- Article
On Radiopharmaceutical Supply Production with Medium-Power Research Reactor: The Case of the Italian TRIGA RC-1 and the Theranostic 161Tb
- Lucrezia Spagnuolo,
- Luigi Lepore and
- Marco Capogni
- + 9 authors
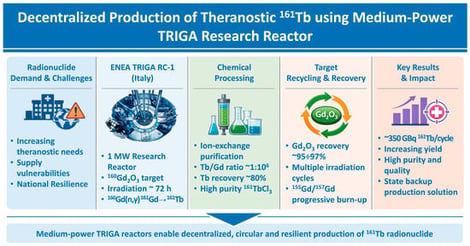
The global demand for medical radionuclides is rapidly increasing, driven by the expansion of diagnostic and therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals, and by recurrent vulnerabilities in international supply chains. While high-flux reactors remain the backbone of large-scale isotope production, low- and medium-power research reactors—such as TRIGA facilities—offer valuable opportunities for decentralised, flexible, and alternative radionuclide generation. Several studies have demonstrated their capability to produce emerging therapeutic or diagnostic isotopes, including 111Ag, 99Mo/99mTc, 64Cu, 177Lu, and 161Tb, although with yield limitations inherent to moderate neutron flux levels. In Europe, recent initiatives such as PRISMAP, SIMPLERAD, and SECURE aim to strengthen production capacity and diversify radionuclide availability. Within this framework, Italy—lacking operational power reactors—seeks alternative routes to ensure a resilient national supply. This work presents the investigation carried out within the SECURE project to assess the feasibility of an Italian production cycle for medical-grade 161Tb at the ENEA TRIGA RC-1 Research Reactor (Rome). The study integrates reactor-specific irradiation analyses, the development of chemical separation and target recovery processes, and a comprehensive economic evaluation within a full lifecycle perspective. The results highlight the potential and constraints of a TRIGA-based production for supporting future Italian theranostic needs.
13 February 2026



![Five unit self-organizing neural network classifier of two-phase flow. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [28]. Copyright 2025, Elsevier.](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/jne/jne-07-00015/article_deploy/html/images/jne-07-00015-g001-550.jpg)