Journal Description
Organics
Organics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on organic chemistry published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Cluster of Chemical Reactions and Catalysis: Catalysts, Chemistry, Electrochem, Inorganics, Molecules, Organics, Oxygen, Photochem, Reactions, Sustainable Chemistry.
Impact Factor:
1.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.8 (2024)
Latest Articles
A Quantum Chemical Study on the Relative Stability of Diaminodinitroethylene Isomers
Organics 2026, 7(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/org7010008 - 10 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
This study aims to investigate the relative stability of the diaminodinitroethylene isomers (cis, trans, and gem). To achieve this goal, calculations at several levels of theory were carried out. The B3LYP, PBE0, and CAM-B3LYP functionals, based on density functional theory (DFT), were used.
[...] Read more.
This study aims to investigate the relative stability of the diaminodinitroethylene isomers (cis, trans, and gem). To achieve this goal, calculations at several levels of theory were carried out. The B3LYP, PBE0, and CAM-B3LYP functionals, based on density functional theory (DFT), were used. G4 and MP2 calculations were also executed. All calculation methods predicted that the gem isomer is the most stable, while the cis isomer is the least stable. The energy order obtained for the isomers studied was rationalized by analysis of the detected intramolecular hydrogen bonding, electron delocalization, charge distribution, and changes in atomic energies in the structures studied. The origins of the superior stability of the gem isomer are demonstrated and justified.
Full article
Open AccessCommunication
Chemo- and Regioselective 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Nitrile Imines to 5-Arylmethylene-2-methylthiohydantoins
by
Maria E. Filkina, Lev A. Lintsov, Victor A. Tafeenko, Maxim E. Kukushkin and Elena K. Beloglazkina
Organics 2026, 7(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/org7010007 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition reactions of nitrile imines are a powerful tool for the construction of spirocyclic frameworks, yet controlling chemoselectivity remains challenging when dipolarophiles contain multiple reactive sites. In this study, we investigated the cycloaddition of nitrile imines with 5-arylmethylene-2-methylthiohydantoins, which possess both exocyclic
[...] Read more.
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition reactions of nitrile imines are a powerful tool for the construction of spirocyclic frameworks, yet controlling chemoselectivity remains challenging when dipolarophiles contain multiple reactive sites. In this study, we investigated the cycloaddition of nitrile imines with 5-arylmethylene-2-methylthiohydantoins, which possess both exocyclic C=C and endocyclic C=N bonds. Nitrile imines were generated from hydrazonoyl chlorides under basic conditions and reacted with the thiohydantoin substrates under optimized reaction conditions. The cycloaddition proceeded smoothly, affording spiro-fused thiohydantoin–pyrazoline derivatives. In all cases, the reaction occurred selectively at the exocyclic C=C bond, while the C=N bond remained unreactive even in the presence of excess dipole. This chemoselectivity is attributed to the greater steric accessibility of the exocyclic double bond. These results clarify key factors governing nitrile imine chemoselectivity and provide a reliable approach to structurally complex spirocyclic thiohydantoin derivatives.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Design of Sustainable Copper-Based Hybrid Catalyst Using Aqueous Extract of Curcuma longa L. for One-Pot Synthesis of 1,2,3-Triazole
by
Felipe Pinto, Isadora Barbosa Frederico, Conceição F. A. Olguin, Gabrielle Peiter, Julia C. M. Willig, Helio A. Stefani, Giancarlo V. Botteselle and Flavia Manarin
Organics 2026, 7(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/org7010006 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A sustainable hybrid material, CuO/Cu2O, was synthesized using an aqueous extract of Curcuma longa L. as a reducing and stabilizing agent. The material was characterized by UV-Vis spectroscopy, FTIR, XRD, SEM, EDX, and TEM. XRD analysis revealed peaks corresponding to CuO
[...] Read more.
A sustainable hybrid material, CuO/Cu2O, was synthesized using an aqueous extract of Curcuma longa L. as a reducing and stabilizing agent. The material was characterized by UV-Vis spectroscopy, FTIR, XRD, SEM, EDX, and TEM. XRD analysis revealed peaks corresponding to CuO and Cu2O phases with crystallite sizes of 15.88 nm and 16.71 nm, respectively. TEM images showed nearly spherical particles with some agglomeration and an average particle diameter of 8.17 nm. The hybrid material exhibited catalytic activity toward the synthesis of 1,2,3-triazoles in water, under low catalyst loading and mild reaction conditions. This work highlights the potential of Curcuma longa-mediated synthesis as a low-cost, eco-friendly alternative for producing efficient catalysts, contributing to the advancement of green chemistry and sustainable nanomaterial applications in organic synthesis.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Aqueous Radical Photopolymerization Catalyzed by Resorufin
by
Wenqiao Zhou and Chunming Liu
Organics 2026, 7(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/org7010005 - 15 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Commercially available resorufin was shown to function as an organic photocatalyst for visible-light-induced aqueous radical polymerization under low-irradiance illumination. Polymers with narrow molecular weight distributions and high monomer conversions were successfully synthesized from acrylate and acrylamide monomers. The photopolymerization catalyzed by resorufin was
[...] Read more.
Commercially available resorufin was shown to function as an organic photocatalyst for visible-light-induced aqueous radical polymerization under low-irradiance illumination. Polymers with narrow molecular weight distributions and high monomer conversions were successfully synthesized from acrylate and acrylamide monomers. The photopolymerization catalyzed by resorufin was consistent with a reductive quenching mechanism. Good temporal control of the reaction was achieved by toggling visible light irradiation.
Full article
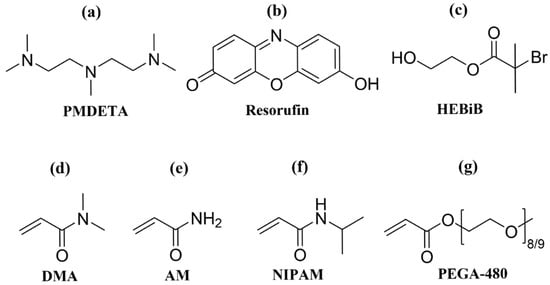
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Metalloenzyme-like Catalytic System for the Epoxidation of Olefins with Dioxygen Under Ambient Conditions
by
Lin Lei, Linjian Wu, Yongjian Qiu and Yaju Chen
Organics 2026, 7(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/org7010004 - 7 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The development of a metalloenzyme-like catalytic system for the efficient oxidation of olefins under a dioxygen (O2) atmosphere at room temperature is of significant interest in the field of catalysis. Herein, we present a highly active and selective aerobic epoxidation of
[...] Read more.
The development of a metalloenzyme-like catalytic system for the efficient oxidation of olefins under a dioxygen (O2) atmosphere at room temperature is of significant interest in the field of catalysis. Herein, we present a highly active and selective aerobic epoxidation of olefins using metalloenzyme-like catalysts based on a non-heme ligand, tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (TPA). Notably, manganese chloride complexed with TPA (Mn(TPA)Cl2) demonstrated excellent activity for the epoxidation of trans-stilbene using O2 as the oxidant in the presence of a co-reductant at 30 °C. A quantitative conversion of 99% and high yield of 98%, as determined by gas chromatography using an external standard method, were achieved under optimum reaction conditions. Furthermore, Mn(TPA)Cl2 exhibited a good substrate tolerance to styrene derivatives with electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups, cyclic olefins with different substituents and substitution degrees, as well as long-chain olefins. Coupled with a high turnover frequency (TOF) of up to 30,720 h−1, these results underscore the potential of Mn(TPA)Cl2 as a promising metalloenzyme-like catalytic platform for the aerobic synthesis of diverse epoxides from olefins under ambient conditions.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Natural Dye Extracts from African Plants for the Photooxygenation of α-Terpinene to the Anthelmintic Ascaridole
by
Chinyere Chidimma Enyi, Gloria Ihuoma Ndukwe, Godswill Kuta Fekarurhobo and Michael Oelgemöller
Organics 2026, 7(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/org7010003 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this study, the singlet oxygen photosensitization potential of three natural African plant extracts was investigated using the photooxygenation of α-terpinene (1). Utilizing visible light, the Carpolobia lutea extract achieved high conversions towards the anthelmintic ascaridole (2) of >60%
[...] Read more.
In this study, the singlet oxygen photosensitization potential of three natural African plant extracts was investigated using the photooxygenation of α-terpinene (1). Utilizing visible light, the Carpolobia lutea extract achieved high conversions towards the anthelmintic ascaridole (2) of >60% after 90 min of irradiation, while the extracts of Hibiscus sabdariffa and Justicia secunda failed to induce significant photoreactivity. Quenching using 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (DABCO) confirmed a singlet oxygen pathway for irradiation with the C. lutea extract. Further separation of the C. lutea extract and subsequent photooxygenation screening established several active fractions for ascaridole generation. Advanced HPLC–MS analyses of these active fractions revealed several photosensitizing constituents. These findings establish C. lutea extract as a sustainable and effective photosensitiser with comparable performance to commercial dyes.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Helical Molecular Cages with sp-Conjugated Linkages
by
Wei Wu, Takahiro Kojima and Hiroshi Sakaguchi
Organics 2026, 7(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/org7010002 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A conjugated helical cage, comprising two 1,3,5-tris(phenylethynyl)benzene units connected by diyne linkers, was successfully synthesized. X-ray crystallography revealed helical molecular structures with large twisted angles and a 1:1 mixture of P- and M-enantiomers. Variable-temperature-NMR measurement indicated the racemization process between the enantiomers
[...] Read more.
A conjugated helical cage, comprising two 1,3,5-tris(phenylethynyl)benzene units connected by diyne linkers, was successfully synthesized. X-ray crystallography revealed helical molecular structures with large twisted angles and a 1:1 mixture of P- and M-enantiomers. Variable-temperature-NMR measurement indicated the racemization process between the enantiomers occurs rapidly on the NMR timescale. The rapid interconversion is attributed to the flexible diyne linkages, even though they were believed to be rigid.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Photodynamic Agents of Synthetic Curcuminoids with Antibacterial and Anticancer Activities
by
Sung-Jen Hung, Lo-Yun Chiang, Yi-An Hong, Kai-Chih Chang, Yang-Je Cheng, Hsin-Ying Wu, Hussana Hamid, Anren Hu, Tzenge-Lien Shih and Hao-Ping Chen
Organics 2026, 7(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/org7010001 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Our previous study demonstrated that thiophene-substituted synthetic curcumin analogs possessed better antibacterial activity and stability than natural curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, or bisdemethoxycurcumin in antibacterial photodynamic therapy (aPDT). In addition, the activity of the furan-substituted analogs was weaker than that of the thiophene-substituted compounds. As
[...] Read more.
Our previous study demonstrated that thiophene-substituted synthetic curcumin analogs possessed better antibacterial activity and stability than natural curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, or bisdemethoxycurcumin in antibacterial photodynamic therapy (aPDT). In addition, the activity of the furan-substituted analogs was weaker than that of the thiophene-substituted compounds. As oxygen, sulfur, and selenium belong to the same group in the periodic table, the antibacterial and anticancer activities of these three different elemental analogs were compared and investigated. The thiophene-substituted analog (compound 3) exhibited the most potent antibacterial activity in aPDT experiments. However, the furan-substituted analog (compound 1) exhibited the most potent anticancer activity. These results indicate that the differences in atomic radii or energy levels in these compounds produce different cell-attack results on generated free radicals. Ruthenium(II) complexes have a good reputation for use in PDT for cancer treatment. Our results show that complexation of ruthenium(II) with thiophene-substituted curcumin analogs does not enhance their antibacterial or anticancer activity.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Tranexamic Acid-Phenol Smart Scaffolds with Imine Linker: Unlocking Antimicrobial Potential Through In Vitro and In Silico Insights
by
Jovana S. Dragojević, Žiko Milanović, Kristina Milisavljević, Nevena Petrović, Jelena Petronijević, Nenad Joksimović, Vera M. Divac, Marijana Kosanić and Marina D. Kostić
Organics 2025, 6(4), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040054 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A novel series of Schiff bases (3a–3k), incorporating tranexamic acid (TXA) and phenol-derived aldehydes via imine linkers, was synthesized and structurally characterized. The antimicrobial activity of the compounds was evaluated against a range of clinically and environmentally relevant bacterial
[...] Read more.
A novel series of Schiff bases (3a–3k), incorporating tranexamic acid (TXA) and phenol-derived aldehydes via imine linkers, was synthesized and structurally characterized. The antimicrobial activity of the compounds was evaluated against a range of clinically and environmentally relevant bacterial and fungal strains. Among them, derivatives 3i and 3k, bearing bromine and chlorine substituents on the phenol ring, exhibited the most potent antimicrobial effects, particularly against Penicillium italicum and Proteus mirabilis (MIC as low as 0.014 mg/mL). To elucidate the underlying mechanism of action, in silico molecular docking studies were conducted, revealing strong binding affinities of 3i and 3k toward fungal sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51B), with predicted binding energies surpassing those of the reference antifungal ketoconazole. Additionally, UV-Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy assays demonstrated good stability of compound 3k in PBS and its effective binding to human serum albumin (HSA), respectively. ADMET and ProTox-II predictions further supported the drug-likeness, low toxicity (Class 4), and favorable pharmacokinetic profile of compound 3k. Collectively, these findings highlight TXA–phenol imine derivatives as promising scaffolds for the development of next-generation antimicrobial agents, particularly targeting resistant fungal pathogens.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Theoretical Modeling of BODIPY-Helicene Circularly Polarized Luminescence
by
Giovanni Bella, Giuseppe Bruno and Antonio Santoro
Organics 2025, 6(4), 53; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040053 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Density functional theory (DFT) and its extension, time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT), have become fundamental tools for modeling chiral excited states and supporting experimental chiroptical spectroscopies. In this connection, the interest in understanding the asymmetric emission through the circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) technique peaked in
[...] Read more.
Density functional theory (DFT) and its extension, time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT), have become fundamental tools for modeling chiral excited states and supporting experimental chiroptical spectroscopies. In this connection, the interest in understanding the asymmetric emission through the circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) technique peaked in the current decade. In the present work, we are computationally faced with an emerging class of luminophores which combines the luminogenic source of the BODIPY unit with the intrinsic chirality of the helicene pendant to obtain a chiral radiative deactivation. In particular, a meso-substituted BODIPY-[6]helicene was deeply examined through a DFT multistep approach to attain an appreciable level of theory for the CPL simulation. Among the multitude of alternatives, TPSSTPSS exchange-correlation functional with 6-311G(d,p) basis set revealed to be the best computational protocol to emulate the CPL spectral profile with regard to peak intensity, band position, and chiral sign for both M and P form.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Anion Transfer Reactions from Chiral Hypervalent Iodine Macrocycles
by
Mina Dumre Pandey, Tahir Awais, Krishna Pandey, Samsul Arafin, Eli Jones and Kyle N. Plunkett
Organics 2025, 6(4), 52; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040052 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The direct chlorination, bromination and azidation of beta keto esters, 2-acetyl-1-tetralone and methyl 1-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-indene-2-carboxylate is achieved utilizing anion-coordinated hypervalent iodine benziodazoles derived from hypervalent iodine macrocycles. This reaction, which introduces the halogen, azido or cyano group at the alpha carbon atom of beta
[...] Read more.
The direct chlorination, bromination and azidation of beta keto esters, 2-acetyl-1-tetralone and methyl 1-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-indene-2-carboxylate is achieved utilizing anion-coordinated hypervalent iodine benziodazoles derived from hypervalent iodine macrocycles. This reaction, which introduces the halogen, azido or cyano group at the alpha carbon atom of beta keto esters, is accomplished in chloroform at 60 °C and results in the formation of a chiral center. Depending on the structure of the benziodazole reagent, the reaction can have mild enantioselectivity. The reaction between 2-acetyl-1-tetralone and phenylalanine-derived hypervalent iodine benziodazoles results in the chlorinated product with 26% enantiomeric excess.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis of Fused Cyclic Aryl Amino Carbon Carbene Salt Precursors ([f-CArACH]+) Incorporating an Auxiliary Arene and Isolation of a Cu(I) Complex
by
Polidoros Chrisovalantis. Ioannou, Nikolaos Tsoureas and Sevasti-Panagiota Kotsaki
Organics 2025, 6(4), 51; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040051 - 10 Nov 2025
Abstract
The synthesis of a small library of fused Cyclic Aryl Amino Carbon (f-CArAC) carbene precursors in the form of 1,1,2,4-tetraaryl-1H-isoindol-2-ium triflate (6), (7-R) (R = tBu, CF3) or 3,3-dimethyl-2,8-bis-arene-substituted-3,4-dihydro-isoquinolin-2-ium hydrogen-dichloride (8) and 2,4,8-tri(substituted)-isoquinolin-2-ium tosylate
[...] Read more.
The synthesis of a small library of fused Cyclic Aryl Amino Carbon (f-CArAC) carbene precursors in the form of 1,1,2,4-tetraaryl-1H-isoindol-2-ium triflate (6), (7-R) (R = tBu, CF3) or 3,3-dimethyl-2,8-bis-arene-substituted-3,4-dihydro-isoquinolin-2-ium hydrogen-dichloride (8) and 2,4,8-tri(substituted)-isoquinolin-2-ium tosylate salts (12) has been achieved. All of them feature an arene incorporated on the annulated benzene ring of the corresponding heterocycle, introduced at the early stages of their synthesis via the Suzuki cross-coupling reaction between 2,6-dibromo-benzaldehyde and the desired aryl boronic acid. The terphenyl-2′carbaldehyde by-products of this Suzuki reaction are useful starting points for the preparation of two new iminium iodide salts (10-R) (R = H, CF3) as potential precursors to access ACyclic Amino Carbon (ACAC) carbenes. Compounds (6) and (7-tBu) react readily with hydroxide either in THF or in a biphasic Et2O/aqueous OH− solution to produce the substituted isoindolinols (13) and (14), respectively. The thermal dehydration of the former generates the corresponding f-CArAC carbene in situ, which is trapped by Cu(I)Cl furnishing, a rare example of a two-coordinate Cu(I) complex (15) supported by this new ligand scaffold.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Generalization of High-Throughput Experimentation in Organic Chemistry: Case Study on the Flortaucipir Synthesis
by
Gaëtan Ossard, Milene Macedo Hornink, Sabrina Lebrequier, David-Alexandre Buisson, Jean-Christophe Cintrat and Eugénie Romero
Organics 2025, 6(4), 50; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040050 - 5 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
High-Throughput Experimentation has undergone an outstanding evolution in the past two decades and has proven to be a game-changer in the acceleration of reaction discovery and optimization. Despite a good implementation in the pharmaceutical industry and a demonstrated accessibility to the technology, the
[...] Read more.
High-Throughput Experimentation has undergone an outstanding evolution in the past two decades and has proven to be a game-changer in the acceleration of reaction discovery and optimization. Despite a good implementation in the pharmaceutical industry and a demonstrated accessibility to the technology, the generalization of High-Throughput Experimentation as a standard method for optimizing reactions is not yet observed. The perspective aims at discussing the necessity of generalizing such technologies, supported by the case study: the optimization by High-Throughput Experimentation of a key step in the synthesis of Flortaucipir, an FDA-approved imaging agent for Alzheimer’s diagnosis.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dichloro-Bis(1-Alkyl/Styryl-Benzimidazole)-Cobalt(II) Pre-Catalyst for Ethylene Dimerization
by
Shaima Hkiri, Neslihan Şahin, Romain Sabourin, Rémi Brandt, İsmail Özdemir and David Sémeril
Organics 2025, 6(4), 49; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040049 - 4 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A series of five cobalt(II) complexes, dichloro-bis(1-benzyl-benzimidazole)-cobalt(II) (1a), dichloro-bis[1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-benzimidazole]-cobalt(II) (1b), dichloro-bis((Z)-1-styryl-benzimidazole)-cobalt(II) (1c), dichloro-bis[(Z)-1-(2-fluorostyryl)-benzimidazole]-cobalt(II) (1d) and dichloro-bis(1-cinnamyl-benzimidazole)-cobalt(II) (1e), were evaluated in ethylene dimerization. Four of these complexes were described for
[...] Read more.
A series of five cobalt(II) complexes, dichloro-bis(1-benzyl-benzimidazole)-cobalt(II) (1a), dichloro-bis[1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-benzimidazole]-cobalt(II) (1b), dichloro-bis((Z)-1-styryl-benzimidazole)-cobalt(II) (1c), dichloro-bis[(Z)-1-(2-fluorostyryl)-benzimidazole]-cobalt(II) (1d) and dichloro-bis(1-cinnamyl-benzimidazole)-cobalt(II) (1e), were evaluated in ethylene dimerization. Four of these complexes were described for the first time and fully characterized by IR, elemental analysis, mass and NMR spectroscopy. In the solid state, the cobalt atom exhibited a typical tetrahedral geometry and was found to be coordinated to two chlorine atoms and two benzimidazole rings. In the presence of 20 bar of ethylene and diethylaluminium chloride as a co-catalyst, the complex with styryl substituents on the benzimidazole rings, complex 1c, exhibited the highest activity with a turnover frequency of 3430 mol(ethylene)·mol(Co)−1·h−1.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Recent Advances in the Synthesis of 4H-Benzo[d][1,3]oxathiin-4-ones and 4H-Benzo[d][1,3]dioxin-4-ones
by
Liling Pan and Ke Yang
Organics 2025, 6(4), 48; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040048 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
4H-Benzo[d][1,3]oxathiin-4-ones and 4H-benzo[d][1,3]dioxin-4-ones, as important classes of sulfur- or oxygen-containing heterocyclic compounds, possess significant application potential in the fields of pharmaceutical chemistry, agriculture, and the food industry due to their distinctive structural characteristics and diverse
[...] Read more.
4H-Benzo[d][1,3]oxathiin-4-ones and 4H-benzo[d][1,3]dioxin-4-ones, as important classes of sulfur- or oxygen-containing heterocyclic compounds, possess significant application potential in the fields of pharmaceutical chemistry, agriculture, and the food industry due to their distinctive structural characteristics and diverse biological activities. In recent years, efficient synthetic strategies for these compounds have witnessed remarkable progress. This review summarizes significant advancements in the construction of these heterocycles from 2012 to the present.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Efficient Degradation of Cis-Polyisoprene by GQDs/g-C3N4 Nanoparticles Under UV Light Irradiation
by
Cilong Chen, Jinrui Liu, Bangsen Li, Dashuai Zhang, Peisong Zhang, Jianjun Shi and Zaifeng Shi
Organics 2025, 6(4), 47; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040047 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Rubber material with high elasticity and viscoelasticity has become the most widely used universal material, and the study of the aging failure mechanism of rubber has been meaningful research in the polymer materials field. Cis-polyisoprene was employed to analyze the mechanism of
[...] Read more.
Rubber material with high elasticity and viscoelasticity has become the most widely used universal material, and the study of the aging failure mechanism of rubber has been meaningful research in the polymer materials field. Cis-polyisoprene was employed to analyze the mechanism of oxidative degradation under artificial UV irradiation, and the GQDs/g-C3N4 photocatalysis with a 2D layered structure prepared by the method of microwave-assisted polymerization enabled to accelerate the degradation procedure. The results showed that the oxidation of cis-polyisoprene occurred during the irradiation for 3 days and the structure of cis-polyisoprene changed. The α-H of the double bond was attacked by oxygen to form hydroperoxide. Then, aldehydes and ketones generated as the addition reaction of double bonds occurred. The content of the hydrogen of C=C reduced, and the oxidative degradation was dominant at the initial aging stage. The crosslinking reaction was dominant at the final aging stage and the average molecular weight decreased from 15.49 × 104 to 8.78 × 104. The GQDs could promote the charge transfer and the photodegradation efficiency and inhibit the electron–hole recombination. The light capture ability of GQDs was improved after compositing with g-C3N4. The free radicals ·O22− generated after adding GQDs/g-C3N4 nanoparticles, and the molecular weight of cis-polyisoprene decreased to 5.79 × 104, with the photocatalytic efficiency increasing by 20%. This work provided academic bases and reference values for the application of photocatalysts in the field of natural rubber degradation and rubber wastewater treatment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Synthetic Routes and Bioactivity Profiles of the Phenothiazine Privileged Scaffold
by
Aigul E. Malmakova and Alan M. Jones
Organics 2025, 6(4), 46; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040046 - 10 Oct 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This review offers a focused overview of the strategies used to build and modify phenothiazine (PTZ) derivatives. It covers both classical synthetic approaches and advances reported since 2014, including transition metal-catalyzed transformations and greener techniques, such as electrosynthesis, microwave-assisted reactions, and ultrasound-promoted methods.
[...] Read more.
This review offers a focused overview of the strategies used to build and modify phenothiazine (PTZ) derivatives. It covers both classical synthetic approaches and advances reported since 2014, including transition metal-catalyzed transformations and greener techniques, such as electrosynthesis, microwave-assisted reactions, and ultrasound-promoted methods. Each strategy is evaluated with respect to efficiency, scalability, and sustainability. In parallel, the review surveys the diverse bioactivity profiles of PTZ derivatives, ranging from antipsychotic, anticancer, and antimicrobial activities to emerging applications in photodynamic therapy and neuroprotection. By correlating synthetic accessibility with biological potential, this review provides an integrated perspective that highlights advances achieved since 2014 and outlines future opportunities for rational PTZ design and applications.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Song Remains the Same, but the Enzymes Don’t: Imidazolium ILs as Potential Disruptors of Fatty Acid Metabolism
by
Savina Stoyanova and Milen G. Bogdanov
Organics 2025, 6(4), 45; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040045 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study examined twenty-eight N-methylimidazolium ionic liquids (ILs) with various substituents and anions to assess their impact on the activity of Carnitine Acetyltransferase (CAT), an indispensable enzyme in human metabolism. In vitro experiments demonstrated that these compounds inhibited CAT in a concentration-dependent
[...] Read more.
This study examined twenty-eight N-methylimidazolium ionic liquids (ILs) with various substituents and anions to assess their impact on the activity of Carnitine Acetyltransferase (CAT), an indispensable enzyme in human metabolism. In vitro experiments demonstrated that these compounds inhibited CAT in a concentration-dependent manner, with IC50 values ranging from 0.93 to 30.8 mM. Structural analysis of the ILs revealed the following structure–activity relationships: (i) the length of the hydrocarbon chain at N3 markedly affects CAT activity, with longer chains resulting in stronger inhibition; (ii) the degree of unsaturation and the presence of polar groups are not essential for increased activity; (iii) the effect of the anion aligns with the Hofmeister series. One of the most potent compounds, 1-decyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide [C10C1im]Br, was identified as a mixed inhibitor of CAT with a Ki of 0.77 mM. These findings raise concerns about the biocompatibility of commonly used imidazolium ILs, as they may interfere with fatty acid oxidation by inhibiting their cellular transport.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of MW Irradiation on the Reaction Between (2R,7R,11S,16S)-1,8,10,17-tetraazapentacyclo[8.8.1.1.8,170.2,70.11,16]icosane and p-Substituted Phenols
by
Diego Quiroga, Jaime Ríos-Motta and Augusto Rivera
Organics 2025, 6(4), 44; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040044 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
4,4′-substituted-2,2′-((hexahydro-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-1,3(2H)-diyl)bis(methylene))bisphenols (1a–d) and 2,6-bis{[3-(2-hydroxy-5-substitutedbenzyl)octahydro-1H-benzimidazol-1-yl]methyl}-4-substitutedphenols (2a–b) were synthesized via microwave (MW) irradiation of aminal (2R,7R,11S,16S
[...] Read more.
4,4′-substituted-2,2′-((hexahydro-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-1,3(2H)-diyl)bis(methylene))bisphenols (1a–d) and 2,6-bis{[3-(2-hydroxy-5-substitutedbenzyl)octahydro-1H-benzimidazol-1-yl]methyl}-4-substitutedphenols (2a–b) were synthesized via microwave (MW) irradiation of aminal (2R,7R,11S,16S)-1,8,10,17-tetraazapentacyclo[8.8.1.1.8,170.2,70.11,16]icosane 2 with p-substituted phenols. Microwave (MW) irradiation improved reaction rates and yields at 80 °C. Compounds 1a–d were racemic, and 2a–b were diastereomeric. NMR spectra revealed key signals for the perhydrobenzimidazole fragment, aromatic rings, and aminal carbons. Differences in the 13C NMR spectra highlighted structural variations, such as distinct carbonyl and methoxyl signals in 2d. MW irradiation at higher temperatures (100–120 °C) reduced yields of 1, especially for phenols with methyl (Me) and methoxy (OMe) groups, suggesting a shift toward the formation of compound 2. Additionally, higher temperatures led to polymerization byproducts, emphasizing the impact of MW energy on reaction pathways. These results provide valuable insights for designing molecules with potential applications in materials science and medicinal chemistry.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Degrees of Sulfonation: Mapping the Reactivity Landscape of Acridine and Acridone
by
Péter Kisfaludi, Sára Spátay, Péter Huszthy and Ádám Golcs
Organics 2025, 6(3), 43; https://doi.org/10.3390/org6030043 - 12 Sep 2025
Abstract
Although sulfonated acridines and acridones are valuable scaffolds in diagnostics and materials science, to our best knowledge, there is no comprehensive study that addresses how the degree of sulfonation depends on reaction parameters. To fill this gap, we investigated the sulfonation behavior of
[...] Read more.
Although sulfonated acridines and acridones are valuable scaffolds in diagnostics and materials science, to our best knowledge, there is no comprehensive study that addresses how the degree of sulfonation depends on reaction parameters. To fill this gap, we investigated the sulfonation behavior of unsubstituted acridine and acridone under classical conditions, using sulfuric acid, oleum, and chlorosulfonic acid. A factorial experimental design was applied to systematically evaluate the influence of temperature and reagent excess on the extent of sulfonation, while keeping the reaction time constant. Products were analyzed by HPLC–MS/MS to determine the degree of sulfonation and its distribution. Regioselectivity and product isolation were not addressed in this study. Our results provide a foundational dataset for controlling sulfonation level for these heterocycles and can help future synthetic applications where defined sulfonation patterns are desired.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Atoms, Crystals, Molecules, Organics, Symmetry, Inorganics
Advances in Molecular Symmetry and Chirality Research
Topic Editors: Ralph N. Salvatore, Guzman Gil-RamirezDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Sci, Spectroscopy Journal, Chemistry, Organics, Catalysts, Molecules, Photochem
Photogenerated Intermediates: Spectral Capture, Theoretical Characterization and Chemical Reactivity
Topic Editors: Rui Fausto, Licinia L. G. JustinoDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Organics
Recent Advances in Selective Oxidation
Guest Editors: Lei Liu, Xigong LiuDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
Organics
Advanced Oxidation Processes for Efficient Removal of Organic Pollutants in Water Treatment
Guest Editor: Yan WangDeadline: 10 June 2026
Special Issue in
Organics
Organic Supramolecular Chemistry of Natural Products
Guest Editor: Ruilong ShengDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Organics
Advanced Research Papers in Organics
Collection Editors: Wim Dehaen, Michal Szostak, Huaping Xu












