- Systematic Review
Efficacy of Resin Infiltrants in Non-Cavitated Occlusal Carious Lesions: A Systematic Review
- Samille Biasi Miranda,
- Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins and
- Marcos Antonio Japiassú Resende Montes
- + 6 authors
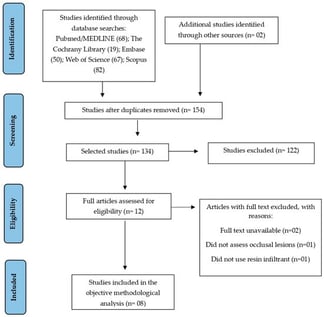
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy of resin infiltrants (RIs) in controlling non-cavitated occlusal carious lesions (NCOCLs) in primary and permanent teeth. Methods: This systematic review followed PRISMA guidelines. Randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and in vitro/ex vivo studies comparing RI with placebo or other materials were included. Searches were conducted in five databases and gray literature up to December 2025. Risk of bias was assessed using the RoB 2.0 tool for RCT and an adapted instrument for in vitro/ex vivo studies. Certainty of evidence was evaluated using the GRADE tool, and data were synthesized qualitatively. Results: Eight studies were included, of which only two were RCTs, and six were in vitro and ex vivo studies. RCTs showed reduced caries progression in infiltrant-treated groups compared with controls, with efficacy comparable to conventional sealants. In vitro studies demonstrated improved resin penetration and sealing ability with optimized protocols. Risk of bias ranged from low to moderate. Certainty of clinical evidence was low, primarily due to the limited number of RCTs and methodological limitations. Conclusions: RIs may be effective in managing NCOCLs, with performance comparable to conventional preventive approaches. However, the limited number of clinical trials and short follow-up periods reduce the strength of the evidence. Long-term clinical studies are needed to confirm the sustained effectiveness and durability of RIs.
6 February 2026