- Article
Highly Parallel Sorting Network Verification Using FPGAs
- Philippos Papaphilippou
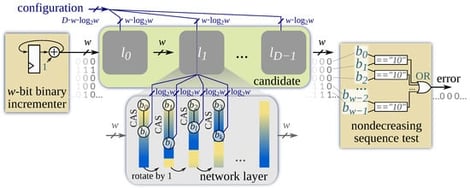
Sorting networks are of prime importance as circuits, with applications in sorting small data chunks, big data analytics, permuting packets, and system interconnects. Finding optimal sorting networks is a highly complex problem, and knowledge on optimal sorting networks is limited. When optimising the network depth or the number of comparators, one of the most expensive tasks is considered to be verification, that is, to verify that the candidate compare-and-swap network actually sorts the data. This grows exponentially with the size of the sorting network. However, FPGAs allow vast amounts of internal parallelism, and our presented work exploits this flexibility using dataflow techniques to achieve unparalleled amounts of speedup for sorting network verification. This work can be used in a modular way to accelerate the search for optimal sorting networks with a high number of inputs, as well for similar verification problems.
4 February 2026



![Layout of NAND2 in 45nm technology: the complete layout on the left and only visible layer 1 (active area), 9 (poly-silicon), 10 (contacts), and 11 (metal supply and ground connections) in the middle [33].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/chips/chips-05-00002/article_deploy/html/images/chips-05-00002-g001-550.jpg)