- Article
Yttrium-Enhanced Passive Films in Austenitic Stainless Steel
- Maksym Bichev,
- Denis Miroshnichenko and
- Mariia Shved
- + 6 authors
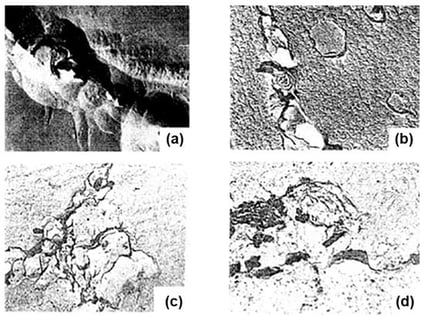
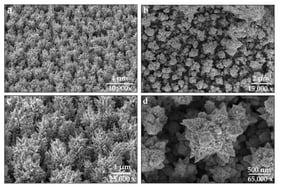
It has been demonstrated that a monomolecular surface film with semiconducting characteristics forms on an austenitic, corrosion- and heat-resistant chromium–nickel steel with 0.10 wt.% C, 20 wt.% Cr, 9 wt.% Ni, and 6 wt.% Mn (10Kh20N9G6), microalloyed with yttrium, in aqueous 1 M H2SO4. This passive layer exhibits semiconducting behavior, as confirmed by electrochemical impedance and capacitance measurements. For the first time, key electronic parameters, including the flat-band potential, the thickness of the semiconductor layer, and the Fermi energy, have been determined from experimental Mott–Schottky plots obtained for the interphase boundary between the yttrium-microalloyed austenitic Cr–Ni steel (10Kh20N9G6) and aqueous 1 M H2SO4. The results reveal a systematic shift in the flat-band potential toward more negative values with increasing yttrium content in the alloy, indicating a modification of the electronic structure of the passive film. Simultaneously, a decrease in the Fermi energy is observed, suggesting an increase in the work function of the metal surface due to the presence of yttrium. These findings contribute to a deeper understanding of passivation mechanisms in yttrium-containing stainless steels. The formation of a semiconducting passive film is essential for enhancing the electrochemical stability of stainless steels, and the role of rare-earth microalloying elements, such as yttrium, in this process is of both fundamental and practical interest.
16 January 2026