- Article
Blockchain-Enabled Human Resource Management for Enhancing Transparency, Trust, and Talent Mobility in the Digital Era
- Mitra Madanchian and
- Hamed Taherdoost
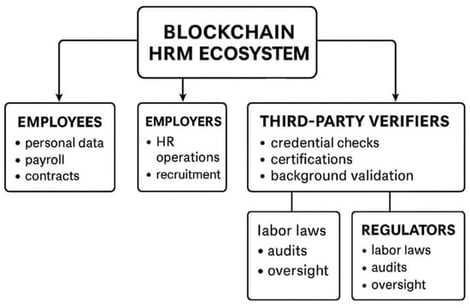
Traditional Human Resource Management (HRM) systems are criticized for lacking transparency, being inefficient, and offering ample opportunities for fraud because of their centralized design and reliance on manual processes. This work proposes a blockchain-enabled framework for HRM that enhances the transparency, trust, and global mobility of talents by integrating distributed ledgers, consensus protocols, and smart contract networks into Human Resources (HR) functions. A four-layer theoretical model—data, consensus, smart contract, and application layers—is developed and comparatively examined against traditional HR systems to show how blockchain principles can be systematically mapped into HR processes. This study shows how blockchain-driven HRM can ensure tamper-evident employee records, automate contractual and payroll operations, and enhance auditability and compliance. By informing the framework with established technology adoption perspectives, this paper extends both the theoretical and managerial understanding of blockchain in HR. In comparison with previous studies that were limited to either recruitment or credential verification, this article presents an overarching, cross-layer synthesis that connects blockchain architectures with end-to-end HR functions, thus providing a clear conceptual foundation for its future enterprise adoption in the digital economy.
8 January 2026