- Article
Experimental Fracture Characterization from Uniaxial to Plane Strain Tension Using the Tight Radius V-Bend Test with Application to Machined and Sheared Edge Conditions
- Patrick Cleary,
- Rhys Northcote and
- Cliff Butcher
- + 4 authors
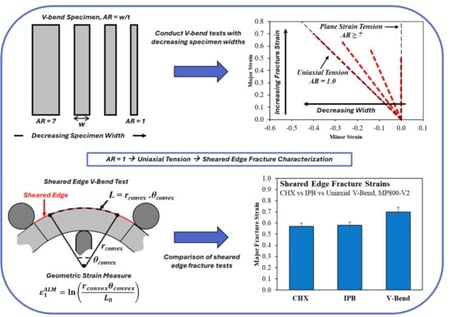
The VDA 238-100 tight radius bend test has gained widespread acceptance for plane strain fracture characterization of sheet metals in proportional loading without necking. The VDA test features a 60 × 60 mm2 square blank with a 0.2 mm or 0.4 mm radius punch to provide plane strain bending where the fracture limit of the material is lowest. However, the through-thickness gradients that suppress necking and promote fracture on the convex surface in tension can be exploited to efficiently characterize the fracture strain from uniaxial to plane strain tension by varying the sample width. In this study, V-bend tests were conducted for various sample widths for four advanced high-strength steels: 980GEN3, DP1180, MP800-V1, and MP800-V2 with the local fracture strains measured using digital image correlation. Reducing the width-to-thickness ratio below five altered the stress state at the failure location, with an aspect ratio of one providing edge fractures under uniaxial tension. This aspect ratio was then applied to 980GEN3 and MP800 steel samples with punched edges as it provides an efficient method for sheared edge fracture characterization that is not susceptible to necking as with common sheared edge tensile tests. To mitigate strain averaging inherent in DIC near surfaces, a geometric-based arc length methodology was proposed. The sheared edge fracture limits from the V-bend tests were then compared with the results from conical hole expansion and in-plane bend tests. The sheared edge formability was observed to have a material-dependent sensitivity to the test method. MP800-V2, with centerline segregation, exhibited a pronounced sensitivity to the applied deformation mode with absolute differences in fracture strains of 0.13 while the MP800-V1 and 980GEN3 did not.
5 February 2026



![Evaluation of safety, estimated cell potential, cost, abundance, volumetric expansion rate, practical gravimetric energy densities at the cell level, gravimetric energy density, and volumetric energy density for Mg-S, Ca-S, Na-S, K-S, Al-S, and Li-S batteries. Reproduced with permission from [37].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/solids/solids-07-00007/article_deploy/html/images/solids-07-00007-ag-550.jpg)