- Article
Artificial Intelligence-Based Evaluation of Permanent First Molar Extraction Indications in Children Using Panoramic Radiographs
- Serap Gülçin Çetin,
- Ömer Faruk Ertuğrul and
- Veysel Eratilla
- + 1 author
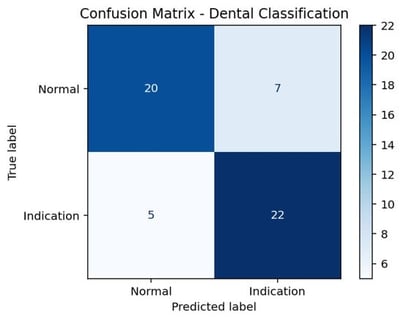
Background: The aim of this study was to develop an artificial intelligence (AI)-based decision support model for evaluating the extraction indication of permanent first molars in pediatric patients using panoramic radiographs, and to investigate the potential contribution of this model to the clinical decision-making process. Methods: This retrospective observational study analyzed 1000 panoramic radiographs obtained from children aged 8–10 years who attended the Clinics of Batman University Faculty of Dentistry for routine dental examination. Among the radiographs meeting the inclusion criteria, a total of 176 panoramic images were selected based on dental maturation assessment using the Demirjian tooth development staging system. Cases in which the permanent second molar was classified as Demirjian stages E–F were labeled as “extraction indication present”, while the remaining stages were labeled as “extraction indication absent”. A balanced dataset was created, consisting of 88 cases in each group. Image features were extracted using Gabor filters and Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG). The selected features were analyzed using a Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier with a radial basis function (RBF) kernel. Model performance was evaluated using accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, F1-score, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC–AUC). Results: The proposed Gabor–HOG–SVM-based AI model achieved an overall classification accuracy of 77.78% with an AUC value of 0.77 in distinguishing between “extraction indication present” and “extraction indication absent” cases. For the extraction-indicated group, the sensitivity was 0.81 and the F1-score was 0.79, whereas for the non-indicated group, the sensitivity and F1-score were 0.74 and 0.77, respectively. No statistically significant differences were observed between the groups in terms of age or sex distribution (p > 0.05). Conclusions: This study demonstrates that artificial intelligence-based analysis of panoramic radiographic images can provide an objective and reproducible decision support approach for evaluating extraction indications of permanent first molars in pediatric patients. The proposed model should be considered as an adjunctive tool to reduce observer-dependent variability rather than a replacement for clinical judgment, and its clinical applicability should be further validated through multicenter and multi-parametric studies.
17 February 2026