- Article
Ketone Body β-Hydroxybutyrate Enhances Hypothalamic Leptin and Insulin Responsiveness
- Ran Xu,
- Nozomi Takahashi and
- Kentaro Kaneko
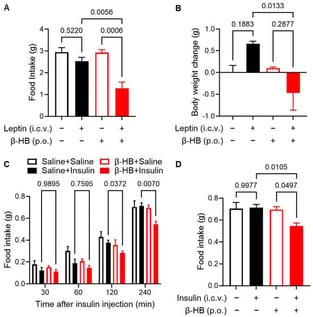
Background/Objectives: Obesity is characterized by dysregulated hypothalamic energy homeostasis and reduced central responsiveness to the anorexigenic hormones leptin and insulin. β-Hydroxybutyrate (β-HB), a major ketone body, has recently garnered attention as a signaling metabolite. However, its effects on hypothalamic leptin and insulin responsiveness remain unclear. This study aimed to investigate the effects of β-HB on hypothalamic hormone responsiveness and the associated molecular mechanisms, primarily using a high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mouse model. Methods: Male mice were fed an HFD to induce obesity and treated with β-HB via oral or intracerebroventricular (ICV) administration. Feeding behavior following leptin and insulin administration was evaluated, and activation of hypothalamic leptin-induced STAT3 signaling and insulin-induced Akt signaling was analyzed. In addition, mRNA expression of inflammation-related and appetite-regulating genes was assessed by quantitative PCR. Normal mice also received chronic ICV administration of β-HB from the onset of HFD feeding, and changes in body weight and cumulative food intake were measured. Results: Both oral and ICV administration of β-HB significantly enhanced the anorexigenic responses to leptin and insulin in HFD-induced obese mice. At the molecular level, leptin-induced STAT3 phosphorylation and insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation were enhanced in the hypothalamus. Gene expression analysis revealed reduced SOCS3 and TNFα expression and increased POMC expression. Furthermore, chronic ICV administration of β-HB from the onset of HFD feeding significantly suppressed body weight gain and the increase in cumulative food intake. Conclusions: This study demonstrates that β-HB improves hypothalamic leptin and insulin responsiveness in obese mice and modulates the associated molecular environment. These findings suggest that β-HB acts as a metabolically responsive signaling molecule regulating hypothalamic function, providing a basis for novel metabolic intervention strategies against obesity.
10 February 2026