- Article
Evaluation of Tool Wear Characteristics and Machining Performance During Longitudinal–Torsional Ultrasonic Vibration Drilling of Al/Ti Stacks
- Zhaoju Zhu,
- Shiying Geng and
- Yiping Huang
- + 2 authors
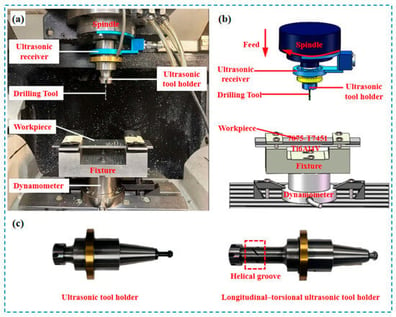
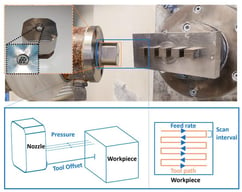
Al/Ti stacks are widely used in aerospace manufacturing due to their heterogeneous and multi-property material characteristics. However, during integrated hole-making processes, the significant differences in material properties often induce abrupt variations in cutting force, leading to uneven loading along the cutting edge and non-uniform tool wear. These issues complicate the drilling process and severely hinder the advancement of manufacturing and assembly technologies for aerospace components. To address these issues, longitudinal–torsional ultrasonic vibration drilling (LTUVD) is implemented in drilling of Al/Ti stacks, which superimposes high-frequency axial and tangential vibrations onto conventional drilling, enabling a spatial elliptical cutting trajectory and periodic material separation. A spatial kinematic model of LTUVD is developed to analyze the effects of key parameters on the tool motion trajectory and chip variations. Drilling experiments are conducted on Al/Ti stacks at a defined cutting condition (30 m/min, 0.1 mm/rev) to compare the performance of conventional drilling (CD), ultrasonic vibration-assisted drilling (UVAD), and LTUVD under various conditions. The results show that LTUVD can significantly outperform the other two methods in reducing thrust force, chip breaking (especially in the titanium layer), mitigating tool wear, and improving hole wall surface quality. In addition, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analyses further reveal that LTUVD can effectively suppress thermal and adhesive wear, thereby extending tool life.
10 February 2026