- Article
Effect of Probiotic Supplementation on Muscle Strength After Myocardial Revascularization: A Randomized, Controlled, Triple-Blind Clinical Trial
- Isabela Militão Gimenes,
- Ester Godoy Silvestre and
- Ricardo Fernandes
- + 5 authors
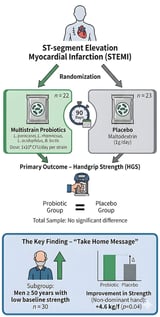
Evidence suggests that gut dysbiosis may contribute to acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and its complications, including reduced physical performance and muscle weakness. We hypothesized that probiotic supplementation could improve muscle strength during post-AMI recovery. In a randomized, controlled, triple-blind clinical trial, adults and older adults undergoing myocardial revascularization received either a multistrain probiotic formulation (Lacticaseibacillus paracasei, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus, Lacticaseibacillus acidophilus, and Bifidobacterium lactis) or placebo for 90 days. The primary outcome was handgrip strength (HGS). Forty-five participants completed the study. No significant between-group differences were observed in the main analysis. However, in an exploratory subgroup of men aged 50 years and older with low baseline HGS (n = 30), probiotic supplementation led to a greater improvement in non-dominant HGS after 90 days compared with placebo (mean difference: +4.6 kg/f; p = 0.04). A baseline-adjusted ANCOVA confirmed a significant baseline-by-treatment interaction for the non-dominant hand (β = +0.33; 95% CI: +0.02 to +0.62; p = 0.038), indicating greater improvements among participants with lower initial strength. Although the primary analysis yielded null results, these exploratory findings indicate a potential benefit of probiotic supplementation in a clinically vulnerable subgroup of revascularized men with low baseline strength. Larger and prospectively powered trials are warranted to confirm these observations. Trial registration: RBR-6ztyb7.
11 February 2026