Journal Description
Nanomanufacturing
Nanomanufacturing
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the fabrication of miniaturized devices or objects, their scalability, and their eventual industrial production, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 23.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Nanomanufacturing is a companion journal of Nanomaterials.
Latest Articles
Preparation and Transport Properties of Mn2.16Ga Single Crystal
Nanomanufacturing 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing6010005 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
In recent years, antiferromagnetic kagome materials have attracted considerable attention in condensed matter physics owing to their distinctive lattice geometry. In this work, high-quality single crystals of D019-structured Mn2.16Ga were grown using the flux method, and their magnetotransport properties were systematically
[...] Read more.
In recent years, antiferromagnetic kagome materials have attracted considerable attention in condensed matter physics owing to their distinctive lattice geometry. In this work, high-quality single crystals of D019-structured Mn2.16Ga were grown using the flux method, and their magnetotransport properties were systematically studied. Measurements of magnetization versus field (M–H), temperature-dependent magnetization (M–T), and the anomalous Hall effect confirm that the crystal undergoes a magnetic-structural transition driven by both temperature and the magnetic field. Remarkably, a coexistence of positive and negative longitudinal magnetoresistance (MR) is observed in Mn2.16Ga. The MR shows a field-induced sign change from negative to positive. The negative MR is attributed to field-modified magnetic ordering, whereas the positive MR originates mainly from interlayer electron conduction in the kagome lattice and distortion of the in-plane triangular arrangement of Mn magnetic moments. These results offer valuable insights into the electronic and magnetic transport behavior of Mn-based antiferromagnetic single crystals.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
rPET Nanofiber Membranes for Air Filtration: High Performance via Electrospinning Optimization
by
Gabriela Brunosi Medeiros, Paulo Augusto Marques Chagas, Gustavo Cardoso da Mata, Daniela Patrícia Freire Bonfim, Daniela Sanches de Almeida and Mônica Lopes Aguiar
Nanomanufacturing 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing6010004 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
Although recycled poly(ethylene terephthalate) (rPET) is an attractive, sustainable feedstock for electrospinning, optimization of processing variables for filtration performance remains limited. This study quantifies how polymer concentration, flow rate, and applied voltage govern fiber morphology and key filtration metrics—collection efficiency (η),
[...] Read more.
Although recycled poly(ethylene terephthalate) (rPET) is an attractive, sustainable feedstock for electrospinning, optimization of processing variables for filtration performance remains limited. This study quantifies how polymer concentration, flow rate, and applied voltage govern fiber morphology and key filtration metrics—collection efficiency (η), pressure drop (ΔP), quality factor (Qf), and porosity—in rPET membranes. A fractional factorial design was employed to model interactions and identify trade-offs in filtration performance. The optimal condition was obtained at 16 wt.% PET, 1.2 mL·h−1, and 22 kV, yielding uniform fibers with an average diameter of 328.6 nm and high filtration efficiencies (95.65–99.99%). The permeability constants were 1.07 × 10−12 m2 (20 wt.% PET) and 1.15 × 10−13 m2 (8 wt.% PET), indicating an increase in permeability with increasing polymer concentration and fiber diameter. The 20 wt.% PET membrane delivered the highest Qf of 0.0646 Pa−1 with a low ΔP of 48.5 Pa at 4.8 cm·s−1, reflecting a favorable balance between collection and airflow resistance. In summary, higher PET concentrations reduce flow resistance and improve Qf, whereas lower concentrations yield finer fibers and high η at the expense of permeability. rPET nanofiber membranes, therefore, represent a sustainable and versatile route to high-efficiency, lower-pressure-drop air filters for residential, industrial, and commercial environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nanomanufacturing: Feature Papers 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Machine Learning-Based Algorithm for the Design of Multimode Interference Nanodevices
by
Roney das Mercês Cerqueira, Vitaly Félix Rodriguez-Esquerre and Anderson Dourado Sisnando
Nanomanufacturing 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing6010003 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Multimode interference photonic nanodevices have been increasingly used due to their broad functionality. In this study, we present a methodology based on machine learning algorithms for inverse design capable of providing the output port position (x-axis coordinate) and MMI region length
[...] Read more.
Multimode interference photonic nanodevices have been increasingly used due to their broad functionality. In this study, we present a methodology based on machine learning algorithms for inverse design capable of providing the output port position (x-axis coordinate) and MMI region length (y-axis coordinate) for achieving higher optical signal transfer power. This is sufficient to design Multimode Interference 1 × 2, 1 × 3, and 1 × 4 nanodevices as power splitters in the wavelength range between 1350 and 1600 nm, which corresponds to the E, S, C, and L bands of the optical communications window. Using Multilayer Perceptron artificial neural networks, trained with k-fold cross-validation, we successfully modeled the complex relationship between geometric parameters and optical responses with high precision and low computational cost. The results of this project meet the requirements for photonic device projects of this nature, demonstrating excellent performance and manufacturing tolerance, with insertion losses ranging from 0.34 dB to 0.58 dB.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Addressing Challenges in Porous Silicon Fabrication for Manufacturing Multi-Layered Optical Filters
by
Noha Gaber, Diaa Khalil and Amr Shaarawi
Nanomanufacturing 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing6010002 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The motivation for this work is to study the cause and present mitigation for some challenges faced in preparing porous silicon. This enables benefiting from the appealing benefits of porous silicon that offers a wide range, simple technique for varying the refractive index.
[...] Read more.
The motivation for this work is to study the cause and present mitigation for some challenges faced in preparing porous silicon. This enables benefiting from the appealing benefits of porous silicon that offers a wide range, simple technique for varying the refractive index. Such challenges include the refractive index values, sensitivity to oxidation, some fabrication parameters, and other factors. Additionally, highly doped p-type silicon is preferred to form porous silicon, but it causes high losses, which necessitates its detachment. We investigate some possible causes of refractive index change, especially after detaching the fabricated layers from the silicon substrate. Thereby, we could recommend simple but essential precautions during fabrication to avoid such a change. For example, the native oxide formed in the pores has a role in changing the porosity upon following some fabrication sequence. Oppositely, intrinsic stress doesn’t have a significant role. On another aspect, the effect of differing etching/break times on the filter’s responses has been studied, along with other subtle details that may affect the lateral and depth homogeneity, and thereby the process success. Solving such homogeneity issues allowed reaching thick layers not suffering from the gradient index. It is worth highlighting that several approaches have been reported; unlike these, our method doesn’t require sophisticated equipment that might not be available in every lab. To well characterize the thin films, it has been found essential that freestanding monolayers are used for this purpose. From which, the wavelength-dependent refractive index and absorption coefficient have been determined in the near infrared region (1000–2500 nm) for different fabricated conditions. Excellent fitting with the measured interference pattern has been achieved, indicating the accurate parameter extraction, even without any ellipsometry measurements. This also demonstrates the refractive index homogeneity of the fabricated layer, even with a large thickness of over 16 µm. Subsequently, multilayer structures have been fabricated and tested, showing the successful nano-manufacturing methodology.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advancements in Two-Photon Polymerization (2PP) for Micro and Nanoscale Fabrication
by
Prithvi Basu
Nanomanufacturing 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing6010001 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Two-photon polymerization (2PP) is revolutionizing micro- and nanoscale manufacturing by enabling true 3D fabrication with feature sizes far below the diffraction limit—capabilities that traditional lithography cannot match. By using ultrafast femtosecond laser pulses and nonlinear absorption, 2PP initiates polymerization only at the laser’s
[...] Read more.
Two-photon polymerization (2PP) is revolutionizing micro- and nanoscale manufacturing by enabling true 3D fabrication with feature sizes far below the diffraction limit—capabilities that traditional lithography cannot match. By using ultrafast femtosecond laser pulses and nonlinear absorption, 2PP initiates polymerization only at the laser’s focal point, offering unmatched spatial precision. This paper highlights key advancements driving the field forward: the development of new materials engineered for 2PP with improved sensitivity, mechanical strength, and the introduction of high-speed, parallelized fabrication strategies that significantly enhance throughput. These innovations are shifting 2PP from a prototyping tool to a viable method for scalable production. Applications now range from custom biomedical scaffolds to complex photonic and metamaterial structures, demonstrating their growing real-world impact. We also address persistent challenges—including slow writing speeds and limited material options—and explore future directions to overcome these barriers. With continued progress in materials and hardware, 2PP is well positioned to become a cornerstone of next-generation additive manufacturing.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Silver Nanoparticles for Conductive Inks Functionalization on Paper Substrates
by
Sonia Ceron, David Barba and Miguel A. Dominguez
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(4), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040019 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this work, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) used in conductive inks were synthesized for implementation in printable and flexible electronics. The nanoparticles were obtained using silver nitrate as a precursor agent, sodium citrate as a reductive/protective agent and sodium borohydride as a reductive, whose
[...] Read more.
In this work, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) used in conductive inks were synthesized for implementation in printable and flexible electronics. The nanoparticles were obtained using silver nitrate as a precursor agent, sodium citrate as a reductive/protective agent and sodium borohydride as a reductive, whose concentrations were varied for optimization. The optical absorption, morphology, size-distribution, crystallinity and stability over time of the processed nanoparticles were determined upon the content of the chemical contents. The AgNPs-based inks were then tested as conductive wires drawn on different common flexible substrates to measure their electrical characteristics and demonstrate their relevance in printable electronics.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Self-Assembly of Block Copolymers to Prepare Advanced Materials with Hierarchical Functional Nanostructures
by
Yanzhen Liu, Yang Liu, Fengfeng Feng and Weijie Wang
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(4), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040018 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Block copolymers with diverse compositions and topologies can self-assemble into multi-hierarchical structures, yielding materials with a wide range of functional properties. By adjusting external stimuli such as temperature, solvent polarity, mechanical force, and light exposure, these polymers form various nanostructures—including nanocrystals, micelles, and
[...] Read more.
Block copolymers with diverse compositions and topologies can self-assemble into multi-hierarchical structures, yielding materials with a wide range of functional properties. By adjusting external stimuli such as temperature, solvent polarity, mechanical force, and light exposure, these polymers form various nanostructures—including nanocrystals, micelles, and vesicles in solution; spherical, cylindrical, and lamellar microphases in bulk; and even “fractal” morphologies at interfaces. These hierarchical materials exhibit tailored functionality based on molecular design, enabling broad applications in nanomedicine, electronic devices, optical elements, and catalytic systems. In this review, we first summarize synthetic strategies for block copolymers with varying compositions and architectures. We then discuss their self-assembly behaviors and resulting nanoscale morphologies in bulk, solution, and interfacial environments. Several representative examples of assembled block copolymer systems and their practical applications are highlighted. Finally, we offer perspectives on future developments in the fabrication and application of block copolymer-based nanomaterials. This review provides an overview of strategies and examples for constructing precision nanostructures via block copolymer self-assembly, aiming to inspire further advances in nanomanufacturing technologies.
Full article
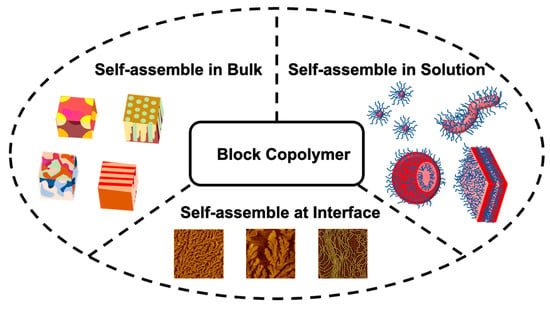
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Time-Dependent Hydrothermal Synthesis of TiO2 in the Presence of Zn2+: Effects on Photoconductivity
by
Tilemachos Georgakopoulos, Georgios Samourgkanidis, Nadia Todorova, Christos Trapalis and Katerina Pomoni
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(4), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040017 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles were synthesized via hydrothermal treatment of tetrabutyl titanate in sulfuric acid, with controlled reaction times (10 h and 24 h) and zinc sulfate as a modifier. XRD confirmed exclusive formation of the anatase phase, with longer reaction times promoting crystallite
[...] Read more.
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles were synthesized via hydrothermal treatment of tetrabutyl titanate in sulfuric acid, with controlled reaction times (10 h and 24 h) and zinc sulfate as a modifier. XRD confirmed exclusive formation of the anatase phase, with longer reaction times promoting crystallite growth. SEM and BET analyses showed that introducing Zn during synthesis suppressed agglomeration, decreased the particle size, and modified porosity while maintaining the mesoporous nature of all samples. UV–Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy showed a band gap near 3.2 eV, which was unaffected by Zn content or morphology. Photoconductivity studies showed a several-orders-of-magnitude increase in conductivity under vacuum conditions, especially in samples heat-treated for 24 h, due to the generation of oxygen vacancies and

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sodium-Doped Carbon Dots as Fluorescent Sensor for Highly Selective Detection of TNP Explosives in the Environment
by
Tianyu Gao, Xuehua Sun and Hongmei Chai
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(4), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040016 - 23 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Given the environmental hazards of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (TNP) and the limitations of existing detection methods, sodium-doped fluorescent carbon dots (Na-CDs) were successfully synthesized via a one-step hydrothermal method using citric acid and ascorbic acid as carbon sources. Compared with undoped carbon quantum dots, Na-CDs
[...] Read more.
Given the environmental hazards of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (TNP) and the limitations of existing detection methods, sodium-doped fluorescent carbon dots (Na-CDs) were successfully synthesized via a one-step hydrothermal method using citric acid and ascorbic acid as carbon sources. Compared with undoped carbon quantum dots, Na-CDs exhibited nearly identical surface functional groups but significantly enhanced fluorescence stability and markedly improved selective responsiveness toward TNP. Accordingly, a Na-CD-based fluorescent probe was developed for the highly selective detection of TNP. Results demonstrated a good linear relationship between the relative fluorescence intensity change (F0 − F)/F0 and TNP concentration ranging from 7 × 10−7 to 2 × 10−5 mol/L, with a detection limit of 3.5 × 10−8 mol/L. When applied to detect TNP in local river water samples, the method achieved recoveries of 95.40–104.0%, confirming its reliability for real-world environmental sample analysis. This study develops a novel, sensitive, and highly selective approach for monitoring TNP in environmental systems.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Tuning Optical and Photoelectrochemical Properties of TiO2/WOx Heterostructures by Reactive Sputtering: Thickness-Dependent Insights
by
Lucas Diniz Araujo, Bianca Sartori, Matheus Damião Machado Torres, David Alexandro Graves, Benedito Donizeti Botan-Neto, Mariane Satomi Weber Murase, Nilton Francelosi Azevedo Neto, Douglas Marcel Gonçalves Leite, Rodrigo Sávio Pessoa, Argemiro Soares da Silva Sobrinho and André Luis Jesus Pereira
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(4), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040015 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Metal-oxide heterostructures represent an effective strategy to overcome the limitations of pristine TiO2, including its ultraviolet-only light absorption and rapid electron–hole recombination, which hinder its performance in solar-driven applications. Among various configurations, coupling TiO2 with tungsten oxide (WOx)
[...] Read more.
Metal-oxide heterostructures represent an effective strategy to overcome the limitations of pristine TiO2, including its ultraviolet-only light absorption and rapid electron–hole recombination, which hinder its performance in solar-driven applications. Among various configurations, coupling TiO2 with tungsten oxide (WOx) forms a favorable type-II band alignment that enhances charge separation. However, a comprehensive understanding of how WOx overlayer thickness affects the optical and photoelectrochemical (PEC) behavior of device-grade thin films remains limited. In this study, bilayer TiO2/WOx heterostructures were fabricated via reactive DC magnetron sputtering, with controlled variation in WOx thickness to systematically investigate its influence on the structural, optical, and PEC properties. Adjusting the WOx deposition time enabled precise tuning of light absorption, interfacial charge transfer, and donor density, resulting in markedly distinct PEC responses. The heterostructure obtained with 30 min of WOx deposition demonstrated a significant enhancement in photocurrent density under AM 1.5G illumination, along with reduced charge-transfer resistance and improved capacitive behavior, indicating efficient charge separation and enhanced charge storage at the electrode–electrolyte interface. These findings underscore the potential of sputtered TiO2/WOx bilayers as advanced photoanodes for solar-driven hydrogen generation and light-assisted energy storage applications.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Friction and Wear Performance of Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced Co-Based Atmospheric Plasma-Sprayed Coatings
by
Ilias Georgiopoulos, Dimitra Giasafaki, Dia Andreouli and Chara I. Sarafoglou
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(4), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040014 - 24 Sep 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
Atmospheric plasma spraying was used to create composite coatings employing mixed alloy matrices supplemented with carbon-based solid lubricants as feedstock materials. The current study’s goal was to examine the tribological properties of these coatings and explore the potential benefits of using CNTs as
[...] Read more.
Atmospheric plasma spraying was used to create composite coatings employing mixed alloy matrices supplemented with carbon-based solid lubricants as feedstock materials. The current study’s goal was to examine the tribological properties of these coatings and explore the potential benefits of using CNTs as a nano-additive to minimize wear and friction while enhancing lubrication conditions in tribosystems such as piston ring–cylinder liner systems. Pin-on-disk measurements are used to correlate the chemical composition of feedstock materials with the friction coefficient and wear rate during coating operation. The enhanced behavior of the produced coatings is investigated. The anti-wear performance of Co-based cermet and metal alloys coatings, as well as the enhanced lubrication conditions during operation, are shown. In-depth discussion is provided regarding how the features of the feedstock powder affect the quality and performance of the produced coatings. The results showed that coatings based on the CoMo alloy exhibited an increase in wear due to CNT agglomeration. In contrast, CNT addition led to an improvement in bonding strength by up to 33%, a reduction in wear rate by up to 80%, and a decrease in the coefficient of friction from approximately 0.70 to 0.35 in CoNi cermet coatings. These findings demonstrate the role of CNTs in coating performance for demanding tribological applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Innovative Synthesis and Applications of Functional Nanomaterials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Thermal and Electrical Properties of Cement-Based Materials Reinforced with Nano-Inclusions
by
Spyridoula G. Farmaki, Panagiota T. Dalla, Dimitrios A. Exarchos, Konstantinos G. Dassios and Theodore E. Matikas
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(3), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5030013 - 1 Sep 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study explores the influence of various nano-inclusions on the electrical and thermal properties of cement-based materials. Specifically, it investigates the incorporation of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) and Graphene Nanoplatelets (GNPs) as reinforcement materials in cement composites. These advanced nanomaterials enhance the mechanical
[...] Read more.
This study explores the influence of various nano-inclusions on the electrical and thermal properties of cement-based materials. Specifically, it investigates the incorporation of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) and Graphene Nanoplatelets (GNPs) as reinforcement materials in cement composites. These advanced nanomaterials enhance the mechanical strength, durability, and functional properties of cementitious matrices. A series of experimental tests was conducted to evaluate the thermal and electrical behavior of nano-reinforced concrete, employing nondestructive evaluation techniques, such as Infrared Thermography (IRT) and Electrical Resistivity measurements. The results indicate that increasing the concentration of nanomaterials significantly improves both the thermal and electrical conductivity of the composites. Optimum performance was observed at a CNT dosage of 0.6% and a GNP dosage of 1.2% by weight of cement in cement paste, while in concrete, both nanomaterials showed a significant decrease in resistivity beginning at 1.0%, with optimal performance at 1.2%. The study also emphasizes the critical role of proper dispersion techniques, such as ultrasonication, in achieving a homogeneous distribution of nanomaterials within the cement matrix. These findings highlight the potential of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and GNPs to enhance the multifunctional properties of cement-based materials, paving the way for their application in smart and energy-efficient construction applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nano-Thin Oxide Layers Formed on Hydrogen Plasma Modified Crystalline Si for Advanced Applications
by
Sashka Alexandrova, Anna Szekeres and Evgenia Valcheva
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(3), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5030012 - 12 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Since the early days of silicon manufacturing, hydrogen gas treatment has been used to control the defect concentrations. Its beneficial effect can be enhanced using hydrogen plasma as a source of active atomic hydrogen. Hydrogen plasma modification of c-Si surface can be challenging
[...] Read more.
Since the early days of silicon manufacturing, hydrogen gas treatment has been used to control the defect concentrations. Its beneficial effect can be enhanced using hydrogen plasma as a source of active atomic hydrogen. Hydrogen plasma modification of c-Si surface can be challenging because the plasma can induce precursors of defect centers that can persist at the interface and/or grown oxide after subsequent thermal oxidation. In the present study, we investigate nanoscale silicon dioxides with thicknesses in the range of 6–22 nm grown at low temperature (850 °C) in dry oxygen on radio frequency (RF) hydrogen plasma-treated silicon surface. The properties of these oxides are compared to oxides grown following standard Radio Corporation of America (RCA) Si technology. Electroreflectance measurements reveal better interface quality with enhanced electron mobility and lowered oxidation-induced stress levels when the oxides are grown on H-plasma modified c-Si substrates. These results are in good accordance with the reduced defect concentration established from the analysis of the current–voltage (I-V) and multifrequency capacitance–voltage (C-V) characteristics of metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) capacitors incorporating the Si-SiO2 structures. The study proves the potential of hydrogen plasma treatment of Si prior to oxidation for various Si-based applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Multiscale 2PP and LCD 3D Printing for High-Resolution Membrane-Integrated Microfluidic Chips
by
Julia K. Hoskins, Patrick M. Pysz, Julie A. Stenken and Min Zou
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(3), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5030011 - 12 Jul 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study presents a microfluidic chip platform designed using a multiscale 3D printing strategy for fabricating microfluidic chips with integrated, high-resolution, and customizable membrane structures. By combining two-photon polymerization (2PP) for submicron membrane fabrication with liquid crystal display printing for rapid production of
[...] Read more.
This study presents a microfluidic chip platform designed using a multiscale 3D printing strategy for fabricating microfluidic chips with integrated, high-resolution, and customizable membrane structures. By combining two-photon polymerization (2PP) for submicron membrane fabrication with liquid crystal display printing for rapid production of larger components, this approach addresses key challenges in membrane integration, including sealing reliability and the use of transparent materials. Compared to fully 2PP-based fabrication, the multiscale method achieved a 56-fold reduction in production time, reducing total fabrication time to approximately 7.2 h per chip and offering a highly efficient solution for integrating complex structures into fluidic chips. The fabricated chips demonstrated excellent mechanical integrity. Burst pressure testing showed that all samples withstood internal pressures averaging 1.27 ± 0.099 MPa, with some reaching up to 1.4 MPa. Flow testing from ~35

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
MgO–C Refractories with Al2O3 and TiO2 Nano-Additives: Insights from X-Ray Micro-Computed Tomography and Conventional Techniques for Assessing Corrosion and Oxidation
by
Sevastia Gkiouzel, Vasileios Ioannou, Christina Gioti, Konstantinos C. Vasilopoulos, Angelos Ntaflos, Alkiviadis S. Paipetis, Constantinos E. Salmas and Michael A. Karakassides
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(3), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5030010 - 9 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
MgO–C refractory materials were developed by incorporating different ratios of alumina/titania nano-additives which were synthesized chemically. Their physical and mechanical properties, oxidation resistance, slag wettability, bulk density, apparent porosity, cold crushing strength, oxidation index, and closed porosity were tested, evaluated, and compared using
[...] Read more.
MgO–C refractory materials were developed by incorporating different ratios of alumina/titania nano-additives which were synthesized chemically. Their physical and mechanical properties, oxidation resistance, slag wettability, bulk density, apparent porosity, cold crushing strength, oxidation index, and closed porosity were tested, evaluated, and compared using conventional techniques as well as X-ray micro-computed tomography (µCT). This investigation indicated a slight degradation of physical properties and mechanical strengthening which was stronger for samples with increased alumina content. Oxidation and corrosion extent were tested both with X-ray tomography and conventional methods. The first method allowed for the calculation of the oxidation index, the detection of closed porosity, and an improved analysis of the internal corrosion, avoiding the sectioning of the materials. This result confirms the supremacy of the first technique. On the contrary, although conventional methods such as the Archimedes procedure cannot detect close porosity, they provide more accurate measurements of the physical properties of refractories. This study shows that conventional methods exhibit superiority in investigations of the pore structures of refractories for pore sizes in the range 1–2 μm, while the use of the μCT system is limited for pore sizes equal to or larger than 20 μm.
Full article
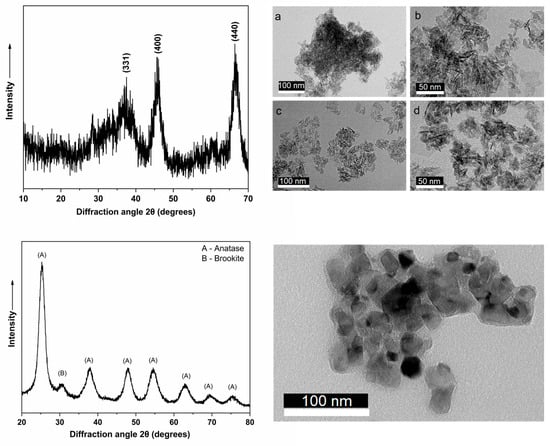
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Same Day Microfluidics: From Design to Device in Under Three Hours
by
Raymond J. Arebalo, Augustin J. Sanchez and Nathan Tompkins
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(3), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5030009 - 27 Jun 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microfluidic devices are used in numerous scientific fields and research areas, but device fabrication is still a time- and resource-intensive process largely confined to the cleanroom or a similarly well-equipped laboratory. This paper presents a method to create microfluidic devices in under three
[...] Read more.
Microfluidic devices are used in numerous scientific fields and research areas, but device fabrication is still a time- and resource-intensive process largely confined to the cleanroom or a similarly well-equipped laboratory. This paper presents a method to create microfluidic devices in under three hours using the silicone polymer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and a laser cut positive master using PDMS double casting without a cleanroom or other large capital equipment. This method can be utilized by an undergraduate student with minimal training in a laboratory with a modest budget. This paper presents “Same Day Microfluidics” as a fabrication method accessible to research groups not currently fabricating their own microfluidic devices and as an option for established research groups to more quickly create prototype devices. The method is described in detail with timing, materials, and technical considerations for each step and demonstrated in the context of a Y-channel coflow device.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
A Capacitive Liquid-Phase Sensor and Its Sensing Mechanism Using Nanoporous Anodic Aluminum Oxide
by
Chin-An Ku, Geng-Fu Li and Chen-Kuei Chung
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(2), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5020008 - 3 Jun 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With the evolution of micro/nanotechnology, anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) has received attention for sensor applications due to its regular and high-aspect-ratio nanopore structure with an excellent sensing performance, especially for electrical and optical sensors. Here, we propose the application of these capacitance and
[...] Read more.
With the evolution of micro/nanotechnology, anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) has received attention for sensor applications due to its regular and high-aspect-ratio nanopore structure with an excellent sensing performance, especially for electrical and optical sensors. Here, we propose the application of these capacitance and porous properties in a facile nanoporous AAO liquid sensor and study an efficient and economical method for preparing AAO substrates for liquid-phase substance sensing. By applying hybrid pulse anodization (HPA), a growth rate of approximately 5.9 μm/h was achieved in AAO fabrication. Compared to traditional low-temperature (0–10 °C) and two-step anodization with a growth rate of 1–3 μm/h, this process is significantly improved. The effect of pore widening on the performance of electrical sensors is also investigated and discussed. After pore widening, the capacitance values of AAO for air as a reference and various liquids, namely deionized water, alcohol, and acetone, are measured as 3.8 nF, 295.3 nF, 243.5 nF, and 210.1 nF, respectively. These results align with the trend in the dielectric constants and demonstrate the ability to clearly distinguish between different substances. The mechanism of AAO capacitive liquid-phase sensors can mainly be explained from two perspectives. First, since an AAO capacitive sensor is a parallel capacitor structure, the dielectric constant of the substance directly influences the capacitance value. In addition, pore widening increases the proportion of liquid filling the structure, enabling the sensor to clearly differentiate between substances. The other is the affinity between the substance and the AAO sensor, which can be determined using a contact angle test. The contact angles are measured as values of 93.2° and 67.7° before and after pore widening, respectively. The better the substance can fully fill the pores, the higher the capacitance value it yields.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
An Overview of Silver Nanowire Polyol Synthesis Using Millifluidic Flow Reactors for Continuous Transparent Conductive Film Manufacturing by Direct Ink Writing
by
Destiny F. Williams and Shohreh Hemmati
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(2), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5020007 - 6 May 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Silver nanowires (AgNWs) have garnered significant attention in nanotechnology due to their unique mechanical and electrical properties and versatile applications. This review explores the synthesis of AgNWs, with a specific focus on the utilization of millifluidic flow reactors (MFRs) as a promising platform
[...] Read more.
Silver nanowires (AgNWs) have garnered significant attention in nanotechnology due to their unique mechanical and electrical properties and versatile applications. This review explores the synthesis of AgNWs, with a specific focus on the utilization of millifluidic flow reactors (MFRs) as a promising platform for controlled and efficient production. It begins by elucidating the exceptional characteristics and relevance of AgNWs in various technological domains and then delves into the principles and advantages of MFRs by showcasing their pivotal role in enhancing the precision and scalability of nanowire synthesis. Within this review, an overview of the diverse synthetic methods employed for AgNW production using MFRs is provided. Special attention is given to the intricate parameters and factors influencing synthesis and how MFRs offer superior control over these critical variables. Recent advances in this field are highlighted, revealing innovative strategies and promising developments that have emerged. As with any burgeoning field, challenges are expected, so future directions are explored, offering insights into the current limitations and opportunities for further exploration. In conclusion, this review consolidates the state-of-the-art knowledge in AgNW synthesis and emphasizes the critical role of MFRs in shaping the future of nanomaterial production and nanomanufacturing.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Anticancer Activity of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Towards Human Lung Cancer Cells
by
Nithin Krisshna Gunasekaran, Nicole Nazario Bayon, Prathima Prabhu Tumkur, Krishnan Prabhakaran, Joseph C. Hall and Govindarajan T. Ramesh
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(2), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5020006 - 3 Apr 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2 NPs) have gained significant attention in various fields, including biomedicine, semiconductors, cosmetics, and fuel cells, due to their unique physico-chemical properties. Notably, green-synthesized CeO2 NPs have demonstrated enhanced potential as drug carriers, particularly in biomedical applications such
[...] Read more.
Cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2 NPs) have gained significant attention in various fields, including biomedicine, semiconductors, cosmetics, and fuel cells, due to their unique physico-chemical properties. Notably, green-synthesized CeO2 NPs have demonstrated enhanced potential as drug carriers, particularly in biomedical applications such as anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antimicrobial, and anti-oxidant therapies. This study aimed to investigate the anticancer effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles synthesized using turmeric rhizomes on human lung cancer cells. The cytotoxicity and proliferation inhibition of these nanoparticles were assessed using MTT and Live/Dead assays, revealing a dose-dependent reduction in cell viability. Additionally, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation was quantified through ROS assays, confirming oxidative stress induction as a key mechanism of cytotoxicity. Cell proliferation analysis further demonstrated that increasing concentrations of CeO2 NPs significantly reduced the multiplication of healthy lung cancer cells. These findings highlight the potential of turmeric-derived CeO2 NPs as a promising therapeutic agent for lung cancer treatment, warranting further exploration of their mechanism of action and in vivo efficacy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Fabricating Silver Nanowire–IZO Composite Transparent Conducting Electrodes at Roll-to-Roll Speed for Perovskite Solar Cells
by
Justin C. Bonner, Bishal Bhandari, Garrett J. Vander Stouw, Geethanjali Bingi, Kurt A. Schroder, Julia E. Huddy, William J. Scheideler and Julia W. P. Hsu
Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5(2), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5020005 - 29 Mar 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study addresses the challenges of efficient, large-scale production of flexible transparent conducting electrodes (TCEs). We fabricate TCEs on polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrates using a high-speed roll-to-roll (R2R) compatible method that combines gravure printing and photonic curing. The hybrid TCEs consist of Ag
[...] Read more.
This study addresses the challenges of efficient, large-scale production of flexible transparent conducting electrodes (TCEs). We fabricate TCEs on polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrates using a high-speed roll-to-roll (R2R) compatible method that combines gravure printing and photonic curing. The hybrid TCEs consist of Ag metal bus lines (Ag MBLs) coated with silver nanowires (AgNWs) and indium zinc oxide (IZO) layers. All materials are solutions deposited at speeds exceeding 10 m/min using gravure printing. We conduct a systematic study to optimize coating parameters and tune solvent composition to achieve a uniform AgNW network. The entire stack undergoes photonic curing, a low-energy annealing method that can be completed at high speeds and will not damage the plastic substrates. The resulting hybrid TCEs exhibit a transmittance of 92% averaged from 400 nm to 1100 nm and a sheet resistance of 11 Ω/sq. Mechanical durability is tested by bending the hybrid TCEs to a strain of 1% for 2000 cycles. The results show a minimal increase (<5%) in resistance. The high-throughput potential is established by showing that each hybrid TCE fabrication step can be completed at 30 m/min. We further fabricate methylammonium lead iodide solar cells to demonstrate the practical use of these TCEs, achieving an average power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 13%. The high-performance hybrid TCEs produced using R2R-compatible processes show potential as a viable choice for replacing vacuum-deposited indium tin oxide films on PET.
Full article
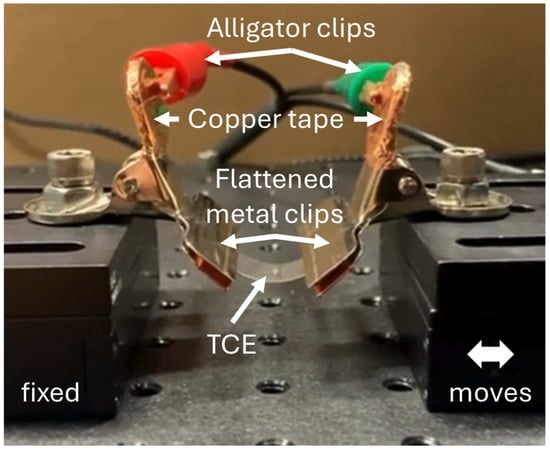
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
JFB, Materials, Metals, Nanomanufacturing, Nanomaterials
Physical Methods for the Synthesis of Materials and Their Applications
Topic Editors: Vincenzo Amendola, Gregory GuisbiersDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Designs, Machines, Materials, Processes, Nanomanufacturing
Digital Manufacturing Technology
Topic Editors: Wenbin Yu, Feiyang Zhao, Jiale ZhaoDeadline: 31 May 2026
Topic in
Micromachines, Nanomanufacturing, Nanomaterials, Processes, Sustainability
Innovative Synthesis and Applications of Functional Nanomaterials
Topic Editors: Paulraj Arunkumar, Arun ThirumuruganDeadline: 31 August 2026
Topic in
Applied Mechanics, Applied Sciences, JMMP, Materials, Metals, Nanomanufacturing
Advances in Manufacturing and Mechanics of Materials
Topic Editors: Young-Min Kim, Minjung Kang, Duck Bong KimDeadline: 30 September 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Nanomanufacturing
Nanoimprinting: From Micro to Nano
Guest Editor: Michael MühlbergerDeadline: 30 June 2026








