- Article
Direct-Write Printed Epoxy Composites with Layered Gradient Structure: Shape Memory and Electromagnetic Shielding Performance
- Junyao Zhou,
- Xianglong Zhu and
- Minghua Zhang
- + 5 authors
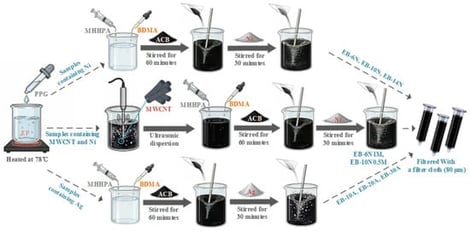
To address the growing problem of electromagnetic pollution, the development of intelligent, multifunctional electromagnetic shielding materials is essential. The objective of this work is to fabricate an intelligent, low-reflection and high-absorption electromagnetic shielding composite via direct ink writing. In this study, epoxy resin (EP) was employed as the matrix, with nickel powder (Ni), multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), and silver powder (Ag) serving as functional fillers. Direct-ink printing enabled the fabrication of uniformly structured composites and layered gradient-structured composites. By precisely varying the filler content through layer-by-layer printing, the gradient-structured composite exhibited an increasing electrical conductivity gradient and a decreasing magnetic permeability gradient along the direction of electromagnetic wave incidence. Comprehensive characterization of microstructure, electrical, magnetic, and dielectric properties, and electromagnetic shielding effectiveness revealed that the uniformly structured composites exhibited higher total shielding effectiveness (SET) and reflection coefficient (R) with increased electrical conductivity. The layered gradient-structured composite achieved an electrical conductivity of 5.44 S/m and an SET of 17.74 dB, with the R value reduced to 0.53. Compared to the highly conductive homogeneous composite used in the bottom layer (R = 0.87), this represents a reduction in reflectivity of approximately 39.1%, thereby mitigating secondary pollution from excessive reflection. Under a DC voltage of 200 V, all composites recovered their original shape within 63 s, with shape fixity (Rf) and recovery (Rr) ratios exceeding 92%. This strong shape memory capability supports conformal coating on complex devices and facilitates material recycling, offering a practical foundation for next-generation multifunctional electromagnetic shielding materials.
9 February 2026