- Article
Electromagnetic and Modeling of Induction Furnaces Using Finite Element Methods
- Ghada Mahmoud Ibrahim,
- Asmaa Sobhy Sabik and
- Adel Saad Nada
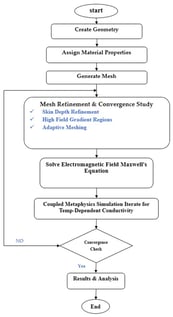
This paper presents a comparative modeling and analysis of an induction furnace for melting aluminum (Al) and copper (Cu), focusing on their electromagnetic behavior and heating performance. The study employs ANSYS Maxwell software version 16.0 with the finite element method (FEM) to simulate eddy current generation, Joule heating, and current density distribution in the metallic workpieces. The effects of coil geometry, input current, and operating frequency (50–100 kHz) on heating efficiency and skin depth are investigated. Estimated heating times based on ohmic losses are provided, revealing significant differences between aluminum and copper due to their distinct electrical and thermal properties. The results demonstrate that higher frequencies concentrate heating near the surface, reducing skin depth, while copper exhibits more uniform heating than aluminum. These findings offer practical insights for optimizing induction furnace design and operation for different non-ferrous metals.
10 February 2026