- Review
Pharmacological and Medicinal Properties of the South American Medicinal Plant Bowdichia virgilioides Kunth and Its Bioactive Products
- Christian Bailly
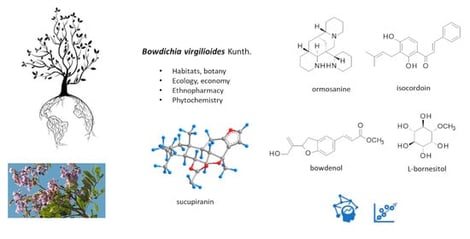
Bowdichia virgilioides Kunth is a tree largely present in South America, notably in the Cerrado savannah. The species is known for the quality of its dense and resistant wood, used in construction and furnishing. B. virgilioides is also a medicinal plant used, from leaves to roots, for the treatment of various human pathologies (pharyngitis, bronchitis, healing wounds, diabetes, and arthritis). The present review provides an analysis of the scientific literature pertaining to B. virgilioides, with a focus on pharmacological activities. Aqueous and organic extracts have been used to treat inflammatory pathologies and to combat infectious diseases caused by microorganisms and parasites. All phytochemicals at the origin of the bioactivities of extracts have been identified, including 37 terpenoids, 8 alkaloids, 21 flavonoids and 13 other products. All natural products are discussed, with a focus on a dozen compounds with well-documented pharmacological properties and/or a known mechanism of action. Key products include ormosanine (alkaloid), vouacapane (diterpenoid), lupeol (terpenoid), isoquercetin (flavonoid), isocordoin (chalcone), and little-known specific products (bowdichine and bowdenol). The botanical and phytochemical analysis shed light on this valuable Fabaceae species with the objective to promote its preservation and cultivation, as well as further pharmacological investigations aimed at rationalizing its long-established ethnobotanical use.
20 February 2026