Journal Description
Businesses
Businesses
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on business published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within RePEc, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 24.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 7.4 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
The Impact of Pricing Strategies on the Growth and Sustainability of Small and Medium Enterprises: Empirical Evidence from South Africa
Businesses 2026, 6(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses6010010 - 12 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study investigated the impact of pricing strategies on the growth and sustainability of small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The study employed a quantitative research approach and sampled 132 SMEs operating in a municipality in South Africa. A self-administered, closed-ended questionnaire was tested
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the impact of pricing strategies on the growth and sustainability of small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The study employed a quantitative research approach and sampled 132 SMEs operating in a municipality in South Africa. A self-administered, closed-ended questionnaire was tested for reliability and validity and thereafter used to collect data from the respondents. This study employed simple linear regression analysis and performed the reliability test. In this study, the data were analysed using descriptive and inferential statistics. The results showed that SMEs primarily used cost-plus, value-based, and competitor-based pricing strategies. However, frequently modifying prices in response to market competition and technological advancements improves business performance. The study found a significant and positive relationship between pricing strategies and growth. Furthermore, a positive and significant nexus between pricing strategies and the sustainability of the SMEs. The practical implication of this study informs the SME managers and owners that SMEs that apply strategic and market-oriented pricing practices are more likely to achieve improved performance outcomes. The study, therefore, emphasises the importance of effective pricing in promoting both growth and long-term sustainability among SMEs. The findings of this study are expected to persuade the SMEs to pay crucial attention to the pricing strategies implemented in the business.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Challenges and Future Trends of Digital and Sustainable Marketing and Consumer Choices)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Customer Perceptions of Hygiene and Trust in Johannesburg’s Informal Food Economy
by
Maasago Mercy Sepadi and Timothy Hutton
Businesses 2026, 6(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses6010009 - 11 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: Street food vending plays a central role in urban nutrition and informal employment across South Africa; however, its sustainability largely depends on consumer trust, which is strongly influenced by perceptions of hygiene. Objectives: This paper investigates customer expectations, observed hygiene behaviours, and
[...] Read more.
Background: Street food vending plays a central role in urban nutrition and informal employment across South Africa; however, its sustainability largely depends on consumer trust, which is strongly influenced by perceptions of hygiene. Objectives: This paper investigates customer expectations, observed hygiene behaviours, and purchasing decisions within Johannesburg’s informal food economy. Drawing on the Health Belief Model and behavioural economics, this study examines how visible hygiene practices shape customer trust, repurchase behaviour, and gendered risk perceptions. Methods: A cross-sectional mixed-methods study was conducted among 110 consumers of street-vended food in Johannesburg’s inner city. Quantitative data were analysed using descriptive statistics and chi-square tests to assess associations between observed hygiene practices, trust, and purchasing behaviour, while qualitative open-ended responses were analysed thematically. Results: Seventy-four per cent of customers reported preferring vendors with visible hygiene practices, defined as the use of gloves or aprons, clean food displays, and observable handwashing. However, only 41% consistently observed handwashing between transactions, and just 45% had seen any form of hygiene certification displayed. An association was observed between customer trust and repeat purchases (p < 0.001) and between PPE use and customer trust (p = 0.011). Women were significantly more hygiene-sensitive (p = 0.029), expressing greater concern about exposed food, hand contact, and environmental conditions. Thematic analysis revealed that over half of the respondents indicated that trust, once compromised by unhygienic conditions, frequently resulted in permanent customer loss. Conclusions: Customer trust in street food vendors is contingent on hygiene. Hygiene visibility is a core driver of loyalty, especially among female consumers. Interventions to improve food safety should incorporate behavioural insights, vendor-customer feedback loops, and public-facing certification strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Consumer Behaviour and Healthy Food Consumption, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Power of Relationships: How Social Bonds Influence Work Happiness and Absenteeism in Warehouse Work
by
Rune Bjerke and Ida Birkeland
Businesses 2026, 6(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses6010008 - 10 Feb 2026
Abstract
Sick leave in physically demanding warehouse logistics poses persistent challenges for employee well-being, operational performance, and sustainable work participation. This study investigates how warehouse employees and supervisors understand drivers of absence and presence, and which workplace resources are perceived as most important for
[...] Read more.
Sick leave in physically demanding warehouse logistics poses persistent challenges for employee well-being, operational performance, and sustainable work participation. This study investigates how warehouse employees and supervisors understand drivers of absence and presence, and which workplace resources are perceived as most important for sustaining work happiness and attendance. Using an explanatory sequential mixed-methods design, phase 1 comprised in-depth interviews with warehouse leaders and focus groups with employees (N = 20). Qualitative findings highlight physical strain and sustained pace demands, but also emphasized psychosocial drivers such as emotional exhaustion, limited recognition, insufficient relational support, and a “push-through” culture that normalized strain and hindered recovery. At the same time, collegial support, humor, and everyday recognition were described as critical resources for coping and maintaining presence. Building on these insights, we used a cross-sectional survey (N = 99) to assess work happiness and perceived negative workplace conditions. Exploratory factor analysis identified four work happiness dimensions—supervisor support and recognition; self-development, meaning and autonomy; interpersonal relationships; and collaboration to achieve goals and four dimensions of negative workplace conditions: structural alienation, work-related exhaustion, adverse social climate, and work intensity. Multiple regression analyses showed that interpersonal relationships were the most consistent protective resource, negatively associated with exhaustion, adverse social climate, and work intensity, while supervisor support and recognition primarily reduced structural alienation. Overall, the findings suggest that social relationships constitute a central resource for sustainable well-being and attendance in physically demanding work, offering actionable implications for HRM.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Sponsorship Dynamics in Low-Media-Coverage Sports: An Examination of Norwegian Individual Athletes and Their Sponsors
by
Mark Romanelli, Andrea Kjærstad and Louis Moustakas
Businesses 2026, 6(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses6010007 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study investigates why companies sponsor individual athletes in sports with low media coverage and how such athletes secure sponsorship agreements. While sport sponsorship research has predominantly focused on mainstream sports and event-based contexts, limited attention has been given to individual athletes in
[...] Read more.
This study investigates why companies sponsor individual athletes in sports with low media coverage and how such athletes secure sponsorship agreements. While sport sponsorship research has predominantly focused on mainstream sports and event-based contexts, limited attention has been given to individual athletes in niche sports. Using a qualitative research design, semi-structured expert interviews were conducted with Norwegian sponsors and elite athletes in long-distance running, trail running, and orienteering. The data were analyzed through qualitative content analysis, informed by the Sponsorship Motive Matrix and the Model of Athlete Brand Image. The findings indicate that sponsorship decisions are primarily driven by market-related motives, complemented by bond and society motives, with cost-effectiveness, authenticity, and value alignment playing important roles. Sponsors prioritize athlete performance, personality, and social media presence, while athletes emphasize financial support and performance optimization. Sponsorship activation is generally limited, and agreements are predominantly in-kind or hybrid. The study concludes that sponsorships in low-media-coverage sports are relational and selective, relying heavily on athlete-driven outreach and social media visibility. These findings extend existing sponsorship frameworks to an underexplored context and offer practical insights for sponsors and athletes in niche sports.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Digital Panopticon: How Remote Work Monitoring Shapes Employee Behavior and Motivation
by
Aleksandar Nikodinovski, Darjan Karabašević and Vuk Mirčetić
Businesses 2026, 6(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses6010006 - 30 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Through systematic literature synthesis (2000–2024) integrating Foucault’s disciplinary power theory, Nissenbaum’s contextual integrity framework, and job design theory, this paper develops the Autonomy-Surveillance Conceptual Framework to explain differential psychological impacts of digital workplace surveillance. The embrace of remote work has increased surveillance practices
[...] Read more.
Through systematic literature synthesis (2000–2024) integrating Foucault’s disciplinary power theory, Nissenbaum’s contextual integrity framework, and job design theory, this paper develops the Autonomy-Surveillance Conceptual Framework to explain differential psychological impacts of digital workplace surveillance. The embrace of remote work has increased surveillance practices among organizations as an increased need to ensure employee productivity in remote settings appears, along with a drive to ensure data security and streamline workflows. Many employees perceive such practices as a breach of privacy, signifying employer distrust. The framework predicts that surveillance creates varying degrees of contextual integrity violation based on job autonomy: high-autonomy knowledge workers experience severe violations through trust erosion, procedural injustice, and temporal autonomy loss, while low-autonomy workers evaluate surveillance primarily through fairness criteria. This paper addresses a critical gap in existing research, which has focused on low-autonomy roles. By examining which roles are most impacted by digital surveillance, this paper seeks to highlight transparency and autonomy-sensitive policies to maximize the associated benefits of digital surveillance, while calling attention to employee well-being, trust, and organizational performance.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study Protocol: A Mixed-Methods Investigation of the Impact of Health and Safety Practices on the Business Performance Among Street Food Vendors in Johannesburg
by
Maasago Mercy Sepadi and Timothy Hutton
Businesses 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses6010005 - 27 Jan 2026
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The informal street food sector serves as a vital component of urban economies in South Africa, providing affordable nutrition and employment. However, this industry struggles to comply with required health and safety practices and standards. This study protocol outlines a mixed-methods investigation into
[...] Read more.
The informal street food sector serves as a vital component of urban economies in South Africa, providing affordable nutrition and employment. However, this industry struggles to comply with required health and safety practices and standards. This study protocol outlines a mixed-methods investigation into hygiene practices, regulatory compliance, and the intersection with business sustainability among informal food vendors in Johannesburg’s inner city. This study aims to investigate how vendors’ perceptions of health risks and benefits influence compliance behaviours and, in turn, how these behaviours impact operational efficiency, financial stability, and customer trust. Grounded in the Health Belief Model (HBM) and the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) framework, the research seeks to explore both behavioural drivers and performance outcomes associated with hygiene adherence. The study will employ structured stall observations, semi-structured vendor interviews, and customer surveys across high-density vending zones. Quantitative data will be analysed using descriptive and inferential statistics, while qualitative data will be thematically analysed and triangulated with observed practices. The expected outcome is to identify key barriers and enablers of hygiene compliance and demonstrate how improved food safety practices contribute to business resilience, customer trust, and urban public health. The findings aim to inform inclusive policy and innovative business support strategies that integrate informal vendors into safer and more sustainable food systems.
Full article

Figure A1
Open AccessArticle
Validation of the Emirati Higher Education Institutions Ethical Climate Scale: A Unidimensional Approach Based on Victor and Cullen’s (1988) Ethical Climate Theory
by
Abdelaziz Abdalla Alowais and Abubakr Suliman
Businesses 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses6010004 - 27 Jan 2026
Abstract
Introduction: Ethical climate theory traditionally conceptualizes organizational ethics as a set of distinct normative dimensions. However, recent evidence suggests that ethical perceptions may converge into a unified climate in culturally cohesive and institutionally regulated contexts. This study aims to validate the Emirati Higher
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Ethical climate theory traditionally conceptualizes organizational ethics as a set of distinct normative dimensions. However, recent evidence suggests that ethical perceptions may converge into a unified climate in culturally cohesive and institutionally regulated contexts. This study aims to validate the Emirati Higher Education Institutions Ethical Climate (EHEC) scale and examine whether the ethical climate operates as a unidimensional construct within Emirati higher education institutions. Methods: A quantitative validation design was employed using survey data from 200 academic and administrative staff across three Emirati universities. Data were analyzed via exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), alongside reliability and validity assessments, using IBM SPSS (Version 27) and AMOS (Version 24). Principal axis factoring without rotation was applied to examine the latent structure, followed by CFA for model fit testing and to compare alternative structures. Results: EFA revealed a single dominant factor with an eigenvalue of 11.8, explaining 47.1% of the total variance, and factor loadings ranging from 0.46 to 0.79. CFA confirmed the adequacy of the one-factor model (χ2/df = 2.31; CFI = 0.93; TLI = 0.91; RMSEA = 0.06; SRMR = 0.05). The scale demonstrated excellent reliability (Cronbach’s α = 0.93; CR = 0.95) and acceptable convergent validity (AVE = 0.48). Comparative analysis showed that the unidimensional model substantially outperformed the traditional five-factor structure. Discussion: These findings indicate that the ethical climate in Emirati higher education institutions is perceived as a single, shared institutional environment rather than as separate ethical dimensions. The validated EHEC scale provides a parsimonious, reliable, and context-sensitive instrument for assessing the ethical climate, suggesting that ethical climate theory may require contextual adaptation in institutionally cohesive and collectivist settings.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Consumers’ Internet Use and Car Sharing in Sweden: Exploring Digitalization in the Sharing Economy
by
John Magnus Roos
Businesses 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses6010003 - 19 Jan 2026
Abstract
This study investigates car sharing participation in Sweden within the broader context of sharing economy platforms. Its objective is to explore the relationship between internet use and car sharing, while accounting for residential area, gender, and age. The analysis is based on nationally
[...] Read more.
This study investigates car sharing participation in Sweden within the broader context of sharing economy platforms. Its objective is to explore the relationship between internet use and car sharing, while accounting for residential area, gender, and age. The analysis is based on nationally representative survey data collected between 2019 and 2023 (N = 8762). Initial results indicate a weak positive association between internet use and car sharing. However, this association disappears when age is considered, suggesting that age mediates the relationship. The final analysis shows that car sharing is more common among urban residents, males, and younger consumers. The findings have implications for theory, managerial practice, and policymaking. The study also addresses methodological limitations and outlines directions for future research on the behavioral, social, and structural factors influencing participation in car sharing services.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Challenges and Future Trends of Digital and Sustainable Marketing and Consumer Choices)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Social Strategies for Business Success: The Key Role of Social Networks in SMEs
by
Luigi Capoani, Piergiorgio Martini, Andrea Izzo and Giacomo Bincoletto
Businesses 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses6010002 - 16 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study aims to explore the relationship between a company manager’s activities and their impact on business performance. Networking is considered a worthy factor in professional and organizational success, providing access to important research, industry insights and future partnerships. Through the analysis of
[...] Read more.
This study aims to explore the relationship between a company manager’s activities and their impact on business performance. Networking is considered a worthy factor in professional and organizational success, providing access to important research, industry insights and future partnerships. Through the analysis of the data used in the study, this paper adopts a methodological approach to examine how managerial networking influences business results, with a particular focus on French small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The findings indicate a strong and positive correlation between the manager’s ability to build and maintain professional relationships and the entire performance of their business. In fact, managers who actively engage in networking often gain access to better business opportunities, funding sources and strategic collaborations that increase growth and competitiveness. Additionally, strong networks facilitate the exchange of knowledge, best practices and innovative ideas, thereby improving decision making and operational efficiency. The review further highlights that networking is not just about expanding contacts, but also about attending meaningful and beneficial affairs that contribute to long-term success. These results underline its importance as a strategic tool for business leaders, sustaining the idea that well-connected managers are better equipped to navigate challenges, catch opportunities and drive sustainable business prosperity in an increasingly competitive market.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Observing Entrepreneurial Opportunity in Entanglement
by
David Leong
Businesses 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses6010001 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper advances a unified theoretical framework that synthesises Shane and Eckhardt’s individual–opportunity nexus, Ramoglou and Tsang’s opportunities-as-propensities perspective, and Davidsson’s tripartite model of new venture ideas, external enablers, and opportunity confidence. Building on these foundations, the paper develops an entrepreneurial entanglement model
[...] Read more.
This paper advances a unified theoretical framework that synthesises Shane and Eckhardt’s individual–opportunity nexus, Ramoglou and Tsang’s opportunities-as-propensities perspective, and Davidsson’s tripartite model of new venture ideas, external enablers, and opportunity confidence. Building on these foundations, the paper develops an entrepreneurial entanglement model that explains how opportunities emerge as probabilistic propensities within dynamic configurations of agents, artefacts, distributed agencies, and spatiotemporal conditions. The model clarifies how material artefacts, socio-cognitive processes, and environmental shifts jointly shape the emergence, visibility, and realisation of entrepreneurial possibilities. By situating opportunity formation within an entangled field—rather than within isolated acts of discovery or creation—the framework deepens understanding of how entrepreneurial actions give rise to potentialities and how these potentialities become actualised under conditions of uncertainty. The analysis contributes to both theory and practice by offering a relational, mechanism-based account of how entrepreneurial behaviour and environmental factors intersect to structure the formation and realisation of opportunities.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Individual Traits Contributing to Entrepreneurial Entry: Character Strengths, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), and Highly Sensitive Person (HSP)
by
Kana Matsuishi and Akira Yasumura
Businesses 2025, 5(4), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5040061 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
Entrepreneurship is increasingly important for economic and societal innovation, yet the individual characteristics that encourage entrepreneurial entry remain insufficiently understood. This study examined whether character strengths, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and highly sensitive person (HSP) traits influence entrepreneurial entry. Two independent web-based
[...] Read more.
Entrepreneurship is increasingly important for economic and societal innovation, yet the individual characteristics that encourage entrepreneurial entry remain insufficiently understood. This study examined whether character strengths, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and highly sensitive person (HSP) traits influence entrepreneurial entry. Two independent web-based surveys were conducted, with ADHD assessed using a psychological scale in Study 1 and self-reported medical diagnosis in Study 2. The Character Strengths Test24 showed a revised factor structure, and an extracted factor (Drive) positively influenced entrepreneurial entry in both samples. ADHD (Hyperactivity/Impulsivity) consistently facilitated entrepreneurial entry, while HSP (Ease of Excitation) inhibited it. The robust positive contribution of ADHD traits across both symptomatic and clinically diagnosed individuals suggests that entrepreneurial potential is not limited by clinical labels and may also be found among individuals who are often marginalized, misunderstood, or discouraged in traditional career pathways. These findings highlight the importance of educational and support systems that not only develop character strengths linked to entrepreneurial drive but also recognize, accommodate, and strategically leverage diverse neuropsychological traits. Empowering individuals with varied cognitive profiles may expand pathways to innovation and contribute to a more inclusive entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Full article
Open AccessOpinion
Guarding the Gates: Exploring a Theological–Philosophical Framework for Cybersecurity and Spiritual Discernment in the Digital Age
by
Laura A. Jones
Businesses 2025, 5(4), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5040060 - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper examines the intersection between Christian theological principles and contemporary cybersecurity challenges, with a focus on the specific vulnerabilities and responsibilities of faith-based organizations. Recognizing that digital threats emerge not only from technological weaknesses but also from human motives and ethical failings,
[...] Read more.
This paper examines the intersection between Christian theological principles and contemporary cybersecurity challenges, with a focus on the specific vulnerabilities and responsibilities of faith-based organizations. Recognizing that digital threats emerge not only from technological weaknesses but also from human motives and ethical failings, this study introduces a Biblically Framed Cybersecurity (BFCy) Model that integrates scriptural ethics with established security practices. Through a narrative literature review and comparative analysis, the research synthesizes Christian concepts, such as stewardship, vigilance, and integrity, with technical standards (including the CIS Controls v8, NIST CSF 2.0, and ISO 27001:2022), mapping biblical narratives to contemporary risks like social engineering, insider threats, and identity theft. The findings underscore that robust cybersecurity requires more than technical solutions; it also demands a culture of moral accountability and spiritual awareness. Practical recommendations, including tables linking biblical values to operational controls, highlight actionable steps for church leaders and faith-based organizations. This study concludes that effective cybersecurity in these contexts is best achieved by aligning technical measures with enduring ethical and spiritual commitments, offering a model that may inform religious and broader organizational approaches to digital risk and resilience.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Succession and Reconstructing Social Capital in Vietnamese Family Businesses
by
James Cooper and John Burgess
Businesses 2025, 5(4), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5040059 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Family businesses play a central role in the ongoing growth and development of the Vietnamese economy. Economic, social, and demographic changes are undermining the transition of family business to succeeding generations. This study examines the challenges of intergenerational succession in Vietnamese family businesses
[...] Read more.
Family businesses play a central role in the ongoing growth and development of the Vietnamese economy. Economic, social, and demographic changes are undermining the transition of family business to succeeding generations. This study examines the challenges of intergenerational succession in Vietnamese family businesses through the lens of social capital theory. The article examines how the next generation of family business leaders in Vietnam is addressing social capital deficiencies that hinder effective business transition. The study employed a constructionist ontology and an interpretivist epistemology, utilising semi-structured interviews with family business owners and managers. The research draws from participants’ perceptions of social, political, and competitive contexts and the subsequent behaviour that is predicated by those contexts. Findings: Economic transformation, driven by disruptions to the business environment through central planning, coupled with demographic shifts and changes in educational attainment, has impacted family structures, complicating intergenerational business transfers. This is compounded by social transformation weakening familial relationships and connections critical to family cooperation and business continuity. The preservation and renewal of social capital are critical issues for succession planning in Vietnamese family businesses. This research addresses gaps in understanding the interplay between the generational divide, social capital, and family business succession in Vietnam.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Competing Identities Under Threat: Ethnocentrism, Xenocentrism, and Touristic Motivation Amid Geopolitical Uncertainty
by
Luis José Camacho, Salvador Pancorbo and Rosilda Miranda
Businesses 2025, 5(4), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5040058 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study examines how geopolitical uncertainty (GEOUN) influences domestic touristic purchase intention (TPI) through consumer ethnocentrism (CETH), consumer xenocentrism (CXEN), and touristic motivation (TMOT) in the Dominican Republic, a tourism-dependent developing economy. Integrating insights from uncertainty-identity theory (UIT), the theory of planned behavior
[...] Read more.
This study examines how geopolitical uncertainty (GEOUN) influences domestic touristic purchase intention (TPI) through consumer ethnocentrism (CETH), consumer xenocentrism (CXEN), and touristic motivation (TMOT) in the Dominican Republic, a tourism-dependent developing economy. Integrating insights from uncertainty-identity theory (UIT), the theory of planned behavior (TPB), and consumer culture theory (CCT), we propose that macro-level geopolitical instability triggers identity-driven and motivational responses that shape consumer travel decisions. Using survey data from 374 Dominican consumers, we find that GEOUN significantly increases ethnocentric attitudes and touristic motivation, which in turn boost domestic travel intention. Touristic motivation emerges as the strongest predictor of TPI and serves as a key mediator linking uncertainty and identity-based factors to travel intention. However, xenocentrism does not significantly predict travel intention, revealing a gap between aspirational foreign affinity and actual choices under uncertainty. These findings extend consumer behavior theory by highlighting how identity-protective and motivational mechanisms shape decision-making under threat. Practically, the results suggest that in volatile environments, tourism marketing should emphasize national belonging, emotional security, and cultural pride to position domestic tourism as both an economic stabilizer and a psychological resource.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Quiet Quitting in Healthcare: The Synergistic Impact of Organizational Culture and Green Lean Six Sigma Practices on Employee Commitment and Satisfaction
by
Anastasia Vasileiou, Georgios Tsekouropoulos, Greta Hoxha, Dimitrios Theocharis and Evangelos Grigoriadis
Businesses 2025, 5(4), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5040057 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Quiet quitting—a subtle form of disengagement where employees withdraw discretionary effort—poses a growing challenge for healthcare organizations. It undermines workforce resilience and compromises care quality. This study explores how organizational culture and Green Lean Six Sigma (GLSS) practices interact to address this issue,
[...] Read more.
Quiet quitting—a subtle form of disengagement where employees withdraw discretionary effort—poses a growing challenge for healthcare organizations. It undermines workforce resilience and compromises care quality. This study explores how organizational culture and Green Lean Six Sigma (GLSS) practices interact to address this issue, fostering employee commitment and job satisfaction. We analyzed data from 312 healthcare professionals using SEM to examine five hypothesized relationships concerning the independent and combined influence of culture and GLSS. The findings reveal that a supportive workplace environment is strongly associated with lower levels of quiet quitting and higher levels of commitment, while structured improvement practices independently contribute to reduced disengagement and greater job satisfaction. This study identifies a synergy between culture and GLSS: a supportive culture enables improvement practices, and successful initiatives reinforce cultural trust. This virtuous cycle promotes motivation, alleviates burnout, and enhances long-term organizational resilience. The results emphasize the importance of leadership investment in both cultural development and participatory improvement practices. Aligning process optimization with ethical and human-centered principles can strengthen engagement and ensure sustainable, high-quality healthcare delivery.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Beyond Industry 5.0: Leadership 5.0—Driving Future-Ready Organizations
by
Gillian Warner-Søderholm and Miika Kuoppamäki
Businesses 2025, 5(4), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5040056 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The aim of this paper is to fill the identified gap in the literature regarding mapping key values within Leadership 5.0. Our study indicates that Leadership 5.0 (L5.0) shows a transformative shift in leadership, demanding innovative leaders to adopt agile and digital mindsets,
[...] Read more.
The aim of this paper is to fill the identified gap in the literature regarding mapping key values within Leadership 5.0. Our study indicates that Leadership 5.0 (L5.0) shows a transformative shift in leadership, demanding innovative leaders to adopt agile and digital mindsets, hence fostering innovation whilst balancing human and technological needs in Industry 5.0 settings. Developing people-centric leadership skills is critical in order to build collaborative innovation between humans and machines. In this way, human expertise is integrated with technology, to drive future-ready organizations. Findings show that L5.0 prioritizes continuous learning environments to adapt to rapidly evolving challenges. This ensures that organizations are agile, resilient, and ready for the future. L5.0 recognizes that intellectual capital—driven by human creativity, emotional intelligence, and collaboration—is essential for sustainable innovation in the digital shift. This paper’s theoretical contribution is a conceptual analysis of L5.0. We present a comprehensive and actionable conceptual model for mapping L5.0. We identify five key L5.0 pillars from the literature: human-centric leadership, future readiness and adaptability, a sustainability and ethics focus, collaboration and inclusion values and an innovation and experimentation approach to leadership. We develop a 30-item L5.0 survey instrument, anchored in the literature, and we conduct initial pilot testing for item clarification. The survey instrument application can provide valuable management insights: a road map for assessing the presence and maturity level of L5.0 in organizations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Review of Energy and Sustainability Management in the Fibre-Based Process Industry
by
Florian Pohlmeyer, Rosario Othen, Christian Möbitz and Thomas Gries
Businesses 2025, 5(4), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5040055 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This systematic literature review critically examines sustainability challenges and opportunities within fibre-based process industries (e.g., paper and nonwoven), pivotal energy-intensive sectors in the EU. Using an adapted PRISMA guideline, it analyses the evolution of sustainability concepts, key regulatory frameworks (e.g., European Green Deal,
[...] Read more.
This systematic literature review critically examines sustainability challenges and opportunities within fibre-based process industries (e.g., paper and nonwoven), pivotal energy-intensive sectors in the EU. Using an adapted PRISMA guideline, it analyses the evolution of sustainability concepts, key regulatory frameworks (e.g., European Green Deal, Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive), and established management tools (e.g., ISO 50001, life cycle assessment). The review uncovers critical gaps, including a persistent lack of integrated approaches across environmental, economic, and social dimensions, alongside superficial strategic embedding of sustainability. Furthermore, regulatory fragmentation significantly hinders effective implementation. The study also highlights uneven technology adoption and practical obstacles for circular economy models, largely because sustainability often remains a parallel function rather than a core business driver. Ultimately, transformative sustainability demands integrated, sector-specific strategies, robust data, and strong leadership. This necessitates streamlined regulations, accelerated technology uptake, and enhanced multi-stakeholder collaboration, embedding sustainability into core business models beyond mere compliance.
Full article
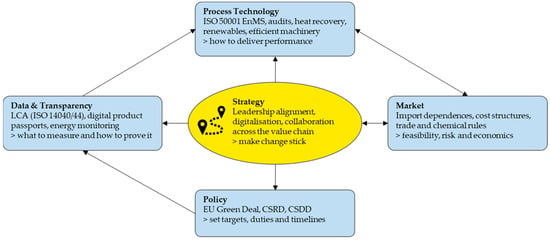
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Emotional Intelligence, Leadership and Human Resources Empowerment in Luxury Hotels: The Case of Athens
by
Theodoros Stavrinoudis, Christos Kakarougkas and Alexandra Georgopoulou
Businesses 2025, 5(4), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5040054 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In recent years, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a noticeable rise in demand for luxury urban hospitality services. Luxury hospitality is not solely about costly offerings; it emphasises creating authentic, personalised, and wellness-focused experiences. Successful luxury hotel operations depend on
[...] Read more.
In recent years, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a noticeable rise in demand for luxury urban hospitality services. Luxury hospitality is not solely about costly offerings; it emphasises creating authentic, personalised, and wellness-focused experiences. Successful luxury hotel operations depend on emotional intelligence, supportive leadership, and HR empowerment. This research aims to identify the variables positively associated with these factors in metropolitan hotels and to propose HRM policies to enhance them. Conducted from March to May 2025 in Athens, Greece, with a sample of 220 luxury five-star hotel employees, the research utilised Exploratory and Confirmatory Factor Analyses. The Exploratory Factor Analysis was performed using the method of Principal Components Extraction, while the Confirmatory Factor Analysis employed Structural Equation Modelling. The analysis of the research findings highlighted specific variables that are positively correlated with the development of the emotional intelligence, supportive leadership, and HR empowerment needed to deliver luxury services in metropolitan destination hotels. This paper provides validated Likert-type scales and practical insights for developing these essential workplace factors in luxury hotels, ultimately improving customer service and employee support.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Inner Drive: Unpacking the Motivations for Consumer Participation as Sellers in Apparel Resale
by
Jack Herman, Jihyun Kim-Vick and Jonghan Hyun
Businesses 2025, 5(4), 53; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5040053 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The global secondhand apparel industry, valued at USD 256B in 2025, is expanding rapidly. The growing acceptance of secondhand fashion and advancements in retail technology have driven millions of individuals to resell, yet little research has analyzed the motivations behind these decisions. Guided
[...] Read more.
The global secondhand apparel industry, valued at USD 256B in 2025, is expanding rapidly. The growing acceptance of secondhand fashion and advancements in retail technology have driven millions of individuals to resell, yet little research has analyzed the motivations behind these decisions. Guided by Consumption Values Theory and Goal-Framing Theory, this qualitative study uses ten in-depth interviews with experienced resellers to examine why individuals participate in apparel reselling. Analysis of the participants’ narratives indicates that financial gain is the dominant driver of participation, followed by the convenience provided by reselling platforms and channels, emotional satisfaction, and contributing to sustainability. Conceptually, the study integrates value-based and goal-based lenses to offer an extensive explanation of reseller motivations, shifting focus from the buyer perspective that has dominated prior research. Practically, the findings suggest that resale platforms can encourage participation by reducing visible fees, enabling faster payout, and simplifying the reselling process, while also making community and environmental benefits more visible. In all, these insights help retailers and sustainability advocates better design approaches that support individual resellers and sustain growth in apparel resale.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Perceived ESG, Accessibility, and Technology Acceptance: An Empirical Study of Online Banking Adoption in Post-Pandemic India
by
Cheng-Wen Lee, Sephali Bera, Ping-Hung Chen and Feng-Yi Lin
Businesses 2025, 5(4), 52; https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5040052 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study examines the key factors influencing online banking adoption in India in the post-COVID-19 period. Building on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), the research integrates traditional factors—perceived ease of use (PEOU), accessibility (ABS), and reliability of the banking system (RBS)—with a novel
[...] Read more.
This study examines the key factors influencing online banking adoption in India in the post-COVID-19 period. Building on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), the research integrates traditional factors—perceived ease of use (PEOU), accessibility (ABS), and reliability of the banking system (RBS)—with a novel construct, perceived environmental, social, and governance performance of banks (PESGB). Data were collected through a structured questionnaire administered to Indian banking customers, and the proposed model was tested using covariance-based structural equation modeling (CB-SEM). The results demonstrate that PEOU, ABS, and PESGB significantly and positively influence customers’ intention to adopt online banking, whereas RBS does not show a significant effect. These findings suggest that in the post-pandemic era, customers prioritize usability, accessibility, and sustainability over traditional concerns of reliability. The study contributes to the extension of TAM by incorporating ESG considerations and offers practical implications for banks to enhance digital adoption by promoting user-friendly services and aligning digital transformation strategies with sustainability commitments.
Full article
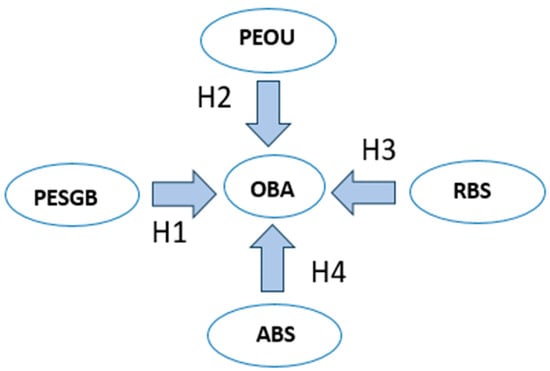
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Businesses, Sustainability, JTAER
Digital Marketing Dynamics: From Browsing to Buying
Topic Editors: José Luís Mendes Loureiro Abrantes, Natália de Lima Figueiredo, Bruno Morgado Ferreira, Luís F. MartinezDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topic in
Businesses, Economies, Humanities, Land, Sustainability, Tourism and Hospitality, Urban Science
Human–Environmental Relations: Ecotourism and Sustainability
Topic Editors: Tamara Gajić, Minja Bolesnikov, Aleksandar ErcegDeadline: 15 July 2026
Topic in
Administrative Sciences, Businesses, Informatics, JTAER
Innovations in New Media: Shaping the Future of Interactive Marketing
Topic Editors: Chenglu Wang, Hongfei Liu, Morgan Yang, Qing Ye, Yunjia ChiDeadline: 30 September 2026
Topic in
Economies, IJFS, Sustainability, Businesses, JRFM
Sustainable and Green Finance
Topic Editors: Otilia Manta, Maria PalazzoDeadline: 31 October 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Businesses
New Technologies in Business Informatics
Guest Editors: Octavian Dospinescu, Valentin Florentin DumitruDeadline: 31 July 2026







