- Article
Supporting Translation and Analysis of the Configuration of an Electrical Substation Automation System Based on the IEC 61850 2.0 Standard
- Marcela Y. Solorio-García,
- Walter A. Mata-López and
- Víctor H. Castillo
- + 2 authors
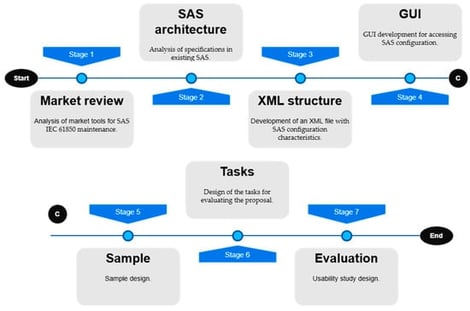
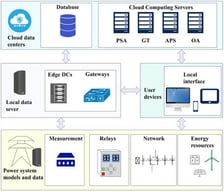
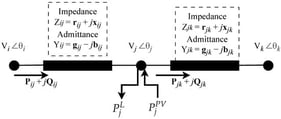
Currently, the smart grid concept represents the modern vision of an automated and highly adaptable electrical grid. Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems are a fundamental component of a smart grid, enabling communication between field equipment and digital environments. For this purpose, they require industrial frameworks, among which IEC 61850 stands out. IEC 61850 has become a widely adopted standard for substation automation systems (SASs). However, despite its widespread adoption, IEC 61850 faces significant implementation challenges, including the potential complexity of data modeling, which often leads to discrepancies in semantic interpretation and, consequently, different readings among SAS configuration users. A disparity in the semantic interpretation of a process can negatively affect SAS operation, leading to execution errors or interoperability issues. Translating and analyzing SAS configurations can identify and resolve semantic interpretation discrepancies across these systems. The purpose of this research was to determine the degree to which a user interface was perceived as useful to support the translation and analysis of SAS configurations based on the IEC 61850 standard. To this end, a software tool was proposed as the central artifact to address the socio-technical dimension of a custom-built SCADA system at a Latin American state enterprise. The tool serves as the local, intelligent, and real-time operational layer in that system and was rated by users experienced with IEC 61850 as highly usable. The consistently obtained results suggest potential support for those performing the SAS configuration.
10 February 2026