- Article
Next Generation Intelligent Mobile Edge Networks for Improving Service Provisioning in Indonesian Festivals
- Vittalis Ayu and
- Milena Radenkovic
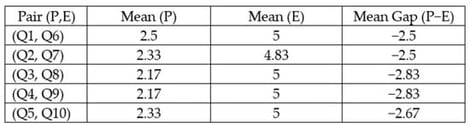
Indonesia is a country of vast geographical and cultural diversity, hosting numerous cultural festivals annually, such as Sekaten, Labuhan, and the Lembah Baliem Festival. However, as the world’s largest archipelago country, Indonesia faces geographical challenges in terms of ensuring the reliability of communication networks, particularly in maintaining user experience in high-density, short-duration traffic burst environments, such as festivals. The nation’s network connectivity relies heavily on satellite networks and Palapa Ring, a national fibre-optic backbone network that comprises a combination of inland and underwater networks, connecting major and remote islands to the global internet. Although this solution can provide a baseline for broadband connectivity, an adaptive intelligent mobile edge-based solution is needed to complement the existing network infrastructure in order to meet the dynamic demands of localised and transient traffic surges across multiple temporary, geographically dispersed festival sites in both urban and rural areas. In this paper, we present a multimodal study that combines network connectivity measurements during a festival with an extensive user analysis of festival participants and organisers to investigate reliability gaps in user experience regarding network connectivity. Our findings show that internet connectivity was intermittently disrupted during the festival, and our user analysis revealed a gap between customer expectations and perceptions of network service quality and the provision of application services in a heterogeneous festival environment. To address this challenge, we propose a novel next-generation intelligent festival mobile edge framework, MobiFest, which integrates the multi-layer Cognitive Cache which has geospatial–temporal edge intelligence for localised service provisioning to improve the delivery of application services in both urban and rural festival environments. In our extensive experiments, we employ smart garbage as our use case and demonstrate how our complex, multimodal intelligent network protocol SmartGarbiC, designed based on MobiFest for garbage management services, outperforms state-of-the-art and benchmark protocols.
6 February 2026