- Article
Hydrothermal Synthesis of FAU-Type Zeolite NaX Using Ladle Slag and Waste Aluminum Cans
- Borislav Barbov,
- Hristina Lazarova and
- Aleksandar Nikolov
- + 1 author
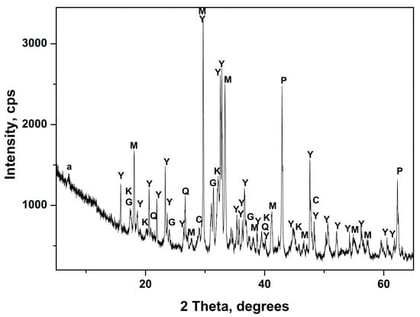
This study explores a sustainable synthesis route for FAU-type zeolite X using acid-treated ladle slag as a silicon source and waste aluminum cans as an alternative aluminum precursor. Conventional zeolite synthesis relies on high-purity reagents, which are costly and environmentally intensive to produce. Previous research has rarely addressed the valorization of ladle slag and metallic aluminum waste for zeolite formation, leaving their potential largely unexplored. The study focuses on the effective utilization of industrial and post-consumer wastes—acid-treated ladle slag and aluminum cans—as precursors for FAU-type NaX zeolite, demonstrating their feasibility as alternative silicon and aluminum sources. Here, zeolite X was synthesized hydrothermally from treated slag combined with either dissolved aluminum cans and commercial sodium aluminate at 90 °C for 6 h. FAU-type zeolite X was successfully synthesized using both aluminum sources, with a SiO2/Al2O3 ratio of approximately 1.4. The results demonstrate that waste-derived precursors can effectively replace conventional chemicals, yielding predominantly NaX zeolite with high crystallinity and minor NaA impurity (as observed by XRD), with experimental yields of 1.47 g for aluminum cans and 1.266 g for sodium aluminate. The obtained zeolite X samples were structurally and texturally characterized by XRD, FTIR, XRF, BET surface area analysis, and thermogravimetric analysis (TG).
3 February 2026