reTURBT, due to changed protocol in our centre because of the COVID-19 pandemic, had presented higher rates of relapse or progression compared to patients treated by standard reTURBT protocol. Methods: A
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The study aimed to find out if the patients without a reTURBT, due to changed protocol in our centre because of the COVID-19 pandemic, had presented higher rates of relapse or progression compared to patients treated by standard reTURBT protocol. Methods: A prospective study was conducted including 43 patients with high-risk T1 non-muscle invasive bladder cancer diagnosed between March 2020 and June 2021. Patients were divided into two groups: those who underwent reTURBT and those who did not, due to limitations during the COVID-19 pandemic. All patients received intravesical BCG induction therapy and were followed for 3 years. The institutional research ethics committee approved the study. Results: A total of 43 patients were included, 17 (39.5%) underwent reTURBT and 26 (60.5%) did not. No significant differences were observed in tumour characteristics between groups. Recurrence occurred in 43.8% of the reTURBT group and 15.4% of the non-reTURBT group. Tumour progression to T2G3 was observed only in the reTURBT group. Survival analysis showed no significant differences in recurrence-free survival between groups (p = 0.299). Conclusions: Omitting reTURBT in carefully selected patients did not result in significantly worse oncological outcomes; however, due to the small sample size, the study is underpowered and these findings should be interpreted with caution. Early BCG administration in the non-reTURBT group may have contributed to favourable recurrence-free survival. However, further prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings and define optimal criteria for safely omitting reTURBT.
Full article
Open AccessCase Report
Retroperitoneal Metastasis of a Primary Testicular Seminoma with Spontaneous Regression: A Case Report
by
Victor Osornio Sánchez, Rodrigo Pérez Becerra, Gerardo Garza Sainz, Luis Trujillo Ortiz, Denisse García López, Denise Gabriela De León Trenado, Maricruz Cespedes Contreras, Adrián Martínez Correa, Aarón Delgado Corral and Carlos Alberto Castro-Fuentes
Uro 2025, 5(4), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5040019 - 30 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Spontaneous regression of testicular cancer with retroperitoneal metastasis is a rare phenomenon and poses challenges in its diagnosis. Methods: A 33-year-old male patient presented with severe lower back pain (10/10) of 4 months’ duration, radiating to the left lower limb, refractory to
[...] Read more.
Background: Spontaneous regression of testicular cancer with retroperitoneal metastasis is a rare phenomenon and poses challenges in its diagnosis. Methods: A 33-year-old male patient presented with severe lower back pain (10/10) of 4 months’ duration, radiating to the left lower limb, refractory to NSAIDs, and significantly impaired ambulation, accompanied by nausea and vomiting. In addition to difficulty initiating urination and defecation, with weight loss of 30 kg, he was referred to the urology service of our hospital. Results: On physical examination, the left testicle showed signs of varicocele without pain. Therefore, laboratory and imaging studies were requested, highlighting elevated β-hCG (156.4 mIU/mL) and LDH (850 IU/L). Testicular ultrasound confirmed the diagnosis of left varicocele, while computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast revealed a conglomerated retroperitoneal mass of more than 5 cm, located in the paravertebral, retrocural, paraaortic, and intercavoaortic regions. Based on these findings, primary treatment with left radical orchiectomy was chosen, which showed regression of the seminomatous tumor. Histopathological examination revealed a seminomatous germ cell tumor (pT0, pN3, M0), clinical stage IIC, with a good prognosis. Therefore, chemotherapy was initiated with four cycles of EP (etoposide 170 mg and cisplatin 35 mg). However, despite standard chemotherapy, the disease progressed until the patient died. Conclusions: Cases of testicular tumor with retroperitoneal metastasis are rare and infrequently present with clinical, testicular, and imaging findings. Therefore, histopathology, accompanied by the intentional identification of mutations associated with the TP53 gene when therapeutic failure exists.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Variations in Female Pelvic Anatomy via MRI: A Retrospective Study at Single Academic Institution
by
Gamal Ghoniem, William Phan, Naila Javaid, Mashrin Lira Chowdhury, Bilal Farhan, Muhammed A. Moukhtar Hammad, Ahmed Ahmed, David Csuka, Dina Saba, Mohammad Helmy and Sonia Lee
Uro 2025, 5(3), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5030018 - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Pelvic floor disorders affect up to 30% of adult females in the United States. Misdiagnosis occurs in nearly 45% to 90% of cases. Standardized pelvic anatomical measurements could improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning. We aimed to evaluate pelvic anatomical variations using
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Pelvic floor disorders affect up to 30% of adult females in the United States. Misdiagnosis occurs in nearly 45% to 90% of cases. Standardized pelvic anatomical measurements could improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning. We aimed to evaluate pelvic anatomical variations using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Methods: We analyzed MRI pelvic measurements from 250 women aged 20–90 years. Exclusion criteria included prior pelvic surgery (except hysterectomy), pelvic cancer, and use of alternative imaging modalities. Key measurements included anterior vaginal wall thickness (AVWT), bladder wall thickness (BWT), vaginal epithelium to bladder urothelium (VWBU), urethral length (UL), and inter-ureteral distances. A comprehensive statistical analysis was performed, including corrections for multiple comparisons. Results: While several anatomical measurements were correlated, a comprehensive analysis was performed to identify markers for clinical diagnoses. After applying Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons, we found no statistically significant association between any of the measured anatomical parameters and a diagnosis of incontinence. Notably, an uncorrected difference in Bladder Wall Thickness (BWT) (p = 0.041) did not hold up to rigorous testing. To further assess its clinical utility, a Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for BWT as a predictor of incontinence yielded an aArea Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.19, indicating poor predictive validity. Conclusions: In this cohort, static anatomical measurements derived from MRI, including BWT, do not appear to be reliable markers for incontinence. Our findings suggest that the pathophysiology of this disorder is likely more dependent on functional or dynamic factors rather than simple static anatomical variations. Future research should focus on standardizing dynamic imaging parameters to better assess pelvic floor function.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Sleep Deprivation: A Lifestyle Risk Factor for Male Infertility
by
Tarak Davuluri, Vivek Aslot, Brayden J. Seliger, Andrew Edgington, Nagalakshmi Nadiminty, Tariq Shah and Puneet Sindhwani
Uro 2025, 5(3), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5030017 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Male infertility is a growing global concern with increasing prevalence in both developing and developed nations. While many associations between environmental factors and male infertility have been explored, the relationship between sleep deprivation and male infertility remains underexplored. This narrative review examines the
[...] Read more.
Male infertility is a growing global concern with increasing prevalence in both developing and developed nations. While many associations between environmental factors and male infertility have been explored, the relationship between sleep deprivation and male infertility remains underexplored. This narrative review examines the reported effects of sleep deprivation on the Hypothalamic––Gonadal (HPG) axis, Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal (HPA) axis, oxidative stress, and testicular function, and their consequential effects on male infertility. Disruption of the HPG axis results in altered follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) levels, leading to fluctuation in testosterone levels, negatively affecting spermatogenesis and other critical reproductive processes. Activation of the HPA axis, often due to stress, elevates cortisol levels, which, in turn, suppresses gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), impairing reproductive function. Reactive oxidative species (ROS) accumulate in periods of oxidative stress and have been shown to damage sperm and reduce their quality. The blood–testis barrier (BTB) is disrupted in states of sleep deprivation, leading to decreased sperm quality. A literature review was conducted using PubMed and Google Scholar to assess peer-reviewed studies from 1990 to 2024, revealing a complex interplay between sleep deprivation and male reproductive dysfunction. While existing studies support a link between sleep disturbances and hormonal dysregulation, further research is needed to establish causal relationships and identify potential therapeutic interventions. Addressing sleep deprivation may represent a modifiable factor in improving male fertility outcomes.
Full article
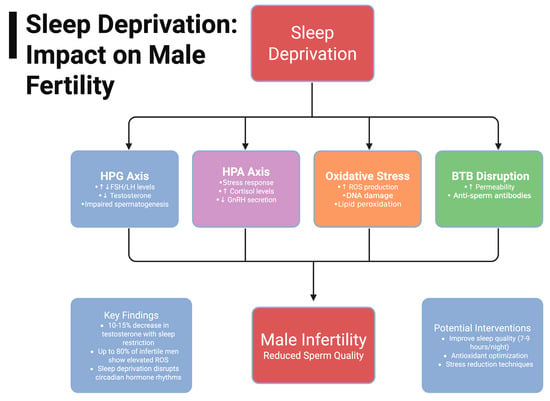
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Buccal Mucosa Graft in Urological Surgery: A State-of-the-Art Review and Expert Opinion
by
Simone Botti, Tommaso Ceccato, Marco Cassaro, Giangiacomo Sanna, Lorenzo Trevisiol and Tommaso Cai
Uro 2025, 5(3), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5030016 - 8 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Buccal mucosa graft (BMG) is increasingly utilized in reconstructive urological surgeries due to its versatility, robust integration, histological characteristics and low morbidity at the donor site. Initially employed in urethral surgery, BMG use has expanded to complex ureteral and penile reconstructive procedures.
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Buccal mucosa graft (BMG) is increasingly utilized in reconstructive urological surgeries due to its versatility, robust integration, histological characteristics and low morbidity at the donor site. Initially employed in urethral surgery, BMG use has expanded to complex ureteral and penile reconstructive procedures. This narrative review examines BMG applications in various urological surgeries, comparing its outcomes to other graft types, with a focus on surgical techniques and patient outcomes. Methods: A narrative review was conducted using PubMed and Scopus to identify relevant studies published over the last three decades on the use of BMG in urological reconstructive surgery. Articles in English addressing BMG harvesting, applications and functional outcomes were analyzed. Results: BMG has demonstrated high success rates in every field of its application, especially in urethral reconstruction with an 83–91% efficacy rate in intermediate follow-up. Studies have also reported positive outcomes in complex ureteral and penile curvature surgeries, with patient satisfaction rates reaching up to 85%. Conclusions: BMG is an adaptable tissue graft for urological reconstructive surgeries, offering favorable outcomes with minimal morbidity. Although the current results are encouraging, larger prospective studies with standardized protocols are necessary to fully validate its long-term efficacy and optimize treatment approaches for complex urological reconstructions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
A Literature Review of Phantom Bladder Perforation: The Curious Case of Bladder Lipoma
by
Surina Patel, Mehreet Kaur Chahal, Scott Durham, Haitham Elsamaloty and Puneet Sindhwani
Uro 2025, 5(3), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5030015 - 1 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Although lipomas are common benign tumors found in adults, lipomas of the bladder are extremely rare. Bladder lipomas are infrequently reported in the urologic literature, with only 19 cases published worldwide. These can present as a mass on cystoscopy and cause irritative
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Although lipomas are common benign tumors found in adults, lipomas of the bladder are extremely rare. Bladder lipomas are infrequently reported in the urologic literature, with only 19 cases published worldwide. These can present as a mass on cystoscopy and cause irritative voiding symptoms, depending on their location. Upon transurethral resection, seeing fat can be concerning for a perforation, as lipoma can be mistaken for extravesical fat. Hence, familiarity with this rare entity is of paramount importance for urologists to prevent unnecessary investigations and interventions that are needed in case of a true bladder perforation. Case presentation: This study presents a case of bladder lipoma in a 73-year-old male with end-stage renal disease who presented for pretransplant urologic evaluation due to microscopic hematuria and irritative lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). During cystoscopy, a bladder mass was seen, and a transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (TURBT) revealed bright yellow adipose tissue immediately underneath the bladder mucosa. Concerns about perforation were obviated when seeing intact detrusor muscle underneath, visually confirming the integrity of the bladder wall. The resection was completed, and the CT scan was re-read with the radiologist, which confirmed the presence of a lipoma that was missed pre-operatively due to patient’s oliguria and collapsed bladder. No catheter drainage or cystogram was performed based on these findings. Outcome: The patient healed without any complications. Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of a mature lipoma. The patient was cleared for transplant from a urologic standpoint and had a successful renal transplantation without delay. Discussion: This case documents the anomalous occurrence of a lipoma within the bladder and supports maintaining a broad differential, including liposarcoma, angiomyolipoma, and other non-malignant fatty tumors during the evaluation of a bladder mass.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Effectiveness of Dalerpen vs. Branded and Other Generic Tadalafil: The “Shift Study”
by
Davide Arcaniolo, Carlos Miacola, Marco Bitelli, Luca Boeri, Tommaso Cai, Carlo Ceruti, Celeste Manfredi, Ilaria Ortensi, Fabrizio Palumbo, Giorgio Piubello, Chiara Polito, Nicolò Schifano and Alessandro Palmieri
Uro 2025, 5(3), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5030014 - 28 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5i), particularly tadalafil and sildenafil, are the first-line therapies for erectile dysfunction (ED). After the patent expiration of branded tadalafil in 2017, generic formulations became available. Despite equivalent efficacy, skepticism persists regarding the effectiveness and safety of generics.
[...] Read more.
Background: Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5i), particularly tadalafil and sildenafil, are the first-line therapies for erectile dysfunction (ED). After the patent expiration of branded tadalafil in 2017, generic formulations became available. Despite equivalent efficacy, skepticism persists regarding the effectiveness and safety of generics. The SHIFT study aimed to evaluate the non-inferiority of a generic tadalafil (Dalerpen) compared with branded and other generic tadalafil in terms of clinical efficacy and patient satisfaction. Methods: A prospective, multicenter study was conducted involving 247 patients treated with tadalafil (either 5 mg or 20 mg) for ED. Patients switched from branded or other generic tadalafil to Dalerpen. Baseline and follow-up assessments included the International Index of Erectile Function—Erectile Function Domain (IIEF-EF) (primary endpoint), Sexual Encounter Profile (SEP-2 and SEP-3), and International Prostatic Symptom Score (IPSS). A one-month follow-up was performed. Results: A total of 247 patients were included in the final analysis. After switching to Dalerpen, significant improvements were observed in both IIEF-EF (18.8 ± 5.6 vs. 16.7 ± 5.4, p < 0.001) and IPSS scores (10.4 ± 6.7 vs. 11.2 ± 6.3, p < 0.001), though the minimal clinically important difference (MCID) was not reached. SEP-3 scores also significantly increased (3 ± 1.2 vs. 2 ± 1.1, p < 0.001). Multivariate analysis identified baseline IIEF, IPSS scores, and post-treatment IPSS as predictors of IIEF-EF improvement (p < 0.001). Switching to Dalerpen was an independent predictor of both IIEF-EF and IPSS improvement. No new adverse events were reported. Conclusions: The SHIFT study demonstrates that Dalerpen is non-inferior to branded tadalafil in terms of clinical efficacy, offering a reliable and cost-effective therapeutic option. Educating patients on bioequivalence and addressing concerns regarding generic drugs are essential to facilitate therapeutic switches.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Biallelic Variants in DNAH12 Gene Linked to Male Infertility: Two New Cases and Literature Review
by
Faisal H. Aljahdali, Rozana Kamal, Zohor Azher, Ahmed S. Zugail, Abdulaziz Baazeem, Aboulfazl Rad and Gabriela Oprea
Uro 2025, 5(3), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5030013 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Although biallelic pathogenic variants in different DNAH gene family members have been associated with infertility, the role of DNAH12 in this disorder is still incompletely understood. To date, few patients have been shown to have infertility due to biallelic variants in this
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Although biallelic pathogenic variants in different DNAH gene family members have been associated with infertility, the role of DNAH12 in this disorder is still incompletely understood. To date, few patients have been shown to have infertility due to biallelic variants in this gene. Here, we report two more unrelated patients with infertility who carry homozygous variants in DNAH12. Methods: This study included two male patients with primary infertility and oligoasthenoteratozoospermia (OAT). Patient 1 was a 32-year-old with 1.5 years of infertility and no chronic illnesses or prior assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs). Patient 2 was a 49-year-old with 24 years of infertility, a history of varicocelectomy, and the occasional use of PRN analgesics for bone pain. Using genome sequencing, we identified two homozygous variants: c.3757C>A, p. Pro1253Thr, and c.11086-1G>A, p.?, in patients 1 and 2, respectively. Results: Our findings add supportive evidence that DNAH12 is a gene implicated in rare cases of male infertility. The identification of these homozygous variants in two additional patients supports the association between DNAH12 variants and reproductive dysfunction. Conclusions: This study highlights the need for further research on the role of DNAH12, including functional studies to clarify the mechanisms contributing to infertility.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Ileal Ureter Replacement: Foundations, Robotic Advances, Horizons
by
Noah N. Nigro, Karen M. Doersch, Sasha J. Vereecken, Carter Niedert, Rohan G. Bhalla and Brian J. Flynn
Uro 2025, 5(2), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5020012 - 3 Jun 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The use of ileum for ureteral reconstruction was first described in 1906. Since then, its utilization has evolved considerably. Early in the history of ileal ureters, urologists were limited by a lack of familiarity with bowel harvesting and handling. The popularization of ileal
[...] Read more.
The use of ileum for ureteral reconstruction was first described in 1906. Since then, its utilization has evolved considerably. Early in the history of ileal ureters, urologists were limited by a lack of familiarity with bowel harvesting and handling. The popularization of ileal conduits for urinary diversions, however, allowed urologists to familiarize themselves with the use of ileum and paved the way for broader applications. With the emergence of laparoscopy and, later, robotic-assisted surgery, the application of ileal ureteral replacement expanded the capabilities of reconstructive urologists. This article describes the historical development of surgical techniques for ileal ureter replacement and the integration of new technologies aiding in improved outcomes, and anticipates potential future directions. In contemporary practice, robotic-assisted ileal ureteral replacement is used in cases of extensive ureteral obstruction or damage. Advantages of the robotic platform include reduced blood loss, shorter recovery time and hospital length of stay, and superior operative ergonomics. Although robotic ileal ureter replacement is a complex and challenging surgery with notable complications, studies have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of this technique in patients with an otherwise end-stage ureter. In addition, the robotic approach has provided urologists the ability to conduct complex reconstructive surgeries including bilateral ureteral replacement in conjunction with bladder augmentation or a urinary diversion. Long-term studies and continued innovation are necessary to further improve the surgical techniques, outcomes, and scope of ileal ureter reconstruction.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Narrative Review of Current Advances and Future Changes Regarding Bladder Cancer Treatment
by
Dominik Godlewski, Sara Czech, Jakub Szpara, Dorota Bartusik-Aebisher and David Aebisher
Uro 2025, 5(2), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5020011 - 3 Jun 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Bladder cancer (BC) remains a clinical challenge due to its complex etiology and high incidence, especially in developed populations. This article presents a broad analysis of the latest advances in BC treatment, offering a new perspective on the growing role of innovative therapies
[...] Read more.
Bladder cancer (BC) remains a clinical challenge due to its complex etiology and high incidence, especially in developed populations. This article presents a broad analysis of the latest advances in BC treatment, offering a new perspective on the growing role of innovative therapies that are effectively changing the standards of oncological care. Focusing on targeted therapy, immunotherapy, antibody–drug conjugates, and breakthrough gene therapies, the paper shows how modern approaches can counteract resistance mechanisms and improve treatment efficacy while limiting toxicity for patients. Progress in the field of immune therapies, including checkpoint inhibitors, offers hope for significant improvement in the outcomes of patients with advanced forms of cancer, and the concept of targeted therapy tailored to the molecular characteristics of the tumor indicates the potential of personalized oncology. Gene and photodynamic therapies, in turn, offer new possibilities for precise action on cancer cells, minimizing the side effects of traditional methods. The article presents innovative therapeutic strategies and results of the latest clinical trials, showing the prospects for the development of BC treatment and highlighting the key challenges facing oncology.
Full article
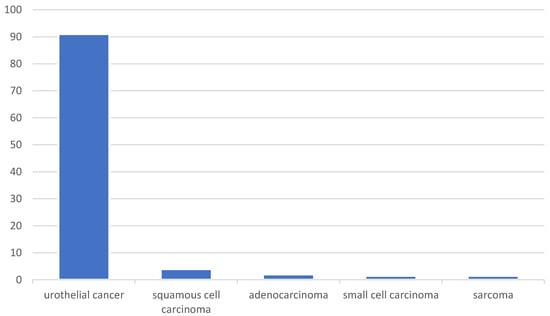
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Navigating Pathways in Prostate Cancer Survivorship: A Comprehensive Review of Challenges, Interventions, and Long-Term Outcomes
by
Anthony Galvez, Dhruv Puri, Elizabeth Tran, Kassandra Zaila Ardines and Yahir Santiago-Lastra
Uro 2025, 5(2), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5020010 - 7 May 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Advances in screening, early detection, and therapeutic innovations have significantly improved survival rates, transforming prostate cancer into a chronic condition for many men. However, these strides have also revealed persistent challenges in survivorship, including treatment-related side effects, disparities in care, and inequities in
[...] Read more.
Advances in screening, early detection, and therapeutic innovations have significantly improved survival rates, transforming prostate cancer into a chronic condition for many men. However, these strides have also revealed persistent challenges in survivorship, including treatment-related side effects, disparities in care, and inequities in outcomes. This review explores the complex landscape of prostate cancer survivorship, with a focus on demographic disparities, barriers to care, symptom burden, and treatment patterns. Our findings highlight how factors such as race, socioeconomic status, and insurance type heavily influence patient outcomes. For instance, Black and Latiné patients often face delays in treatment initiation and are less likely to receive definitive therapies than White patients, leading to poorer survival outcomes. Furthermore, those with Medicaid or no insurance are more likely to receive systemic therapy only or no treatment at all, exacerbating existing inequities. Addressing gaps in diagnosis, treatment access, and survivorship care is essential to developing targeted interventions and policies that promote equitable, patient-centered care for prostate cancer survivors.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
The HIFEM™ Treatment of Stress and Mixed Urinary Incontinence in Parous Women: A Case Series Study
by
Lubomír Mikulášek and Dragana Žarković
Uro 2025, 5(2), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro5020009 - 2 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Purpose: Urinary incontinence (UI) significantly impacts the quality of life, necessitating a range of treatments, from behavioral changes to surgical interventions. Electromagnetic muscle stimulation (HIFEM™) therapy presents an innovative, non-invasive approach to strengthening pelvic floor muscles (PFMs). Subjects and Methods: This retrospective, non-interventional
[...] Read more.
Purpose: Urinary incontinence (UI) significantly impacts the quality of life, necessitating a range of treatments, from behavioral changes to surgical interventions. Electromagnetic muscle stimulation (HIFEM™) therapy presents an innovative, non-invasive approach to strengthening pelvic floor muscles (PFMs). Subjects and Methods: This retrospective, non-interventional case series study explores the efficacy and safety of HIFEM™ treatment in parous women experiencing stress (SUI) and mixed urinary incontinence (MUI). Nineteen women (mean age 54 ± 16) underwent six HIFEM™ sessions, with symptom progression tracked using the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire-Urinary Incontinence Short Form (ICIQ-UI SF), along with comfort and satisfaction questionnaires. Results: At baseline, the mean ICIQ-UI SF score was 7.9 ± 4.2 points. By the final questionnaire administration, the average score had dropped to 4.7 ± 3.5, reflecting a 50.6% reduction from baseline (p < 0.001). According to ICIQ-UI SF Item 6, 21% of subjects achieved complete continence. Additionally, the percentage of subjects experiencing urine leakage before reaching the toilet declined by 40% after the sixth treatment. Post treatment, the number of subjects who leaked urine while coughing or sneezing decreased by 50%. Conclusions: The treatment has shown high efficacy in lowering the ICIQ-SF scores across the study group, with a significant number of subjects regaining entire continence.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, Diseases, JCM, JPM, Uro, Reports
Clinical, Translational, and Basic Research and Novel Therapy on Functional Bladder Diseases and Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunctions
Topic Editors: Hann-Chorng Kuo, Yao-Chi Chuang, Chun-Hou LiaoDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Uro
Prostate Surgery: The Latest Advances and Future Trends
Guest Editors: Akhil K. Das, Bruce GaoDeadline: 20 April 2026









