- Article
Longitudinal Changes in Depression, Anxiety and Stress Symptoms Among Hemodialysis Patients
- Adriana-Luciana Luca,
- Felicia Militaru and
- Eugen Moța
- + 2 authors
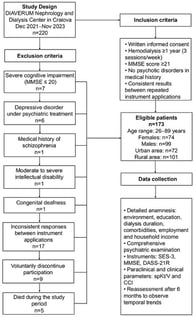
Background/Objectives: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) progresses with the gradual and irreversible loss of renal function. In Romania, given the increasing number of patients undergoing hemodialysis (HD), the prevalence of psychiatric symptoms and disorders in this population has become particularly significant. Although important advances have been made in the management of psychiatric conditions in HD patients, their mental health remains relatively poor. The aim of this study was to observe the severity temporal trends of depression, anxiety and stress symptoms and correlations among HD patients. Methods: A total of 173 patients, underwent a detailed anamnesis, with emphasis dialysis duration, comorbidities and a complex psychiatric evaluation, followed by the application of the Socio-economic Scale (SES-3); Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE); and the Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale 21R (DASS-21R). The dialysis performance (spKt/V) and Charlson Comorbidity (CCI) indices were provided by DIAVERUM Nephrology and Dialysis Center in Craiova. Results: The severity of depression and anxiety symptoms significantly increased over six months, 0.248 ± 1.432 vs. 0.453 ± 1.488 (p < 0.0001; rrb = 0.296) for depression, and −0.090 ± 1.004 vs. 0.089 ± 1.047 (p < 0.0001; rrb = 0.252) for anxiety; while stress-like symptoms remained stable 0.080 ± 1.318 vs. 0.164 ± 1.357 (p = 0.0661; rrb = 0.123), despite improvements in dialysis adequacy (spKt/V). Depression scores were moderately correlated with anxiety and weakly correlated with stress and spKt/V. Anxiety results were moderately correlated with stress, while both anxiety and stress showed negligible correlations with spKt/V. Clinical variables assessed showed moderate predictive value for psychological outcomes in this cohort. Conclusions: Our study confirms the temporal trend of severity of mental symptoms and their persistence among HD patients, highlighting the urge to integrate mental health screening and intervention programs and a multidisciplinary team adapted for each case.
8 February 2026