- Systematic Review
Indeterminate-Grey Zone of HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Compared to HBeAg-Negative Chronic Infection—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Rodanthi Syrigou,
- Dimitra Tiganiti and
- Dimitrios S Karagiannakis
- + 2 authors
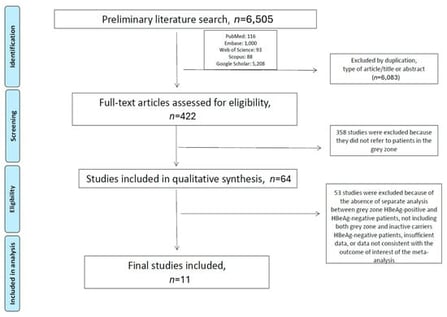
Background and Aim: The management of patients with chronic Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) HBeAg-negative infection in the indeterminate-grey zone (GZ) remains debatable. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare these patients with those with chronic HBV HBeAg-negative infection (inactive carriers; IC/HBeAg-negative), regarding the severity of liver inflammation and fibrosis and the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Methods: A literature search was conducted to identify all published studies comparing GZ/HBeAg-negative patients with IC/HBeAg-negative patients. Data on the severity of liver inflammation and fibrosis were extracted, and pooled relative risks (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. The risk of HCC was estimated by pooled hazard ratios (HR). A random-effects meta-analysis model was performed using R v4.1.2. Results: Eleven studies were finally included. GZ/HBeAg-negative patients had significantly higher mean HBV-DNA and alanine transferase (ALT) levels, compared to their IC/HBeAg-negative counterparts (4089.9 ± 4840.5 vs. 215.9 ± 318.1 IU/mL; p = 0.0004, and 39.6 ± 26.9 IU/L and 20.1 ± 7.6 IU/L/; p < 0.0001, respectively). GZ/HBeAg-negative patients showed a trend towards a higher risk of significant liver inflammation (RR: 5.11; 95%CI: 0.68–38.33; p = 0.1), F2/F3 fibrosis (RR: 2.13; 95%CI: 0.89–5.1; p = 0.09), and cirrhosis (RR: 14.39; 95%CI: 0.5–417.08; p = 0.12), respectively, compared to IC/HBeAg-negative patients. After a median follow-up of 6.2 years, the former group demonstrated a significantly higher risk of developing HCC (HR: 4.7; 95% CI: 1.4–15.6; p < 0.0001). Conclusions: GZ/HBeAg-negative patients have a higher risk of developing HCC compared to IC/HBeAg-negative patients, which raises concerns about the potential need to initiate treatment in this patient group.
4 February 2026