- Article
A Collaborative Dynamic Transit Scheduling Method Integrating Timetable Adjustment and Control-Oriented Trajectory Guidance
- Kunmin Teng,
- Haiqing Liu and
- Xiao Lu
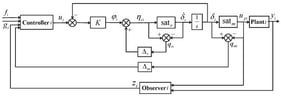
Dynamic scheduling of public transit is crucial for enhancing comprehensive operational benefits such as service quality and operating costs. However, uncertain passenger demands and the uncontrolled block effects of signalized intersections can lead to timetable deviation, significantly affecting scheduling efficiency. This paper proposes a collaborative dynamic transit scheduling method to mitigate the negative coupling effect. A passenger demand-aware dynamic timetable scheduling strategy is developed to improve timetable adherence and operational homogeneity. A control-oriented trajectory guidance strategy is established to enhance the effectiveness of the timetable scheduling strategy and reduce the operating costs considering the blocking effects of signalized intersections and transit actuator constraints. Integrating the two strategies, a collaborative optimization framework using a multi-objective nonlinear programming model is constructed to present an optimal comprehensive benefit scheduling scheme. Simulation results demonstrate that, compared to traditional methods within the same simulation scenarios, the proposed method improves the performance of operational homogeneity, timetable adherence, and energy efficiency by up to 67.6%, 71.03%, and 27.5%, respectively. In addition, it also enables the transit to pass through multiple signalized intersections without stopping, significantly enhancing the transit’s operational stability and operating cost.
12 February 2026



![Gravitational torque of 1-DOF arm: (a) simplified model. (b) torque as function of
θ
[19].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/actuators/actuators-15-00111/article_deploy/html/images/actuators-15-00111-g001-550.jpg)