- Article
A Novel Assessment Model for the Sustainability of Clean Cutting Technology Based on Game Theory
- Zewen Li,
- Wei Zhao and
- Feng Kong
- + 3 authors
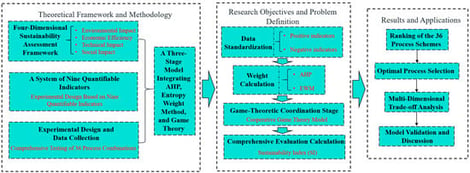
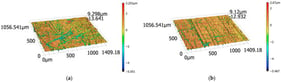
To enhance the sustainability of manufacturing, various clean cutting technologies have been developed, yet their sustainability assessment faces challenges in balancing multiple conflicting objectives and stakeholder interests. This paper proposes a game theory-based evaluation framework that treats environmental, technical, economic, and social dimensions as cooperative players. The Nash equilibrium model is employed to dynamically reconcile subjective weights from the analytic hierarchy process and objective weights from the entropy method, thus achieving optimal weight allocation. Experimental studies on Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy milling compared dry milling, minimum quantity lubrication, and cryogenic minimum quantity lubrication (CMQL) under different parameters. Results demonstrate that the game-theoretic model effectively integrates preferences and achieves Nash equilibrium. CMQL showed superior performance, increasing tool life by approximately 40% and reducing surface roughness by about 25% compared to dry milling. Coated inserts reduced carbon emissions by nearly 30% versus end mills. The Nash equilibrium analysis demonstrates that dry milling with coated inserts attains the highest level of processing sustainability under high-speed conditions due to synergistic environmental and economic advantages, while simultaneously revealing practical trade-offs among competing objectives. This study confirms that the proposed framework enables scientific weight coordination and provides a quantifiable, interpretable decision-making system for sustainable process selection.
14 February 2026