- Article
Photovoltaic-Related “Black Swan” Hypothesis for Electric Power System: Phenomenology, Simulations, Experiences, and Prevention
- Sasa Sladic and
- Even Zivic
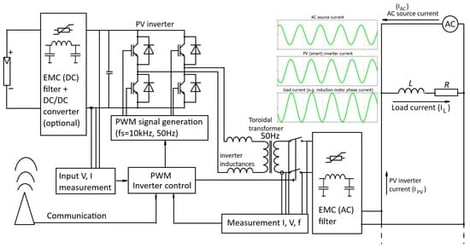
Several blackouts have recently occurred in Europe and elsewhere. Blackouts are mostly the consequence of a series of events rather than a single event. Their intensity and frequency could be related to the stronger penetration of renewables into electric power systems. Although many different renewable power units may be installed, they all have some basic properties: their power is not consistent, and power inverters are used to connect renewables to electric power systems. Photovoltaic systems are the most typical representative of this large group of power sources. These devices have become more sophisticated over the past few years, allowing for the precise control of large photovoltaic fields. In this situation, all power converters act as one. This means that they could be turned on and off during short intervals. Furthermore, their power factor could be independently adjusted. These functions are desirable for small systems; however, their implications for stability at a larger scale are usually not considered. In this study, the stability issues of a system under the high penetration of renewables and a unique control system are investigated. The most prominent case of this influence is a high-impact rare (HR) event, also known as a “black swan”, which could cause a massive blackout in an electric power system.
6 February 2026