- Article
Lanthanum Nitrate Modification of Soybean Protein Activated Carbon for Enhanced Fluoride Adsorption
- Zhengnan Jiang,
- Guanyu Zhou and
- Chunlin He
- + 2 authors
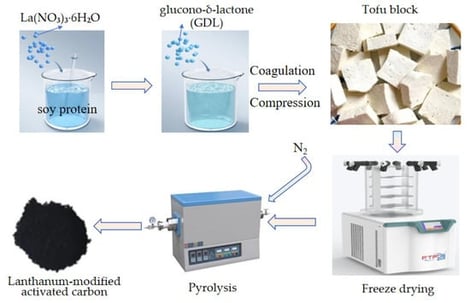
Water with a high fluoride content poses a serious threat to both public health and the natural environment. To enhance fluoride ion removal efficiency, a modified activated carbon adsorbent (HPAC-La) was synthesized by impregnating soybean protein in a lanthanum nitrate solution, followed by freezing–drying and carbonization. The results confirmed that lanthanum nitrate modification significantly improved the adsorption performance. Under optimised experimental conditions (pH = 2.0, [F−] = 300 mg·L−1, 12 h, 298 K), HPAC-La exhibited a maximum adsorption capacity for fluoride ions of 126.7 mg·L−1, significantly higher than that of unmodified HPAC (86.1 mg·L−1). The adsorption process followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and the Langmuir isotherm model, indicating monolayer chemisorption. The mechanism involves ion exchange via surface hydroxyl groups and fluoride coordination with La sites. This study proposes a method for developing highly efficient adsorbents for the treatment of fluoride-contaminated wastewater.
7 February 2026