- Article
Analytical Assessment of Environmental Noise in High- or Low-Risk Neonatal Wards and Neonatal Intensive Care Units
- Leonardo Nava-Velazquez,
- Angélica Saraí Jiménez-Osorio and
- Erika Elizabeth Rodriguez-Torres
- + 4 authors
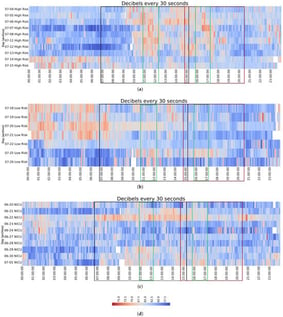
This study analyzed environmental noise levels in neonatal hospital units, including both low- and high-risk nurseries, as well as neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). Continuous 24 h measurements over ten days revealed that average sound levels significantly exceeded international recommendations. Hourly values frequently reached or surpassed 65 dB, with over 20% of daily recordings exceeding this limit, and in some instances, more than 50%. Heatmaps indicated consistent noise patterns: high-risk nurseries experienced peaks during late morning and afternoon, low-risk nurseries at night, while NICU maintained elevated levels throughout the day. The main sources of noise included alarms, medical equipment, and activity from staff or visitors. This highlights the need for hospital policies aimed at protecting the neurosensory health of neonates. These findings provide evidence-based recommendations for creating quieter environments in neonatal care.
10 February 2026