- Article
Apelin Levels in HFrEF and Association with Sustained VT Detected by ICD Interrogation: A Retrospective Pilot Study
- Abdullah Eren Cetin,
- Mustafa Lutfullah Ardic and
- Mevlut Koc
- + 2 authors
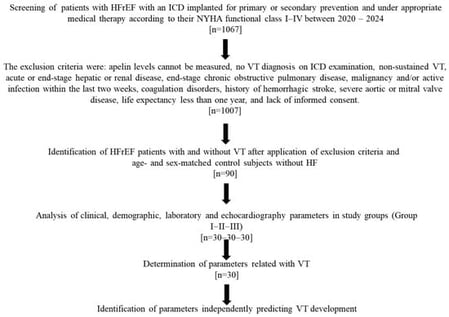
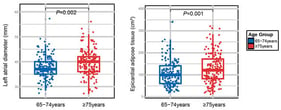
Introduction: The serum apelin level in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and its relationship with ventricular tachycardia (VT) are not clearly known. This study aimed to investigate changes in serum apelin levels in patients with HFrEF and their relationship with VT. Method: This retrospective pilot study included 90 patients with 30 patients in each group: Group I: HFrEF with documented VT; Group II: HFrEF without VT; Group III: control group without HFrEF. In addition to routine parameters, apelin levels were measured. All parameters were compared between Group I–II–III. Parameters associated with VT were identified. Result: Apelin levels were found to be significantly lower in Group I–II than in Group III. Serum glucose, creatinine, and left atrial diameter were shown to be significantly higher in Group I–II than in Group III. HDL cholesterol and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) levels were significantly lower in Group I–II compared with Group III. A positive and negative correlation was found between plasma apelin levels and LVEF and age, respectively. In logistic regression analysis, apelin levels and LVEF were found to independently determine VT (OR = 0.313, 95%CI: 0.124–0.788, p = 0.014 and OR = 0.912, 95%CI: 0.877–0.968, p < 0.001). In the ROC analysis, the cut-off value for apelin was determined to be 0.80 ng/mL, and it distinguished VT status in this sample with acceptable sensitivity and specificity. Discussion: According to the results of our study, apelin levels are significantly reduced in patients with HFrEF, and reduced apelin levels are associated with the presence of VT in these patients.
4 February 2026