- Article
Study on Spatial Effects of Non-Symmetric Cable-Stayed Bridges Under Operational Loads
- Xiaogang Li,
- Qin Wang and
- Shanxing Xiang
- + 3 authors
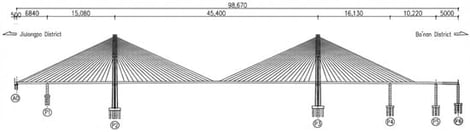
Addressing the issues of the complex mechanical responses and significant spatial effects of asymmetric large-span cable-stayed steel box girder bridges with shared public-rail traffic under operational loads (live load, static wind, and structural temperature differences), this paper uses the Lijiatuo Yangtze River Double-Line Bridge on Chongqing Metro Line 18 as the engineering background to construct multi-scale finite element models for the entire bridge and the closure segment, and validates them against GNSS displacement and strain monitoring data from the actual bridge. The study shows that the spatiotemporal asymmetry of operational live loads induces significant lateral bias effects in the main bridge, resulting in reverse displacements in the mid-span section, and with stress distributions characterized by “oscillation in the side spans and concentration in the mid-span.” The study also shows that, under static wind loads, the bridge’s lateral displacement approximately increases linearly with wind speed, and the mid-span response is higher than that of the side spans, showing significant spatial sensitivity to wind loads. Finally, the study shows that, although the system temperature difference causes small overall displacements, it still induces symmetrical lateral deformations and local stress concentrations near the closure segment. Local refined analyses further reveal the displacement distribution mechanism of the closure segment under operational loads. The health monitoring data agree well with the simulation results, validating the reliability of the numerical model. The research systematically reveals the spatial mechanical behavior of such bridges under operational loads, providing theoretical basis and engineering references for the design optimization and safety monitoring of similar asymmetric cable-stayed bridges.
17 February 2026