Journal Description
Biologics
Biologics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all areas of biologics derived from both novel and established biotechnologies, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Immunology and Microbiology (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 31.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 8.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
A Single-Center Review of Infusion-Associated Reactions in Patients with CLN2 Disease Receiving Cerliponase Alfa
Biologics 2026, 6(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics6010007 - 13 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
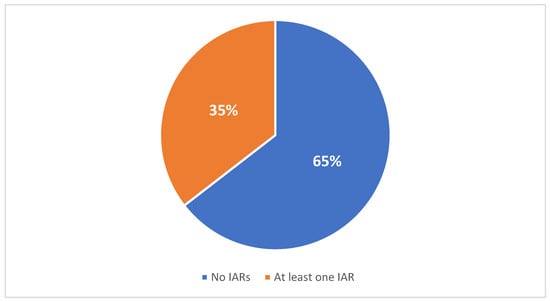
Background: Cerliponase alfa is an intracerebroventricular (ICV) enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) and the only approved treatment for neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 2 (CLN2) disease. While generally well tolerated, infusion-associated reactions (IARs), including hypersensitivity events and anaphylaxis, remain a recognized safety consideration. Methods: This
[...] Read more.
Background: Cerliponase alfa is an intracerebroventricular (ICV) enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) and the only approved treatment for neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 2 (CLN2) disease. While generally well tolerated, infusion-associated reactions (IARs), including hypersensitivity events and anaphylaxis, remain a recognized safety consideration. Methods: This single-center, retrospective study describes the incidence and management of IARs in pediatric patients with CLN2 receiving long-term ICV cerliponase alfa at Great Ormond Street Hospital, London, United Kingdom. Results: Over a 10-year period (2014–2024), 31 patients received approximately 2705 ICV infusions. Eleven patients experienced at least one IAR. Most reactions were mild and transient, typically consisting of pyrexia, vomiting, or rash, and were managed conservatively with antipyretics and antihistamines. Four patients required steroid intervention following recurrent or more pronounced symptoms, which led to improved infusion tolerance. One patient experienced a single episode of anaphylaxis that required treatment with intramuscular adrenaline and intravenous hydrocortisone. Therapy was continued with a revised pre-medication regime, with no further severe reactions. Conclusions: These findings demonstrate that IARs to ICV cerliponase alfa are typically mild and readily manageable within a multidisciplinary framework. They highlight the importance of structured infusion protocols, vigilant monitoring strategies, and a coordinated management approach to ensure the long-term safety of ERT for children with CLN2 disease.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Reverse Vaccinology and Immune Simulation of a Novel Multiepitope Vaccine Targeting Brucella Virulence
by
Mostafa F. Abushahba
Biologics 2026, 6(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics6010006 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Brucella is a major global One Health threat, causing an estimated 2.1 million human infections and substantial livestock losses annually, with no vaccine currently available for humans, underscoring the urgent need for a safe and effective vaccine. Methods: Employing a
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Brucella is a major global One Health threat, causing an estimated 2.1 million human infections and substantial livestock losses annually, with no vaccine currently available for humans, underscoring the urgent need for a safe and effective vaccine. Methods: Employing a reverse vaccinology approach, a novel 175-mer multiepitope vaccine (Mvax) targeting Brucella FrpB was computationally designed in this study, incorporating two B-cell, two MHC class I (MHC-I), and three MHC class II (MHC-II) epitopes selected for their high predicted antigenicity, safety, and IFN-γ-inducing potential. Human β-defensin-3 (hBD3) was fused to the N-terminus as an adjuvant, followed by comprehensive in silico evaluation of the construct. Results: Population coverage analysis predicted 99.59% global MHC class I/II coverage for selected epitopes. In silico analyses predicted that Mvax has high solubility (Protein-SOL score: 0.808), a high antigenicity score (VaxiJen: 1.06), and a negative GRAVY index (−0.881), indicating favorable predicted physicochemical characteristics. iMODS, CABS-Flex 3, and molecular dynamics simulations suggested theoretical stability trends for the modeled vaccine complexes. C-ImmSim immune simulations further predicted elevated Th1 cell populations and associated cytokines (IL-12, IFN-γ, IL-2) following both single and multiple simulated Mvax exposures. Conclusions: The computational analyses described here provide a theoretical modeling basis for an antivirulence multi-epitope vaccine design against human brucellosis, with predicted metrics and simulated immune responses requiring empirical validation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Vaccines)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Interleukin-6: A Central Biomarker in Adult and Pediatric Cancer and Infectious Disease
by
Giorgia Di Benedetto, Carmen Sorice, Immacolata Cantiello, Maria Savarese, Ornella Leone, Michele Antonio Capozza and Mariaevelina Alfieri
Biologics 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics6010005 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
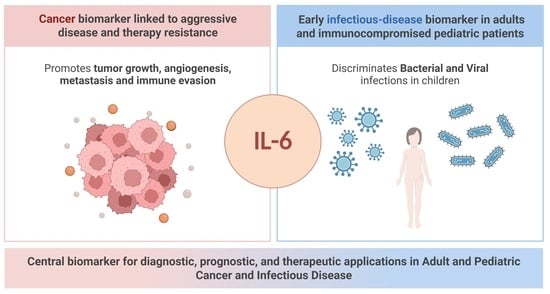
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a multifunctional cytokine with an essential role in immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Produced by immune, stromal and epithelial cells in response to infection or tissue stress, IL-6 regulates immune responses, acute-phase proteins (including serum amyloid A and C-reactive protein), hematopoiesis,
[...] Read more.
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a multifunctional cytokine with an essential role in immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Produced by immune, stromal and epithelial cells in response to infection or tissue stress, IL-6 regulates immune responses, acute-phase proteins (including serum amyloid A and C-reactive protein), hematopoiesis, and tissue remodeling. These effects are mediated via classical and trans-signaling pathways, which activate key intracellular cascades such as JAK/STAT3, MAPK, and PI3K/AKT. Accumulating evidence implicates dysregulated IL-6 signaling in both oncologic and infectious diseases, where it contributes to disease progression, immune evasion, and therapeutic resistance. This review aims to critically examine the role of IL-6 as a biomarker and therapeutic target in these two major clinical contexts: in cancer, IL-6 levels reflect tumor burden, prognosis, and therapy resistance in both adult and pediatric patients; in infectious diseases, circulating IL-6 may support early diagnosis and risk stratification, particularly in vulnerable pediatric populations. By integrating molecular mechanisms with clinical evidence, this review highlights IL-6 as a unifying biomarker linking inflammation, infection, and malignancy. It also addresses current limitations, including assay variability, lack of standardized reference ranges, especially in children, and challenges in clinical implementation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cytokines and Allied Mediators)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Clinical Remission and Its Predictors After 12 Months of Biologic Therapy in Severe Asthma
by
Tatsuro Suzuki, Tomoko Tajiri, Yoshiyuki Ozawa, Yuki Amakusa, Keima Ito, Yuta Mori, Kensuke Fukumitsu, Satoshi Fukuda, Yoshihiro Kanemitsu, Takehiro Uemura, Hirotsugu Ohkubo, Tetsuya Oguri, Eiji Nakatani, Kenichi Yoshimura and Akio Niimi
Biologics 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics6010004 - 19 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The rates and predictors of clinical remission, a novel and practical therapeutic goal in severe asthma, have been inconsistently reported across studies. Data on clinical remission in Japanese patients remain limited. The aim of this study was to assess the rate of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The rates and predictors of clinical remission, a novel and practical therapeutic goal in severe asthma, have been inconsistently reported across studies. Data on clinical remission in Japanese patients remain limited. The aim of this study was to assess the rate of four-component clinical remission and its predictors in Japanese adult patients with severe asthma. Methods: This retrospective study enrolled adult patients with severe asthma who had initiated biologic therapy at least 12 months prior to inclusion at Nagoya City University Hospital. The primary endpoint was the achievement rate of four-component clinical remission, defined as (1) no maintenance oral corticosteroids (OCS); (2) no exacerbations for 12 months; (3) Asthma Control Test (ACT) score ≥ 20; and (4) forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) ≥ 80% of predicted. The secondary endpoint was to identify factors, including airway structural indices measured using chest computed tomography (CT), associated with clinical remission at 12 months. Results: Among 87 patients with severe asthma, 26 (30%) achieved four-component clinical remission after 12 months of biologic therapy. In univariate analysis, clinical remission was more frequently achieved in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis, higher FEV1 (% predicted), higher blood eosinophil counts, higher ACT scores, fewer exacerbations in the previous year, higher Lund–Mackay scores, and smaller airway wall thickness and luminal areas on CT (all p < 0.05). Multivariate analysis revealed that higher blood eosinophil counts and fewer exacerbations in the previous year were independently associated with clinical remission (both p < 0.05). Conclusions: After 12 months of biologic therapy, 30% of patients with severe asthma achieved four-component clinical remission. Higher blood eosinophil counts and fewer prior exacerbations were associated with higher remission rates.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Complement Inhibitors and the Risk of (Breakthrough) Infections—Critical Analysis and Preventive Strategies
by
Nikola Halacova, Miroslava Brndiarova, Branislav Slenker, Anna Ruzinak Bobcakova, Martina Schniederova, Adam Markocsy, Ingrid Urbancikova and Milos Jesenak
Biologics 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics6010003 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
The complement system is a key component of innate immunity, responsible for mediating the rapid clearance of pathogens and coordinating adaptive immune responses. Although complement activation is essential for effective infection control and prevention, its excessive or dysregulated function contributes to the pathogenesis
[...] Read more.
The complement system is a key component of innate immunity, responsible for mediating the rapid clearance of pathogens and coordinating adaptive immune responses. Although complement activation is essential for effective infection control and prevention, its excessive or dysregulated function contributes to the pathogenesis of various immune-mediated disorders. Therefore, therapeutic inhibition of the overactive complement cascade, in which specific components are selectively blocked to suppress pathological activation, plays an important role in the treatment of various complement (immune)-mediated diseases. This article provides an overview of complement inhibition as a therapeutic strategy, highlighting the infectious risks associated with its use. Disruption of complement-dependent host defence mechanisms increases the risk of invasive infections (caused by encapsulated pathogens, e.g., Neisseria spp., Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae type B), which represent a significant clinical challenge. Therefore, the use of complement inhibition should not only be effective but also safe in combination with the application of all possible tools to prevent infections. Strategies, such as vaccination and antibiotic prophylaxis, are crucial to minimise these complications, despite the persistence of the risk of breakthrough infections. Furthermore, this review examines advancements in patient risk stratification, evaluates alternative preventive measures, and identifies key gaps in current clinical practice. Future directions include improving monitoring protocols, creating more selective or locally acting complement inhibitors, and implementing biomarker-driven personalised therapies that maximise benefits while reducing side effects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Monoclonal Antibodies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Functional Hydrogels in Bone Tissue Engineering: From Material Design to Translational Applications
by
Francesco Maria Petraglia, Sabrina Giordano and Angelo Santoro
Biologics 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics6010002 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Bone tissue engineering offers a promising alternative to autografts and allografts for treating critical bone defects. Hydrogels, three-dimensional hydrophilic polymer networks, have emerged as leading scaffold materials due to their ability to mimic native extracellular matrix properties while providing tunable biocompatibility, biodegradability, mechanical
[...] Read more.
Bone tissue engineering offers a promising alternative to autografts and allografts for treating critical bone defects. Hydrogels, three-dimensional hydrophilic polymer networks, have emerged as leading scaffold materials due to their ability to mimic native extracellular matrix properties while providing tunable biocompatibility, biodegradability, mechanical characteristics, and high water content, enabling nutrient transport and cell viability. These scaffolds can be loaded with bioactive cues, including growth factors, peptides, and nanoparticles, and can deliver stem cells, supporting localised and sustained bone regeneration. Recent advances in hydrogel design have improved osteoinductivity and osteoconductivity through controlled physical, chemical, and mechanical properties, and sophisticated fabrication strategies such as 3D bioprinting and nanostructuring. This review provides a comprehensive overview of hydrogel-based scaffolds for bone tissue engineering, discussing material types, bioactive factor delivery, host tissue interactions, including immune modulation and osteogenic differentiation, and the latest preclinical and clinical applications. Finally, we highlight the remaining challenges and critical design requirements for developing next-generation hydrogels that integrate structural integrity with biological functionality.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Targeting the Cellular Prion Protein as a Biomarker for Stem Cells, Cancer, and Regeneration
by
Niccolò Candelise, Nicola Salvatore Orefice, Elisabetta Mantuano and Stefano Martellucci
Biologics 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics6010001 - 24 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
The cellular prion protein (PrPC) displays a functional repertoire that extends well beyond its classical link to transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Abundant in the nervous system and localized within lipid raft microdomains, PrPC has emerged as a multifunctional signaling platform that
[...] Read more.
The cellular prion protein (PrPC) displays a functional repertoire that extends well beyond its classical link to transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Abundant in the nervous system and localized within lipid raft microdomains, PrPC has emerged as a multifunctional signaling platform that regulates cell differentiation, neurogenesis, neuroprotection, and synaptic plasticity. Recent evidence highlights its dynamic expression in stem cell populations, where it participates in multimolecular complexes that control lineage commitment, particularly during neuronal differentiation. PrPC expression tightly correlates with stem cell status, making it a promising biomarker of stemness and developmental progression. Through interactions with growth factors, extracellular matrix components, and synaptic proteins, PrPC functions as a molecular integrator of signals essential for tissue repair and regeneration. Preclinical studies demonstrate that recombinant PrPC can stimulate neurogenesis and tissue repair, while monoclonal antibodies modulate its physiological and pathological functions. Likewise, cell-based therapies leveraging PrPC-enriched stem cells or PrPC-dependent signaling profiles have shown promise in models of neurodegeneration and ischemia. Conversely, dysregulated PrPC expression has also been observed in solid tumors, where it contributes to cancer cell survival, proliferation, metastasis, and therapy resistance, reinforcing its role as a regulator of cell fate and an oncological target. This review integrates stem cell biology, tissue regeneration, and oncology into a unified framework, offering a novel perspective in which PrPC emerges as a shared molecular hub governing both physiological repair and pathological tumor behavior, opening previously unrecognized conceptual and translational opportunities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Protein Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Automated Scale-Down Development and Optimization of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-EMP-100 for Non-Invasive PET Imaging and Targeted Radioligand Therapy of c-MET Overactivation in Cancer
by
Silvia Migliari, Anna Gagliardi, Alessandra Guercio, Maura Scarlattei, Giorgio Baldari, Alex Gibson, Christophe Portal and Livia Ruffini
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040040 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Overactivation of the HGF/c-MET pathway is implicated in various cancers, making its inhibition a promising therapeutic strategy. While several MET-targeting agents are currently approved or in advanced clinical development, patient selection often relies on invasive tissue-based assays. The development of a
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Overactivation of the HGF/c-MET pathway is implicated in various cancers, making its inhibition a promising therapeutic strategy. While several MET-targeting agents are currently approved or in advanced clinical development, patient selection often relies on invasive tissue-based assays. The development of a specific c-MET radioligand for PET imaging and radioligand therapy represents a non-invasive alternative, enabling real-time monitoring of target expression and offering a pathway to personalized treatment. Methods: Radiosynthesis of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-EMP100 was performed using a GMP-certified 68Ge/68Ga generator connected to an automated synthesis module. The radiopharmaceutical production was optimized by scaling down the amount of DOTA-EMP-100 from 50 to 20 μg. Synthesis efficiency and release criteria were assessed according to Ph. Eur. for all the final products by evaluating radiochemical yield (RY%), radiochemical purity, presence of free gallium (by Radio-UV-HPLC) and gallium colloids (by Radio-TLC), molar activity (Am), chemical purity, pH, and LAL test results. Results: An optimized formulation of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-EMP-100, using 40 μg of precursor, provided the best outcome in terms of radiochemical performance. Process validation across three independent productions confirmed a consistent radiochemical yield of 64.5% ± 0.5, high radiochemical purity (>99.99%), and a molar activity of 53.41 GBq/µmol ± 0.8. Conclusions: [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-EMP-100 was successfully synthesized with high purity and reproducibility, supporting its potential for multi-dose application in clinical PET imaging and targeted radioligand therapy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Avcil et al. Efficacy of Dissolvable Microneedle Patches with Skincare Actives in Acne Management: A Monocentric Clinical Study. Biologics 2025, 5, 15
by
Muhammet Avcil, Jens Klokkers, Dohyeon Jeong and Ayhan Celik
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 39; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040039 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
There was an error in the original publication [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Risk of Developing Clostridioides Difficile Infection with the Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
by
Mustafa Gandhi, Harleen Kaur Chela, Maxwell A. Barffour, Emily Bosak, Emily Reznicek, Kevin Luton, Matthew Bechtold and Yezaz A. Ghouri
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040038 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have an increased risk of Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI). While antibiotic exposure has been considered the most prominent risk factor for CDI, proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use is another potential risk factor. Methods: From January 2017
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have an increased risk of Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI). While antibiotic exposure has been considered the most prominent risk factor for CDI, proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use is another potential risk factor. Methods: From January 2017 to April 2021, we examined the University of Missouri’s IBD patients’ medical records. Laboratory-confirmed CDI diagnosis was the main outcome of interest. The usage of PPIs was the exposure of interest. The odds ratio between CDI risk in PPI users and non-users was estimated using logistic regression models. We investigated CDI risk with PPI use duration using stratified analysis. Results: Overall prevalence of CDI was 9%. 358 patients (42%) reported using PPI, with an average duration of ~30 months, with a range of 0.1 to 255. PPI use was associated with a higher risk of CDI in both the unadjusted (OR = 1.58 [0.98–2.53]; p = 0.06) and adjusted models (9.23 [2.11–40.34]; p = 0.003). Only those who used PPIs for less than 30 months had a greater risk of CDI in the stratified analysis (OR = 2.10 [1.16–3.38], p = 0.014). Long-term use (≥30 months) did not increase the incidence of CDI (OR = 0.74 [0.29, 1.83]; p = 0.510). Discussion: This is the single largest study of the US general IBD population to evaluate the association between PPI use and risk of developing CDI. PPI therapy was linked to a significant elevation in CDI risk, restricted to PPI use for up to 30 months. Histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs) did not increase the risk of CDI.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Derivatives: Old Problems and New Possibilities in Regenerative Medicine for Neurological Diseases
by
Elvira Akhmetzyanova, Ilya Shulman, Taisiya Fakhrutdinova, Albert Rizvanov and Yana Mukhamedshina
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040037 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Mesenchymal stem cells are multipotent stromal cells with immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and trophic properties that support tissue repair and regeneration. Increasing evidence suggests that their therapeutic effects are primarily mediated by paracrine signaling, especially through extracellular vesicles, which can cross the blood–brain barrier and
[...] Read more.
Mesenchymal stem cells are multipotent stromal cells with immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and trophic properties that support tissue repair and regeneration. Increasing evidence suggests that their therapeutic effects are primarily mediated by paracrine signaling, especially through extracellular vesicles, which can cross the blood–brain barrier and act as cell-free therapeutic agents. Preclinical and clinical studies in stroke, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, and neurodegenerative diseases report encouraging outcomes but also reveal major challenges, including limited engraftment, donor-related heterogeneity, incomplete understanding of mechanisms, and potential oncogenic risks. Recent advances in biotechnology—such as mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles, genetic engineering using CRISPR/Cas9 or viral vectors, 3D culture systems, and bioengineered delivery platforms—offer new opportunities to overcome these limitations. Early clinical trials demonstrate promising safety and functional improvements, yet results remain inconsistent, highlighting the need for standardized protocols and large-scale controlled studies. This review outlines current knowledge, key challenges, and emerging strategies aimed at optimizing mesenchymal stem cell-based approaches for regenerative neurology.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Aljahili et al. Safety of Switching from a Reference Biologic to Its Biosimilar: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biologics 2025, 5, 6
by
Sarah Saad Aljahili, Samar Sami Alshuwairikh, Ahmed AlKhaldi, Abeer Althiban, Radwan Hafiz, Ghazwa B. Korayem and Hadeel Alkofide
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040036 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the original publication [...]
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
Advancements in Pharmaceutical Lyophilization: Integrating QbD, AI, and Novel Formulation Strategies for Next-Generation Biopharmaceuticals
by
Prachi Atre and Syed A. A. Rizvi
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040035 - 10 Nov 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Lyophilization (freeze-drying) has become a cornerstone pharmaceutical technology for stabilizing biopharmaceuticals, overcoming the inherent instability of biologics, vaccines, and complex drug formulations in aqueous environments. The appropriate literature for this review was identified through a structured search of several databases (such as PubMed,
[...] Read more.
Lyophilization (freeze-drying) has become a cornerstone pharmaceutical technology for stabilizing biopharmaceuticals, overcoming the inherent instability of biologics, vaccines, and complex drug formulations in aqueous environments. The appropriate literature for this review was identified through a structured search of several databases (such as PubMed, Scopus) covering publications from late 1990s till date, with inclusion limited to peer-reviewed studies on lyophilization processes, formulation development, and process analytical technologies. This succinct review examines both fundamental principles and cutting-edge advancements in lyophilization technology, with particular emphasis on Quality by Design (QbD) frameworks for optimizing formulation development and manufacturing processes. The work systematically analyzes the critical three-stage lyophilization cycle—freezing, primary drying, and secondary drying—while detailing how key parameters (shelf temperature, chamber pressure, annealing) influence critical quality attributes (CQAs) including cake morphology, residual moisture content, and reconstitution behavior. Special attention is given to formulation strategies employing synthetic surfactants, cryoprotectants, and stabilizers for complex delivery systems such as liposomes, nanoparticles, and biologics. The review highlights transformative technological innovations, including artificial intelligence (AI)-driven cycle optimization, digital twin simulations, and automated visual inspection systems, which are revolutionizing process control and quality assurance. Practical case studies demonstrate successful applications across diverse therapeutic categories, from small molecules to monoclonal antibodies and vaccines, showcasing improved stability profiles and manufacturing efficiency. Finally, the discussion addresses current regulatory expectations (FDA/ICH) and compliance considerations, particularly regarding cGMP implementation and the evolving landscape of AI/ML (machine learning) validation in pharmaceutical manufacturing. By integrating QbD-driven process design with AI-enabled modeling, process analytical technology (PAT) implementation, and regulatory alignment, this review provides both a strategic roadmap and practical insights for advancing lyophilized drug product development to meet contemporary challenges in biopharmaceutical stabilization and global distribution. Despite several publications addressing individual aspects of lyophilization, there is currently no comprehensive synthesis that integrates formulation science, QbD principles, and emerging digital technologies such as AI/ML and digital twins within a unified framework for process optimization. Future work should integrate advanced technologies, AI/ML standardization, and global access initiatives within a QbD framework to enable next-generation lyophilized products with improved stability and patient focus.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Novel Enzymes for Biologics with Hydrolytic Activity Against Thiolactones: Computational, Catalytic and Antimicrobial Study
by
Maksim Domnin, Anastasia Sarapina, Aysel Aslanli, Olga Senko and Elena Efremenko
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040034 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Various thiolactones are known as biologically active compounds, capable of stimulating the development of several human diseases and quorum sensing of Gram–positive bacteria. The enzymatic hydrolysis of thiolactones represents a promising approach to preventing their action. Methods: Thirteen enzymes, including various lactonases
[...] Read more.
Background: Various thiolactones are known as biologically active compounds, capable of stimulating the development of several human diseases and quorum sensing of Gram–positive bacteria. The enzymatic hydrolysis of thiolactones represents a promising approach to preventing their action. Methods: Thirteen enzymes, including various lactonases and serine hydrolases were studied in this work using several substrates including the homocysteine thiolactone (HTL), and its derivatives the N–acetylhomocysteine thiolactone (C2–HTL) and the isobutyryl–homocystein thiolactone (i–but–HTL). The potential interactions of the ligands with the surface of enzymes molecules were predicted in silico using computational modeling and checked in wet experiments in vitro. Results: Based on the data obtained several enzymes were selected with localization of the thiolactones near their active sites, indicating the possibility of effective catalysis. The lactonase (AiiA), metallo-β-lactamase (NDM-1) and the organophosphate hydrolase with hexahistidine tag (His6–OPH) were among them. Determination of catalytic characteristics of enzymes in the hydrolytic reactions with the HTL and the C2–HTL revealed the maximal value of catalytic efficiency constant for the NDM-1 in the hydrolysis of the HTL (826 M−1 s−1). The maximal activity in the hydrolysis of C2–HTL was established for AiiA (137 M−1 s−1). The polyaspartic (PLD50) and the polyglutamic (PLE50) acids were used to obtain polyelectrolyte complexes with enzymes. The further combination of these complexes with the clotrimazole and polymyxin B possessing antimicrobial properties resulted in notable improvement of their action in relation to Staphylococcus cells. Conclusions: It was revealed that the antimicrobial activity of the polymyxin B is enhanced by 9–10 times against bacteria and yeast when combined with the His6–OPH polyelectrolyte complexes. The antimicrobial activity of clotrimazole was increased by ~7 times against Candida tropicalis cells in the case of the AiiA/PLE50/Clotrimazole combination. These results make the obtained biology attractive and promising for their further advancement to practical application.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Vaccines and Antimicrobial Therapy—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Real-World Long-Term Management of Chronic Urticaria Patients with Omalizumab: Safety, Effectiveness, and Predictive Factors for Successful Outcome
by
Ciro Romano, Domenico Cozzolino, Giuseppina Rosaria Umano and Ernesto Aitella
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040033 - 22 Oct 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Omalizumab is a monoclonal anti-IgE antibody approved for the treatment of chronic urticaria. There are no established or validated prognostic markers currently available to identify likely responders. The aim of this study was to retrospectively analyze a cohort of chronic urticaria patients
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Omalizumab is a monoclonal anti-IgE antibody approved for the treatment of chronic urticaria. There are no established or validated prognostic markers currently available to identify likely responders. The aim of this study was to retrospectively analyze a cohort of chronic urticaria patients treated with omalizumab, in order to determine the clinical and laboratory characteristics associated with complete response to therapy. Methods: Medical records of chronic urticaria patients receiving omalizumab were reviewed. The following parameters were collected: age, sex, disease duration, Urticaria Activity Score over 7 days (UAS7), time to response, total serum IgE levels, presence or absence of atopy, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, eosinophil and basophil counts, presence or absence of autoimmune conditions, and treatment duration. Complete response was classified as dependent on continued drug administration or drug-free (sustained remission after discontinuation). Adverse events were also recorded. Results: Omalizumab was well tolerated by all patients, with no serious adverse events reported. Complete response was achieved in 81.3% of patients; partial and no responses were observed in 8.3% and 10.1%, respectively. The majority of responders (~79.5%) maintained complete control of hives with low-dose omalizumab; subsequently, most of these patients eventually achieved sustained, drug-free remission. Total serum IgE levels appeared to predict complete response, with 164.7 IU/mL identified as the cut-off value potentially distinguishing responders from nonresponders. Conclusions: Omalizumab is a safe and effective treatment for chronic urticaria. Total serum IgE levels may help identify complete responders. Long-term low-dose regimens could be considered to reduce the economic burden on healthcare systems, although this is currently an off-label approach.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Monoclonal Antibodies)
►▼
Show Figures
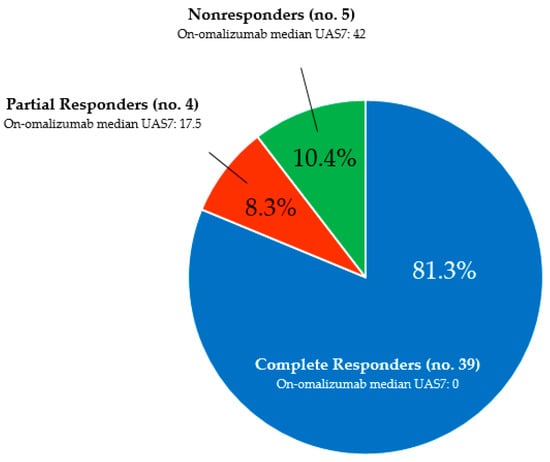
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Regulation of Antioxidant Expression in the Liver Tissue of Obese Rats Treated with Coriander Seed Ethanolic Extract: In Silico and In Vivo Studies
by
Kartika Diana Pertiwi, Novi Silvia Hardiany, Syarifah Dewi and Bimo Ario Tejo
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040032 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Obesity increases reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby triggering oxidative stress. Coriander seeds contain polyphenolic compounds that act as natural antioxidants to reduce oxidative stress. Coriander seed ethanolic extract has been proven to decrease malondialdehyde and increase catalase activity in the liver of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Obesity increases reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby triggering oxidative stress. Coriander seeds contain polyphenolic compounds that act as natural antioxidants to reduce oxidative stress. Coriander seed ethanolic extract has been proven to decrease malondialdehyde and increase catalase activity in the liver of high-fat-diet-fed rats. Thus, coriander seeds are thought to protect against obesity-induced oxidative liver damage; however, their molecular mechanism has not been revealed. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and Forkhead Box O3 (FOXO3) are transcription factors involved in cellular antioxidant regulation (e.g., superoxide dismutase/SOD, glutathione peroxidase/GPx expression, and reduced glutathione/GSH) that are negatively regulated by Kelch-like ECH-associated Protein 1 (Keap1) and 14-3-3 protein to maintain cellular homeostasis. This study aimed to analyze the regulation of antioxidant expression through in silico and in vivo experiments. Methods: The in silico study assessed the potential of coriander seed ethanolic extract to inhibit Keap1 and 14-3-3 using molecular docking. Then, the drug-likeness, pharmacokinetics, and toxicity of the top three compounds were analyzed. Meanwhile, the in vivo study investigated how the coriander seed ethanolic extract impacted the level of Nrf2, FOXO3, and their downstream effectors (T-SOD, MnSOD, GPx, and GSH). The in vivo study involved five groups of rats with obesity induced by a high-fat diet that were fed with 100 mg/kgBW coriander seed ethanolic extract for 12 weeks. Results: The in silico tests revealed that shionoside b had the highest potential to inhibit Keap1 (ΔG = −8.90 kcal/mol; Ki = 298.01 nM) and 14-3-3 protein (ΔG = −6.85 kcal/mol; Ki = 9.46 µM). The in vivo tests showed that the Nrf2, FOXO3, MnSOD, and GPx mRNA expression was significantly different between the groups (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, T-SOD, MnSOD, GPx, and GSH activity were not significantly different between the groups (p > 0.05). Nrf2 was significantly correlated with FOXO3 as well as the T-SOD, MnSOD, and GPx activity, and FOXO3 was significantly correlated with the T-SOD, MnSOD, GPx, and GSH activity. Conclusions: In obese rats, coriander seeds tend to increase Nrf2 and FOXO3 expression, which is positively correlated with their downstream enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidant activity. This is possibly due to the interaction between the coriander seed phytoconstituents and protein inhibitors (Keap1 and 14-3-3), which contribute to the stability and nuclear mobilization of Nrf2 and FOXO3.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Natural Products)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Single Antigen Luminex Bead Assay for the Definition of HLA-Specific Antibodies Revisited: Improved Reactivity by Incubation at 37 Degrees Celsius
by
Claudia Lehmann, Ramona Landgraf and Ilias Doxiadis
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040031 - 11 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Sera from patients before and after organ transplantation were tested at two different temperatures, 21 °C and 37 °C. Currently, organs are transported under normothermic conditions (37 °C). This observational pilot study was conducted to define the effect of the incubation at
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Sera from patients before and after organ transplantation were tested at two different temperatures, 21 °C and 37 °C. Currently, organs are transported under normothermic conditions (37 °C). This observational pilot study was conducted to define the effect of the incubation at 37 °C, comparing the results to the usual temperature of 21 °C for serum–bead incubation. Methods: We used the Luminex-based assay for the identification and characterization of HLA-specific antibodies. The assays were performed using single antigen beads for HLA class I and HLA class II. A total of 42 sera were assessed and tested, and 38 were analyzed on the Luminex 200 platform at both temperatures. Results: We noted varying outcomes: both an increase and a decrease in mean fluorescence intensity values. A shift from negative to positive values (n = 6) and vice versa (n = 1) was observed. Several sera (n = 4 for HLA class I and n = 5 for HLA class II) exhibited no alterations. In general, we observed an increase in the mean fluorescence intensity values by incubation at 37 °C. The analysis at the bead level revealed a significant deviation (37 °C vs. 21 °C) for the bead carrying HLA-A80 (p = 0.0006) and two HLA-DQ beads, DQA1*05:01-DQB1*02:01 (p = 0.0438) and DQA1*01:03-DQB1*06:03 (p = 0.0438). Conclusions: Mimicking physiological temperature conditions for the testing of HLA-specific antibodies will lead to the better and more accurate interpretation of the results. This method shows potential for use in the delisting strategy for highly sensitized patients as well, thus allowing a better and more reliable option for the patient awaiting a suitable crossmatch-negative organ.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Rituximab-Associated Myocardial Injury in a Young Woman with Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: A Case Report
by
Natasha E. Barton, Elizabeth A. Stein, Kathryn Mulvaney and Yevgeniya Scherbak
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040030 - 10 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD20, commonly used to treat autoimmune diseases such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and rheumatoid arthritis. While generally well-tolerated, serious adverse events, including infusion reactions and infections, are well-documented. Case Summary: We report a
[...] Read more.
Background: Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD20, commonly used to treat autoimmune diseases such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and rheumatoid arthritis. While generally well-tolerated, serious adverse events, including infusion reactions and infections, are well-documented. Case Summary: We report a rare case of rituximab-induced ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) in a 26-year-old woman with no cardiovascular risk factors. She developed crushing chest pain after her first 1 g rituximab infusion, with recurrent symptoms upon re-exposure. Cardiac catheterization revealed a left circumflex artery occlusion. Additional workup showed c-ANCA positivity, cryoglobulinemia, pauci-immune glomerulonephritis, and findings consistent with GPA. Rituximab was discontinued, and she was transitioned to steroids, cyclophosphamide, and leuprolide, with no further cardiac events. Discussion: This is the first reported case in a young, previously healthy woman. Clinicians should consider rituximab-associated myocardial injury, especially in autoimmune or hypercoagulable states. Take-Home Message: Remain vigilant for cardiac events during rituximab infusions in patients with inflammatory diseases.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Lactobacillus acidophilus: Boosting Immunity Through IL-6 Induction
by
Isaac Oluseun Adejumo
Biologics 2025, 5(4), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5040029 - 29 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and Objectives: Probiotics are live microorganisms that promote health when consumed in adequate amounts, ensure the balance of bacterial composition in the digestive system, and suppress harmful pathogenic bacteria, with overall implications for animal and human health, welfare and performance. However, a
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Probiotics are live microorganisms that promote health when consumed in adequate amounts, ensure the balance of bacterial composition in the digestive system, and suppress harmful pathogenic bacteria, with overall implications for animal and human health, welfare and performance. However, a lot remains unclear about their functional mechanisms. Materials and Methods: In this study, 14 uncharacterized proteins of Lactobacillus acidophilus were analyzed for subcellular localization, structural and safety profiling and interleukin-6-(IL-6)-inducing potential. Results: Aliphatic index scores were generally high, ranging between 138.39 (LBA1705) and 78.39 (LBA1825). The instability index scores were less than 40 for all the query proteins except for LBA0995. All the proteins produced immunogenic IL-6-inducing peptides, except for LBA0037, LBA1825 and LBA1788. Conclusions: The findings provide insight into understanding the functional mechanism of probiotic Lactobacillus, laying a strong foundation for more experimental studies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Immune Response to Extracellular Matrix Bioscaffolds: A Comprehensive Review
by
Daniela J. Romero, George Hussey and Héctor Capella-Monsonís
Biologics 2025, 5(3), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics5030028 - 5 Sep 2025
Abstract
Extracellular matrix (ECM) bioscaffolds have demonstrated therapeutic potential across a variety of clinical and preclinical applications for tissue repair and regeneration. In parallel, these scaffolds and their components have shown the capacity to modulate the immune response. Unlike synthetic implants, which are often
[...] Read more.
Extracellular matrix (ECM) bioscaffolds have demonstrated therapeutic potential across a variety of clinical and preclinical applications for tissue repair and regeneration. In parallel, these scaffolds and their components have shown the capacity to modulate the immune response. Unlike synthetic implants, which are often associated with chronic inflammation or fibrotic encapsulation, ECM bioscaffolds interact dynamically with host cells, promoting constructive tissue remodeling. This effect is largely attributed to the preservation of structural and biochemical cues—such as degradation products and matrix-bound nanovesicles (MBV). These cues influence immune cell behavior and support the transition from inflammation to resolution and functional tissue regeneration. However, the immunomodulatory properties of ECM bioscaffolds are dependent on the source tissue and, critically, on the methods used for decellularization. Inadequate removal of cellular components or the presence of residual chemicals can shift the host response towards a pro-inflammatory, non-constructive phenotype, ultimately compromising therapeutic outcomes. This review synthesizes current basic concepts on the innate immune response to ECM bioscaffolds, with particular attention to the inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling phases following implantation. We explore how specific ECM features shape these responses and distinguish between pro-remodeling and pro-inflammatory outcomes. Additionally, we examine the impact of manufacturing practices and quality control on the preservation of ECM bioactivity. These insights challenge the conventional classification of ECM bioscaffolds as medical devices and support their recognition as biologically active materials with distinct immunoregulatory potential. A deeper understanding of these properties is critical for optimizing clinical applications and guiding the development of updated regulatory frameworks in regenerative medicine.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Protein Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomolecules, Cells, IJMS, Pathogens, Vaccines, Biologics, Microorganisms, Biomedicines
Advances in Vaccines and Antimicrobial Therapy—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Raffaele D’Amelio, Roberto PaganelliDeadline: 30 September 2026
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Antibiotics, Microorganisms, Poultry, Pathogens, Veterinary Sciences, Biologics
Advances in Infectious and Parasitic Diseases of Animals
Topic Editors: Felipe M. Salvarani, Sheyla Farhayldes Souza Domingues, Júlia Angélica Gonçalves Da SilveiraDeadline: 31 December 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Cancers, Immuno, IJMS, Biologics
New Advancements in Innate Immunity and Cancer Immunotherapy
Topic Editors: Jeonghyun Ahn, Zhiwei HuDeadline: 30 June 2027
Topic in
Biomedicines, IJMS, Medical Sciences, Pharmaceuticals, Cells, Pathogens, Biologics
The Pathogenesis and Treatment of Immune-Mediated Disease
Topic Editors: Ranferi Ocaña-Guzmán, Lucero A. Ramon-LuingDeadline: 31 August 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Biologics
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer
Guest Editor: Yasunari MatsuzakaDeadline: 20 February 2026
Special Issue in
Biologics
Progress in Antibody-Guided Vaccine Design for Viruses
Guest Editor: Gary McLeanDeadline: 10 June 2026
Special Issue in
Biologics
Gene and Stem Cell Therapies for Inherited Metabolic Disorders
Guest Editor: Paul GissenDeadline: 25 September 2026