- Article
Synergistic Antimicrobial Activity of Juniperus excelsa Essential Oil and Streptococcus thermophilus Postbiotic in Inhibiting Foodborne Pathogens in Chicken Meat During Refrigerated Storage (4 °C)
- Nuri Gungor,
- Hatice Yazgan and
- Nur Sima Uprak
- + 2 authors
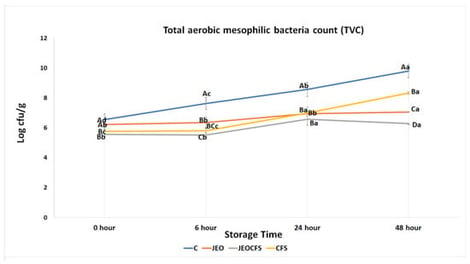
The objective of this study was to evaluate the individual and synergistic antimicrobial efficacy of Juniperus excelsa berry essential oil (JEO) and the cell-free supernatant (CFS) from Streptococcus thermophilus against Escherichia coli (ATCC 43888), Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923), and multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis S2 isolated from chicken meat. In vitro antimicrobial effects were assessed using the agar well diffusion and microdilution methods (MIC and MBC assays). The in vivo antimicrobial effect of these natural bioactive substances in controlling microbial growth in chicken meat stored at 4 °C for 48 h was also evaluated. Bioactive components of JEO were determined via GC–MS, identifying alpha-pinene (84.56%) as the primary compound. In vitro assays revealed that JEO showed high antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive S. aureus with a zone diameter of 35.50 mm (p < 0.05). JEOCFS treatment, which is the combination of CFS and JEO, demonstrated a significant synergistic interaction against S. aureus, resulting in an MIC value of 25 mg/mL. CFS alone exerted a measurable inhibitory effect on S. aureus, with an MIC of 50 mg/mL, indicating its potential antimicrobial capability. Further evaluation of the in vivo antimicrobial efficacy using chicken meat stored at 4 °C revealed that the JEOCFS treatment significantly inhibited microbial growth (p < 0.05). After 48 h of storage under refrigerated conditions, the number of psychrophilic bacteria in the control group reached 8.40 log cfu/g, while it remained significantly lower at 6.44, 5.37, and 6.74 log cfu/g in the JEO, JEOCFS, and CFS treatments, respectively. These results indicate that the synergistic application of JEO and CFS effectively suppresses foodborne pathogens, particularly S. aureus, and extends the microbiological shelf life of refrigerated chicken meat.
7 February 2026