- Article
Structure-Based Virtual Screening for ALOX5 Inhibitors: Combining Scaffold Hopping and Pharmacophore Approaches
- Xiao Li,
- Liang Li and
- Lianxiang Luo
- + 2 authors
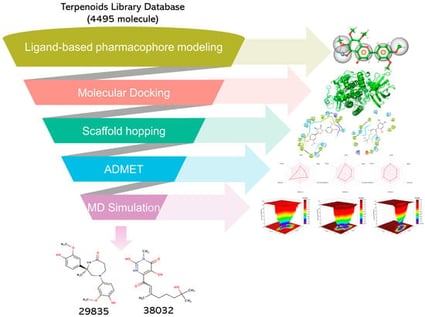
Arachidonic acid 5-lipoxygenase (ALOX5), an enzyme critical for lipid mediator synthesis, demonstrates significant upregulation in clinically distinct disease states. Current research identifies its aberrant activity in neurodegenerative pathologies (e.g., Parkinson’s disease), solid tumors, hematological cancers, metabolic dysregulation linked to diabetic nephropathy, and vascular remodeling in hypertension and coronary artery disease. These findings collectively implicate ALOX5 as a multifunctional driver of chronic inflammation and tissue damage across organ systems. Despite the significant clinical significance of ALOX5, developing effective inhibitors for this target remains challenging, with most candidates still undergoing clinical evaluation. This study employs a multi-stage computational approach to identify novel ALOX5 inhibitors with strong drug-like properties. By compiling compounds with documented ALOX5 inhibitory activity and IC50 values from PubChem, ChEMBL, and MedChemExpress databases, we established a ligand-based pharmacophore model to virtually screen terpenoid derivatives. The selection of terpenoid compounds for virtual screening is primarily due to their dual role as natural products exhibiting significant structural diversity alongside a broad spectrum of known biological activities. This provides an ideal starting point for the efficient discovery of structurally novel lead compounds with drug potential, while also being well-suited for structure-based computational evaluation. Two lead compounds (29835 and 38032) were identified through ADMET property prediction and scaffold modification-guided optimization. Molecular docking analysis revealed superior binding affinities for these candidates (−8.31 and −10.26 kcal/mol, respectively) compared to Zileuton (−7.39 kcal/mol), indicating stable and favorable interactions within the target protein’s active site. The binding stability of these complexes was further confirmed by 100 ns molecular dynamics simulations, which demonstrated sustained structural integrity of the protein–ligand systems. Collectively, computational findings suggest these compounds as promising ALOX5 inhibitors. However, given the theoretical framework of this work, subsequent experimental validation via in vitro and in vivo pharmacological assays is imperative to verify their therapeutic potential.
12 February 2026