- Article
Effects of Eimeria Challenge and Monensin Supplementation on Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, and Intestinal Health of Broilers
- Pamella Pryscila de Alvarenga Bissoli Maciel de Lima,
- José Andrew de Lira Barbosa and
- Felipe Dilelis
- + 5 authors
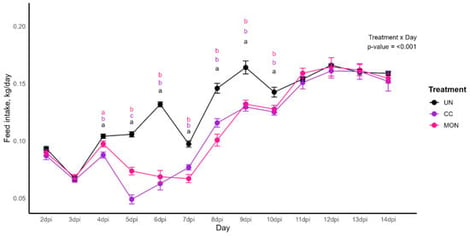
This study aimed to evaluate the performance, nutrient digestibility, intestinal health, and duodenum gene expression of broilers challenged with Eimeria spp. supplemented with or without monensin sodium. A total of 144 male chicks were used, distributed in a completely randomized design with three treatments: unchallenged control (UN), challenged control (CC), and CC + 100 mg/kg of monensin sodium (MON). Six replicates of eight birds each were used. At 14 days of age, the challenged groups were inoculated with a mixture of Eimeria oocysts, 12,500 E. maxima, 62,500 E. acervulina, and 12,500 E. tenella oocysts/chick. Coccidial challenge impaired growth performance and nutrient digestibility and induced intestinal damage, as evidenced by reduced body weight gain and feed intake (p < 0.001), lower apparent digestibility coefficients (p < 0.001), and altered intestinal morphometry and ISI score in the jejunum and cecum (p < 0.001). Monensin supplementation partially alleviated these negative effects, improving performance and nutrient digestibility (p < 0.001) and delaying oocyst excretion (p = 0.006) when compared with the CC group. However, the duodenal expression of tight junction-related genes, as well as intestinal integrity and health parameters, remained impaired despite monensin supplementation. It is concluded that monensin preserves nutrient digestibility and attenuates performance loss in broilers challenged with Eimeria spp. but not reduced intestinal damage.
3 February 2026