-
 Synthesis and Characterization of First High-Energy Anti-Perovskite Compounds by Hydro-Closo-Borate and Oxo-Anions
Synthesis and Characterization of First High-Energy Anti-Perovskite Compounds by Hydro-Closo-Borate and Oxo-Anions -
 Mechanisms of Peptide Binding and Deactivation of Adhesion GPCR
Mechanisms of Peptide Binding and Deactivation of Adhesion GPCR -
 Multiscale Modeling of Macromolecular Interactions between Tau-Amylin Oligomers and Asymmetric Lipid Nanodomains That Link Alzheimer’s and Diabetic Diseases
Multiscale Modeling of Macromolecular Interactions between Tau-Amylin Oligomers and Asymmetric Lipid Nanodomains That Link Alzheimer’s and Diabetic Diseases -
 Synergistic Remediation of Organic Dye by Titanium Dioxide/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite
Synergistic Remediation of Organic Dye by Titanium Dioxide/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite
Journal Description
Molecules
Molecules
is the leading international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of chemistry. Molecules is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The International Society of Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids (IS3NA), the Spanish Society of Medicinal Chemistry (SEQT) and the International Society of Heterocyclic Chemistry (ISHC) are affiliated with Molecules and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Reaxys, CaPlus / SciFinder, MarinLit, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) / CiteScore - Q1 (Chemistry (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 14.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 26 topical sections.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Molecules.
- Companion journals for Molecules include: Foundations and Photochem.
Impact Factor:
4.6 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.9 (2022)
Latest Articles
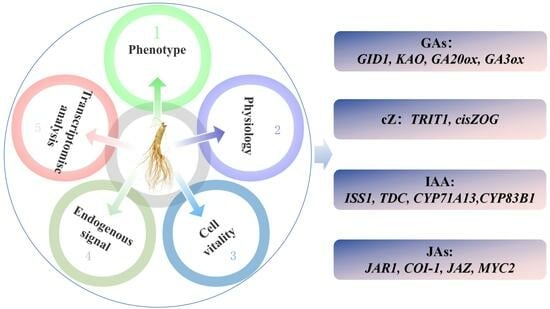
Analysis Transcriptome and Phytohormone Changes Associated with the Allelopathic Effects of Ginseng Hairy Roots Induced by Different-Polarity Ginsenoside Components
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1877; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081877 (registering DOI) - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
The allelopathic autotoxicity of ginsenosides is an important cause of continuous cropping obstacles in ginseng planting. There is no report on the potential molecular mechanism of the correlation between polarity of ginsenoside components and their allelopathic autotoxicity. This study applied a combination of
[...] Read more.
The allelopathic autotoxicity of ginsenosides is an important cause of continuous cropping obstacles in ginseng planting. There is no report on the potential molecular mechanism of the correlation between polarity of ginsenoside components and their allelopathic autotoxicity. This study applied a combination of metabolomics and transcriptomics analysis techniques, combined with apparent morphology, physiological indexes, and cell vitality detection of the ginseng hairy roots, through which the molecular mechanism of correlation between polarity and allelopathic autotoxicity of ginsenosides were comprehensively studied. The hairy roots of ginseng presented more severe cell apoptosis under the stress of low-polarity ginsenoside components (ZG70). ZG70 exerted allelopathic autotoxicity by regulating the key enzyme genes of cis-zeatin (cZ) synthesis pathway, indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) synthesis pathway, and jasmonates (JAs) signaling transduction pathway. The common pathway for high-polarity ginsenoside components (ZG50) and ZG70 to induce the development of allelopathic autotoxicity was through the expression of key enzymes in the gibberellin (GA) signal transduction pathway, thereby inhibiting the growth of ginseng hairy roots. cZ, indole-3-acetamid (IAM), gibberellin A1 (GA1), and jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine (JA-ILE) were the key response factors in this process. It could be concluded that the polarity of ginsenoside components were negatively correlated with their allelopathic autotoxicity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Natural Products Chemistry)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Promising Antileishmanial Activity of Micromeria nervosa Essential Oil: In Vitro and In Silico Studies
by
Rym Essid, Sarra Kefi, Bilel Damergi, Ghassen Abid, Nadia Fares, Selim Jallouli, Islem Abid, Dina Hussein, Olfa Tabbene and Ferid Limam
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1876; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081876 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
The present study aimed to evaluate the leishmanicidal potential of the essential oil (EO) of Micromeria (M.) nervosa and to investigate its molecular mechanism of action by qPCR. Furthermore, in silicointeraction study of the major M. nervosa EO compounds with the
[...] Read more.
The present study aimed to evaluate the leishmanicidal potential of the essential oil (EO) of Micromeria (M.) nervosa and to investigate its molecular mechanism of action by qPCR. Furthermore, in silicointeraction study of the major M. nervosa EO compounds with the enzyme cytochrome P450 sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51) was also performed. M. nervosa EO was analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Results showed that α-pinene (26.44%), t-cadinol (26.27%), caryophyllene Oxide (7.73 ± 1.04%), and α-Cadinene (3.79 ± 0.12%) are the major compounds of M. nervosa EO. However, limited antioxidant activity was observed, as this EO was ineffective in neutralizing DPPH free radicals and in inhibiting β-carotene bleaching. Interestingly, it displayed effective leishmanicidal potential against promastigote (IC50 of 6.79 and 5.25 μg/mL) and amastigote (IC50 of 8.04 and 7.32 μg/mL) forms of leishmania (L.) infantum and L. major, respectively. Molecular mechanism investigation showed that M. nervosa EO displayed potent inhibition on the thiol regulatory pathway. Furthermore, a docking study of the main components of the EO with cytochrome P450 sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51) enzyme revealed that t-cadinol exhibited the best binding energy values (−7.5 kcal/mol), followed by α-cadinene (−7.3 kcal/mol) and caryophyllene oxide (−7 kcal/mol). These values were notably higher than that of the conventional drug fluconazole showing weaker binding energy (−6.9 kcal/mol). These results suggest that M. nervosa EO could serve as a potent and promising candidate for the development of alternative antileishmanial agent in the treatment of leishmaniasis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bioactive Compounds against Parasite, Bacteria and Related Diseases–2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
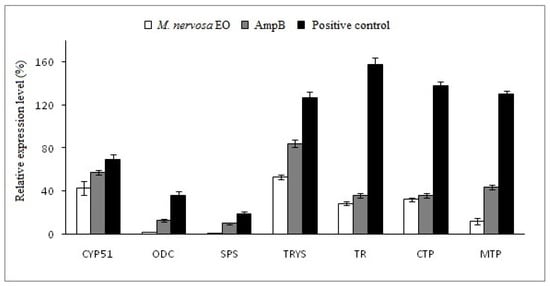
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Recognition Pathway of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain to Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2
by
Can Peng, Xinyue Lv, Zhiqiang Zhang, Jianping Lin and Dongmei Li
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1875; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081875 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2 has spread around the world. The receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is a critical component that directly interacts with host ACE2. Here, we simulate the ACE2 recognition processes of RBD of the WT, Delta, and
[...] Read more.
COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2 has spread around the world. The receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is a critical component that directly interacts with host ACE2. Here, we simulate the ACE2 recognition processes of RBD of the WT, Delta, and OmicronBA.2 variants using our recently developed supervised Gaussian accelerated molecular dynamics (Su-GaMD) approach. We show that RBD recognizes ACE2 through three contact regions (regions I, II, and III), which aligns well with the anchor–locker mechanism. The higher binding free energy in State d of the RBDOmicronBA.2-ACE2 system correlates well with the increased infectivity of OmicronBA.2 in comparison with other variants. For RBDDelta, the T478K mutation affects the first step of recognition, while the L452R mutation, through its nearby Y449, affects the RBDDelta-ACE2 binding in the last step of recognition. For RBDOmicronBA.2, the E484A mutation affects the first step of recognition, the Q493R, N501Y, and Y505H mutations affect the binding free energy in the last step of recognition, mutations in the contact regions affect the recognition directly, and other mutations indirectly affect recognition through dynamic correlations with the contact regions. These results provide theoretical insights for RBD-ACE2 recognition and may facilitate drug design against SARS-CoV-2.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Biomacromolecules)
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis of ω-Chloroalkyl Aryl Ketones via C–C Bond Cleavage of tert-Cycloalkanols with Tetramethylammonium Hypochlorite
by
Natsumi Hanazawa, Masami Kuriyama, Kosuke Yamamoto and Osamu Onomura
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1874; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081874 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
An oxidative C–C bond cleavage of tert-cycloalkanols with tetramethylammonium hypochlorite (TMAOCl) has been developed. TMAOCl is easy to prepare from tetramethylammonium hydroxide, and the combination of TMAOCl and AcOH effectively promoted the C–C bond cleavage in a two-phase system without additional phase-transfer
[...] Read more.
An oxidative C–C bond cleavage of tert-cycloalkanols with tetramethylammonium hypochlorite (TMAOCl) has been developed. TMAOCl is easy to prepare from tetramethylammonium hydroxide, and the combination of TMAOCl and AcOH effectively promoted the C–C bond cleavage in a two-phase system without additional phase-transfer reagents. Unstrained tert-cycloalkanols were transformed into ω-chloroalkyl aryl ketones in moderate to excellent yields under metal-free and mild reaction conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Organic Chemistry)
Open AccessReview
A Comprehensive Review of In Situ Measurement Techniques for Evaluating the Electro-Chemo-Mechanical Behaviors of Battery Electrodes
by
Hainan Jiang, Jie Chen, Xiaolin Li, Zhiyao Jin, Tianjun Chen, Jiahui Liu and Dawei Li
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1873; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081873 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
The global production landscape exhibits a substantial need for efficient and clean energy. Enhancing and advancing energy storage systems are a crucial avenue to optimize energy utilization and mitigate costs. Lithium batteries are the most effective and impressive energy utilization system at present,
[...] Read more.
The global production landscape exhibits a substantial need for efficient and clean energy. Enhancing and advancing energy storage systems are a crucial avenue to optimize energy utilization and mitigate costs. Lithium batteries are the most effective and impressive energy utilization system at present, with good safety, high energy density, excellent cycle performance, and other advantages, occupying most of the market. However, due to the defects in the electrode material of the battery itself, the electrode will undergo the process of expansion, stress evolution, and electrode damage during electro-chemical cycling, which will degrade battery performance. Therefore, the detection of property changes in the electrode during electro-chemical cycling, such as the evolution of stress and the modulus change, are useful for preventing the degradation of lithium-ion batteries. This review presents a current overview of measurement systems applied to the performance detection of batteries’ electrodes, including the multi-beam optical stress sensor (MOSS) measurement system, the digital image correlation (DIC) measurement system, and the bending curvature measurement system (BCMS), which aims to highlight the measurement principles and advantages of the different systems, summarizes a part of the research methods by using each system, and discusses an effective way to improve the battery performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Materials for Emerging Electrochemical Devices)
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Volatile Aroma Components in Different Parts of Shiitake Mushroom (Lentinus edodes) Treated with Ultraviolet C Light-Emitting Diodes Based on Gas Chromatography–Ion Mobility Spectroscopy
by
Daihua Hu, Yulin Wang, Fanshu Kong, Danni Wang, Chingyuan Hu, Xu Yang, Xiaohua Chen, Wang Chen and Zili Feng
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1872; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081872 (registering DOI) - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Further assessment of ultraviolet C light-emitting diode (UVC-LED) irradiation for influencing shiitake mushrooms’ (Lentinus edodes) volatile and sensory properties is needed. In this study, a comparison of UVC-LED irradiation treatment on the flavor profiles in various parts of shiitake mushrooms was
[...] Read more.
Further assessment of ultraviolet C light-emitting diode (UVC-LED) irradiation for influencing shiitake mushrooms’ (Lentinus edodes) volatile and sensory properties is needed. In this study, a comparison of UVC-LED irradiation treatment on the flavor profiles in various parts of shiitake mushrooms was conducted using gas chromatography–ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS) and sensory analysis. Sixty-three volatile compounds were identified in shiitake mushrooms. The fresh shiitake mushrooms were characterized by the highest values of raw mushroom odors. After UVC-LED treatment, the content of C8 alcohols decreased, especially that of 1-octen-3-ol, while the content of aldehydes increased, especially the content of nonanal and decanal. The score of fatty and green odors was enhanced. For fresh samples, the mushroom odors decreased and the mushroom-like odors weakened more sharply when treated in ethanol suspension than when treated with direct irradiation. The fruit odors were enhanced using direct UVC-LED irradiation for fresh mushroom samples and the onion flavor decreased. As for shiitake mushroom powder in ethanol suspension treated with UVC-LED, the sweaty and almond odor scores decreased and the vitamin D2 content in mushroom caps and stems reached 668.79 μg/g (dw) and 399.45 μg/g (dw), respectively. The results obtained from this study demonstrate that UVC-LED treatment produced rich-flavored, quality mushroom products.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Dry Reforming of Methane over Pyrochlore-Type La2Ce2O7-Supported Ni Catalyst: Effect of Particle Size of Support
by
Zeling Zhou, Chao Li, Junfeng Zhang, Qiliang Gao, Jiahao Wang, Qingde Zhang and Yizhuo Han
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1871; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081871 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
The properties of supports (such as oxygen vacancies, oxygen species properties, etc.) significantly impact the anti-carbon ability due to their promotional effect on the activation of CO2 in dry reforming of methane (DRM). Herein, pyrochlore-type La2Ce2O7 compounds
[...] Read more.
The properties of supports (such as oxygen vacancies, oxygen species properties, etc.) significantly impact the anti-carbon ability due to their promotional effect on the activation of CO2 in dry reforming of methane (DRM). Herein, pyrochlore-type La2Ce2O7 compounds prepared using co-precipitation (CP), glycine nitrate combustion (GNC) and sol–gel (S-G) methods, which have highly thermal stability and unique oxygen mobility, are applied as supports to prepare Ni-based catalysts for DRM. The effect of the calcining temperature (500, 600 and 700 °C) on La2Ce2O7(CP) has also been investigated. Based on multi-technique characterizations, it is found that the synthesis method and calcination temperature can influence the particle size of the La2Ce2O7 support. Changes in particle size strongly modulate the pore volume, specific surface area and numbers of surface oxygen vacancies of the La2Ce2O7 support. As a result, the distribution of supported Ni components is affected due to the different metal–support interaction, thereby altering the activity of the catalysts for cracking CH4. Moreover, the supports’ abilities to adsorb and activate CO2 are also adjusted accordingly, accelerating the removal of the carbon deposited on the catalysts. Finally, La2Ce2O7(CP 600) with an appropriate particle size exhibits the best catalytic activity and stability in DRM.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Strategies for Metal Catalysis in Heterogeneous System)
Open AccessArticle
Revealing the Critical Role of Global Electron Density Transfer in the Reaction Rate of Polar Organic Reactions within Molecular Electron Density Theory
by
Luis R. Domingo and Mar Ríos-Gutiérrez
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1870; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081870 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
The critical role of global electron density transfer (GEDT) in increasing the reaction rate of polar organic reactions has been studied within the framework of Molecular Electron Density Theory (MEDT). To this end, the series of the polar Diels–Alder (P-DA) reactions of cyclopentadiene
[...] Read more.
The critical role of global electron density transfer (GEDT) in increasing the reaction rate of polar organic reactions has been studied within the framework of Molecular Electron Density Theory (MEDT). To this end, the series of the polar Diels–Alder (P-DA) reactions of cyclopentadiene with cyanoethylene derivatives, for which experimental kinetic data are available, have been chosen. A complete linear correlation between the computed activation Gibbs free energies and the GEDT taking place at the polar transition state structures (TSs) is found; the higher the GEDT at the TS, the lower the activation Gibbs free energy. An interacting quantum atoms energy partitioning analysis allows for establishing a complete linear correlation between the electronic stabilization of the electrophilic ethylene frameworks and the GEDT taking place at the polar TSs. This finding supports Parr’s proposal for the definition of the electrophilicity ω index. The present MEDT study establishes the critical role of the GEDT in the acceleration of polar reactions, since the electronic stabilization of the electrophilic framework with the electron density gain is greater than the destabilization of the nucleophilic one, making a net favorable electronic contribution to the decrease in the activation energy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Computational and Theoretical Chemistry)
Open AccessArticle
Characterization and Flame-Retardant Properties of Cobalt-Coordinated Cyclic Phosphonitrile in Thermoplastic Polyurethane Composites
by
Xiangcong Zeng, Zhi Xu, Haoxun Li, Yun Xiong, Yigang Ding, Lili Xu and Shengpeng Liu
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1869; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081869 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Halogen-free organophosphorus flame retardants have promising application prospects due to their excellent safety and environmental protection properties. A cobalt-coordinated cyclic phosphonitrile flame retardant (Co@CPA) was synthesized via a hydrothermal method using hexachlorocyclotriphosphonitrile (HCCP), 5-amino-tetrazolium (5-AT), and cobalt nitrate hexahydrate (Co(NO3)2∙6H2O) as starting materials.
[...] Read more.
Halogen-free organophosphorus flame retardants have promising application prospects due to their excellent safety and environmental protection properties. A cobalt-coordinated cyclic phosphonitrile flame retardant (Co@CPA) was synthesized via a hydrothermal method using hexachlorocyclotriphosphonitrile (HCCP), 5-amino-tetrazolium (5-AT), and cobalt nitrate hexahydrate (Co(NO3)2∙6H2O) as starting materials. The structure was characterized using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-NMR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) composites were prepared by incorporating 10-(2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphame-10-oxide (ODOPB), Co@CPA, and silicon dioxide (SiO2) via melt blending. The flame-retardant performance and thermal stability of the TPU composites were evaluated through limiting oxygen index (LOI), vertical combustion (UL-94), TG, and cone calorimetric (CCT) tests. SEM and Raman spectroscopy were used to analyze the surface morphology and structure of the residual carbon. A synergistic flame-retardant effect of ODOPB and Co@CPA was observed, with the most effective flame retardancy achieved at a TPU:ODOPB:Co@CPA:SiO2 ratio of 75:16:8:1. This composition exhibited an LOI value of 26.5% and achieved a V-0 rating in the UL-94 test. Furthermore, compared to pure TPU, the composite showed reductions in total heat release, CO production, and CO2 production by 6.6%, 39.4%, and 48.9%, respectively. Our research findings suggest that Co@CPA demonstrates outstanding performance, with potential for further expansion in application areas. Different metal-based cyclic phosphonitrile compounds are significant in enriching phosphorus-based fine chemicals.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Catalytically Active SiO2 Aerogels Comprising Chelate Complexes of Palladium
by
Nataliya A. Sipyagina, Nikita E. Vlasenko, Alena N. Malkova, Gennady P. Kopitsa, Yulia E. Gorshkova, Sergey Yu. Kottsov and Sergey A. Lermontov
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1868; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081868 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
A series of silica-based aerogels comprising novel bifunctional chelating ligands was prepared. To produce target aerogels, two aminosilanes, namely (3-aminopropyl)trimethoxysilane (APTMS) and N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (AEAPTMS), were acylated by natural amino acids ((S)-(+)-2-phenylglycine or L-phenylalanine), followed by gelation and supercritical drying
[...] Read more.
A series of silica-based aerogels comprising novel bifunctional chelating ligands was prepared. To produce target aerogels, two aminosilanes, namely (3-aminopropyl)trimethoxysilane (APTMS) and N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (AEAPTMS), were acylated by natural amino acids ((S)-(+)-2-phenylglycine or L-phenylalanine), followed by gelation and supercritical drying (SCD). Lithium tetrachloropalladate was used as the metal ion source to prepare strong complexes of Pd2+ with amino acids covalently bonded to a silica matrix. Aerogels bearing chelate complexes retain the Pd2+ oxidation state after supercritical drying in CO2, but the Pd ion is reduced to Pd metal after SCD in isopropanol. Depending on the structure of amino complexes, Pd-containing aerogels showed catalytic activity and selectivity in the hydrogenation reactions of C=C, C≡C and C=O bonds.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Porous Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
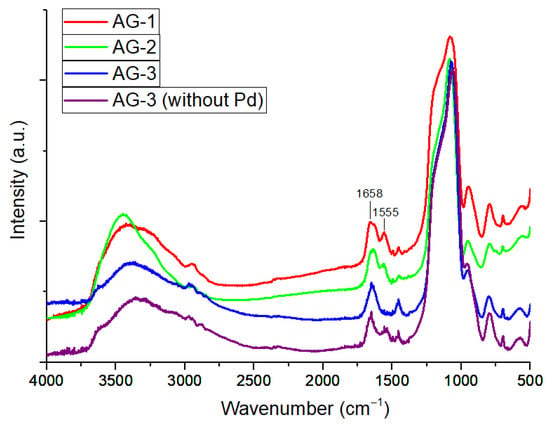
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
NIMO: A Natural Product-Inspired Molecular Generative Model Based on Conditional Transformer
by
Xiaojuan Shen, Tao Zeng, Nianhang Chen, Jiabo Li and Ruibo Wu
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1867; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081867 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Natural products (NPs) have diverse biological activity and significant medicinal value. The structural diversity of NPs is the mainstay of drug discovery. Expanding the chemical space of NPs is an urgent need. Inspired by the concept of fragment-assembled pseudo-natural products, we developed a
[...] Read more.
Natural products (NPs) have diverse biological activity and significant medicinal value. The structural diversity of NPs is the mainstay of drug discovery. Expanding the chemical space of NPs is an urgent need. Inspired by the concept of fragment-assembled pseudo-natural products, we developed a computational tool called NIMO, which is based on the transformer neural network model. NIMO employs two tailor-made motif extraction methods to map a molecular graph into a semantic motif sequence. All these generated motif sequences are used to train our molecular generative models. Various NIMO models were trained under different task scenarios by recognizing syntactic patterns and structure–property relationships. We further explored the performance of NIMO in structure-guided, activity-oriented, and pocket-based molecule generation tasks. Our results show that NIMO had excellent performance for molecule generation from scratch and structure optimization from a scaffold.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Computational Approaches in Drug Discovery and Design)
►▼
Show Figures
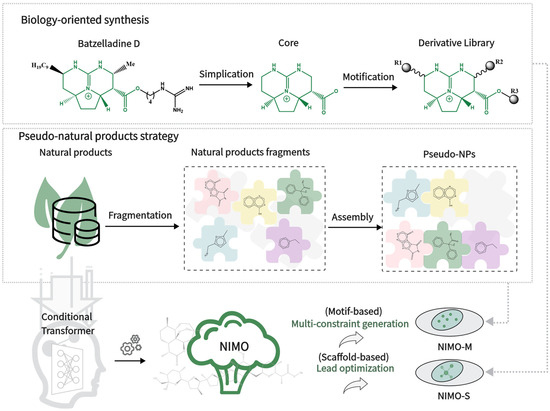
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sesquiterpene Lactones Containing an α-Methylene-γ-Lactone Moiety Selectively Down-Regulate the Expression of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 by Promoting Its Ectodomain Shedding in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells
by
Quy Van Vu, Shinsei Sayama, Masayoshi Ando and Takao Kataoka
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1866; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081866 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Alantolactone is a eudesmane-type sesquiterpene lactone containing an α-methylene-γ-lactone moiety. Previous studies showed that alantolactone inhibits the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway by targeting the inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB) kinase. However, in the present study, we demonstrated that alantolactone selectively down-regulated the
[...] Read more.
Alantolactone is a eudesmane-type sesquiterpene lactone containing an α-methylene-γ-lactone moiety. Previous studies showed that alantolactone inhibits the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway by targeting the inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB) kinase. However, in the present study, we demonstrated that alantolactone selectively down-regulated the expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 1 (TNF-R1) in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Alantolactone did not affect the expression of three adaptor proteins recruited to TNF-R1. The down-regulation of TNF-R1 expression by alantolactone was suppressed by an inhibitor of TNF-α-converting enzyme. Alantolactone increased the soluble forms of TNF-R1 that were released into the culture medium as an ectodomain. The structure–activity relationship of eight eudesmane derivatives revealed that an α-methylene-γ-lactone moiety was needed to promote TNF-R1 ectodomain shedding. In addition, parthenolide and costunolide, two sesquiterpene lactones with an α-methylene-γ-lactone moiety, increased the amount of soluble TNF-R1. Therefore, the present results demonstrate that sesquiterpene lactones with an α-methylene-γ-lactone moiety can down-regulate the expression of TNF-R1 by promoting its ectodomain shedding in A549 cells.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Role of Natural Products in Inflammation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of the Nitrogen Fertilization on the Yield, Biometric Characteristics and Chemical Composition of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni Grown in Poland
by
Joanna Śniegowska, Anita Biesiada and Alan Gasiński
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1865; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081865 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni is a plant native to South America that has gathered much interest in recent decades thanks to diterpene glycosides, called steviosides, which it produces. These compounds are characterised by their sweetness, which is 250–300 times higher than saccharose, and they
[...] Read more.
Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni is a plant native to South America that has gathered much interest in recent decades thanks to diterpene glycosides, called steviosides, which it produces. These compounds are characterised by their sweetness, which is 250–300 times higher than saccharose, and they contain almost no caloric value. Stevia is currently also grown outside the South American continent, in various countries characterised by warm weather. This research aimed to determine whether it is viable to grow Stevia rebaudiana plants in Poland, a country characterised by a cooler climate than the native regions for stevia plants. Additionally, the impact of adding various dosages and forms of nitrogen fertiliser was analysed. It was determined that Stevia rebaudiana grown in Poland is characterised by a rather low concentration of steviosides, although proper nitrogen fertilisation can improve various characteristics of the grown plants. The addition of 100 kg or 150 kg of nitrogen per hectare of the field in the form of urea or ammonium nitrate increased the yield of the stevia plants. The stevioside content can be increased by applying fertilisation using 100 kg or 150 kg of nitrogen per hectare in the form of ammonium sulfate. The total yield of the stevia plants grown in Poland was lower than the yield typically recorded in warmer countries, and the low concentration of steviosides in the plant suggests that more research about growing Stevia rebaudiana in Poland would be needed to develop profitable methods of stevia cultivation.
Full article
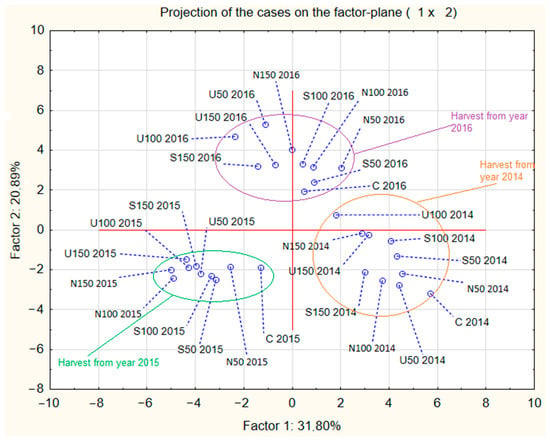
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Moisturizing Effects of Camellia oleifera Oil and Its Potential Applications
by
Lijun Zhou, Yunlan Peng, Zhou Xu, Jingyi Chen, Ningbo Zhang, Tao Liang, Tao Chen, Yao Xiao, Shiling Feng and Chunbang Ding
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1864; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081864 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Camellia oleifera oil (CO oil) extracted from C. oleifera seeds has a 2300-year consumption history in China. However, there is relatively little research regarding its non-edible uses. This study determined the physicochemical properties of CO oil extracted via direct pressing, identified its main
[...] Read more.
Camellia oleifera oil (CO oil) extracted from C. oleifera seeds has a 2300-year consumption history in China. However, there is relatively little research regarding its non-edible uses. This study determined the physicochemical properties of CO oil extracted via direct pressing, identified its main components using GC-MS, and evaluated its antioxidant, moisturizing, and anti-inflammatory activities. The results revealed that CO oil’s acid, peroxide, iodine, and saponification values were 1.06 ± 0.031 mg/g, 0.24 ± 0.01 g/100 g, 65.14 ± 8.22 g/100 g, and 180.41 ± 5.60 mg/g, respectively. CO oil’s tocopherol, polyphenol, and squalene contents were 82.21 ± 9.07 mg/kg, 181.37 ± 3.76 mg/kg, and 53.39 ± 6.58 mg/kg, respectively; its unsaturated fatty acid (UFA) content was 87.44%, and its saturated fatty acid (SFA) content was 12.56%. CO oil also demonstrated excellent moisture retention properties, anti-inflammatory effects, and certain free radical scavenging. A highly stable CO oil emulsion with competent microbiological detection was developed using formulation optimization. Using CO oil in the emulsion significantly improved the formulation’s antioxidant and moisturizing properties compared with those of the emulsion formulation that did not include CO oil. The prepared emulsion was not cytotoxic to cells and could reduce cells’ NO content; therefore, it may have potential nutritional value in medicine and cosmetics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Plant Sourced Compounds: Extraction, Identification and Bioactivity)
►▼
Show Figures
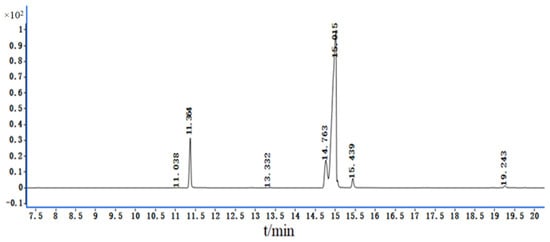
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Chemical Composition of Volatile and Extractive Components of Canary (Tenerife) Propolis
by
Valery A. Isidorov, Andrea M. Dallagnol and Adam Zalewski
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1863; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081863 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
The vegetation of the Canary Islands is characterized by a large number of endemic species confined to different altitudinal levels. It can be assumed that these circumstances determine the characteristic features of the chemical composition of local beekeeping products, including propolis. We report,
[...] Read more.
The vegetation of the Canary Islands is characterized by a large number of endemic species confined to different altitudinal levels. It can be assumed that these circumstances determine the characteristic features of the chemical composition of local beekeeping products, including propolis. We report, for the first time, the chemical composition of propolis from Tenerife (Canary Islands). The volatile emissions of three propolis samples collected from different apiaries are represented by 162 C1–C20 compounds, of which 144 were identified using the HS-SPME/GC-MS technique. The main group of volatiles, consisting of 72 compounds, is formed by terpenoids, which account for 42–68% of the total ion current (TIC) of the chromatograms. The next most numerous groups are formed by C6–C17 alkanes and alkenes (6–32% TIC) and aliphatic C3–C11 carbonyl compounds (7–20% TIC). The volatile emissions also contain C1–C6 aliphatic acids and C2–C8 alcohols, as well as their esters. Peaks of 138 organic C3–C34 compounds were recorded in the chromatograms of the ether extracts of the studied propolis. Terpene compounds form the most numerous group, but their number and content in different samples is within very wide limits (9–63% TIC), which is probably due to the origin of the samples from apiaries located at different altitudes. A peculiarity of the chemical composition of the extractive substances is the almost complete absence of phenylcarboxylic acids and flavonoids, characteristic of Apis mellifera propolis from different regions of Eurasia and North America. Aromatic compounds of propolis from Tenerife are represented by a group of nine isomeric furofuranoid lignans, as well as alkyl- and alkenyl-substituted derivatives of salicylic acid and resorcinol.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Biological Activities and Chemical Composition of Bee Products and Derivatives)
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of Ipsapirone Derivatives Based on Chromatographic and Chemometric Approaches
by
Wiktor Nisterenko, Damian Kułaga, Mateusz Woziński, Yash Raj Singh, Beata Judzińska, Karolina Jagiello, Katarzyna Ewa Greber, Wiesław Sawicki and Krzesimir Ciura
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1862; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081862 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Drug discovery is a challenging process, with many compounds failing to progress due to unmet pharmacokinetic criteria. Lipophilicity is an important physicochemical parameter that affects various pharmacokinetic processes, including absorption, metabolism, and excretion. This study evaluated the lipophilic properties of a library of
[...] Read more.
Drug discovery is a challenging process, with many compounds failing to progress due to unmet pharmacokinetic criteria. Lipophilicity is an important physicochemical parameter that affects various pharmacokinetic processes, including absorption, metabolism, and excretion. This study evaluated the lipophilic properties of a library of ipsapirone derivatives that were previously synthesized to affect dopamine and serotonin receptors. Lipophilicity indices were determined using computational and chromatographic approaches. In addition, the affinity to human serum albumin (HSA) and phospholipids was assessed using biomimetic chromatography protocols. Quantitative Structure–Retention Relationship (QSRR) methodologies were used to determine the impact of theoretical descriptors on experimentally determined properties. A multiple linear regression (MLR) model was calculated to identify the most important features, and genetic algorithms (GAs) were used to assist in the selection of features. The resultant models showed commendable predictive accuracy, minimal error, and good concordance correlation coefficient values of 0.876, 0.149, and 0.930 for the validation group, respectively.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Chromatography and Spectrometry in Food Safety and Pharmaceutical Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures
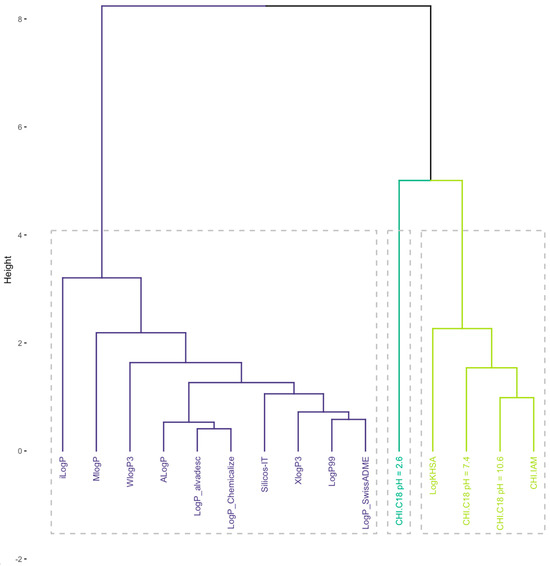
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Study on the Efficient Preparation of α-Ketoglutarate with L-Glutamate Oxidase
by
Shuhui Niu, Fang Liu, Yaping Wang, Ben Rao and Yueying Wang
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1861; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081861 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Alpha-ketoglutaric acid (α-KG), as an intermediate product of the tricarboxylic acid cycle, plays a crucial role in peptide and amino acid synthesis. In order to reduce costs and improve efficiency in the oxidative production of α-ketoglutaric acid, this study successfully synthesized and expressed
[...] Read more.
Alpha-ketoglutaric acid (α-KG), as an intermediate product of the tricarboxylic acid cycle, plays a crucial role in peptide and amino acid synthesis. In order to reduce costs and improve efficiency in the oxidative production of α-ketoglutaric acid, this study successfully synthesized and expressed L-glutamate oxidase (LGOXStr) from Streptomyces viridosporus R111 and catalase (KatGEsc) from Escherichia coli H736. Two immobilization methods and the conditions for one-step whole-cell catalysis of α-ketoglutaric acid were investigated. α-Ketoglutaric acid has broad applications in the pharmaceutical, food, and chemical industries. The specific research results are as follows: (1) By fusing the sfGFP tag, L-glutamate oxidase (LGOXStr r) and catalase (KatGEsc) were successfully anchored to the outer membrane of Escherichia coli cells, achieving one-step whole-cell catalysis of α-ketoglutaric acid with a conversion efficiency of up to 75%. (2) Through the co-immobilization of LGOXStr and KatGEsc, optimization of the preparation parameters of immobilized cells, and exploration of the immobilization method using E.coli@ZIF-8, immobilized cells with conversion rates of over 60% were obtained even after 10 cycles of reuse. Under the optimal conditions, the production rate of α-ketoglutaric acid reached 96.7% in a 12 h reaction, which is 1.1 times that of E. coli@SA and 1.29 times that of free cells.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dissipation and Safety Analysis of Dimethomorph Application in Lychee by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry with QuEChERS
by
Siwei Wang, Xiaonan Wang, Yanping Liu, Qiang He and Hai Tian
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1860; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081860 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study presents a method for analyzing dimethomorph residues in lychee using QuEChERS extraction and HPLC-MS/MS. The validation parameters for this method, which include accuracy, precision, linearity, and recovery, indicate that it meets standard validation requirements. Following first-order kinetics, the dissipation dynamic of
[...] Read more.
This study presents a method for analyzing dimethomorph residues in lychee using QuEChERS extraction and HPLC-MS/MS. The validation parameters for this method, which include accuracy, precision, linearity, and recovery, indicate that it meets standard validation requirements. Following first-order kinetics, the dissipation dynamic of dimethomorph in lychee was determined to range from 6.4 to 9.2 days. Analysis of terminal residues revealed that residues in whole lychee were substantially greater than those in the pulp, indicating that dimethomorph residues are predominantly concentrated in the peel. When applied twice and thrice at two dosage levels with pre-harvest intervals (PHIs) of 5, 7, and 10 days, the terminal residues in whole lychee ranged from 0.092 to 1.99 mg/kg. The terminal residues of the pulp ranged from 0.01 to 0.18 mg/kg, with the residue ratio of whole lychee to pulp consistently exceeding one. The risk quotient (RQ) for dimethomorph, even at the recommended dosage, was less than one, indicating that the potential for damage was negligible. This study contributes to the establishment of maximum residue limits (MRLs) in China by providing essential information on the safe application of dimethomorph in lychee orchards.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Analytical Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Systematic Review of Statins for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Safety, Efficacy, and Mechanism of Action
by
Shiqin Zhang, Xiaoling Ren, Bingzheng Zhang, Tian Lan and Bing Liu
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1859; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081859 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the liver component of a cluster of conditions, while its subtype, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), emerges as a potentially progressive liver disorder that harbors the risk of evolving into cirrhosis and culminating in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). NASH and
[...] Read more.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the liver component of a cluster of conditions, while its subtype, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), emerges as a potentially progressive liver disorder that harbors the risk of evolving into cirrhosis and culminating in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). NASH and cardiovascular disease (CVD) have common risk factors, but compared to liver-related causes, the most common cause of death in NASH patients is CVD. Within the pharmacological armamentarium, statins, celebrated for their lipid-modulating prowess, have now garnered attention for their expansive therapeutic potential in NASH. Evidence from a plethora of studies suggests that statins not only manifest anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties but also impart a multifaceted beneficial impact on hepatic health. In this review, we used “statin”, “NAFLD”, “NASH”, and “CVD” as the major keywords and conducted a literature search using the PubMed and Web of Science databases to determine the safety and efficacy of statins in patients and animals with NASH and NAFLD, and the mechanism of statin therapy for NASH. Simultaneously, we reviewed the important role of the intestinal microbiota in statin therapy for NASH, as it is hoped that statins will provide new insights into modulating the harmful inflammatory microbiota in the gut and reducing systemic inflammation in NASH patients.
Full article
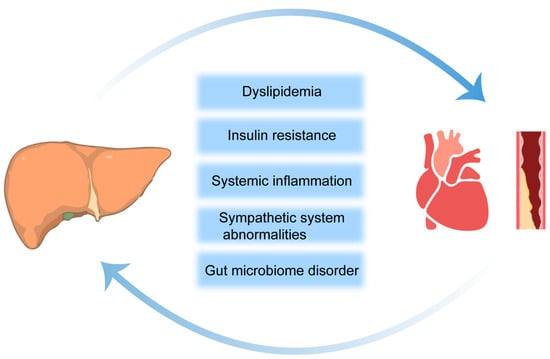
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Recent Progress in Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials for Flame Retardance and Fire-Warning Applications
by
Weiliang Lin, Yao Yuan, Lulu Xu and Wei Wang
Molecules 2024, 29(8), 1858; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081858 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Graphene-like 2D nanomaterials, such as graphene, MXene, molybdenum disulfide, and boron nitride, present a promising avenue for eco-friendly flame retardants. Their inherent characteristics, including metal-like conductivity, high specific surface area, electron transport capacity, and solution processability, make them highly suitable for applications in
[...] Read more.
Graphene-like 2D nanomaterials, such as graphene, MXene, molybdenum disulfide, and boron nitride, present a promising avenue for eco-friendly flame retardants. Their inherent characteristics, including metal-like conductivity, high specific surface area, electron transport capacity, and solution processability, make them highly suitable for applications in both structural fire protection and fire alarm systems. This review offers an up-to-date exploration of advancements in flame retardant composites, utilizing pristine graphene-like nanosheets, versatile graphene-like nanosheets with multiple functions, and collaborative systems based on these nanomaterials. Moreover, graphene-like 2D nanomaterials exhibit considerable potential in the development of early fire alarm systems, enabling timely warnings. This review provides an overview of flame-retarding and fire-warning mechanisms, diverse multifunctional nanocomposites, and the evolving trends in the development of fire alarm systems anchored in graphene-like 2D nanomaterials and their derivatives. Ultimately, the existing challenges and prospective directions for the utilization of graphene-like 2D nanomaterials in flame retardant and fire-warning applications are put forward.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Macromolecular Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
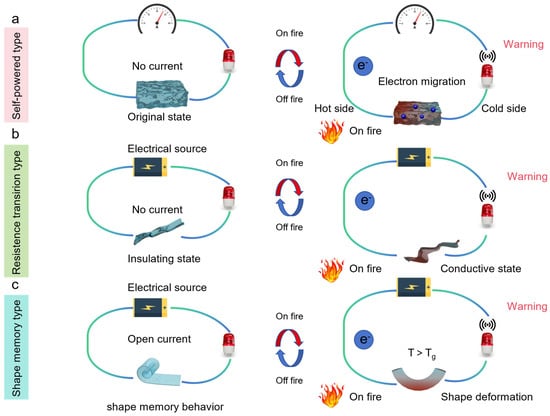
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Molecules Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Vol. 29 (2024)
- Vol. 28 (2023)
- Vol. 27 (2022)
- Vol. 26 (2021)
- Vol. 25 (2020)
- Vol. 24 (2019)
- Vol. 23 (2018)
- Vol. 22 (2017)
- Vol. 21 (2016)
- Vol. 20 (2015)
- Vol. 19 (2014)
- Vol. 18 (2013)
- Vol. 17 (2012)
- Vol. 16 (2011)
- Vol. 15 (2010)
- Vol. 14 (2009)
- Vol. 13 (2008)
- Vol. 12 (2007)
- Vol. 11 (2006)
- Vol. 10 (2005)
- Vol. 9 (2004)
- Vol. 8 (2003)
- Vol. 7 (2002)
- Vol. 6 (2001)
- Vol. 5 (2000)
- Vol. 4 (1999)
- Vol. 3 (1998)
- Vol. 2 (1997)
- Volumes not published by MDPI
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
10 April 2024
Meet Us at the 18th International Symposium on Macrocyclic and Supramolecular Chemistry, 6–10 May 2024, Hangzhou, China
Meet Us at the 18th International Symposium on Macrocyclic and Supramolecular Chemistry, 6–10 May 2024, Hangzhou, China

Topics
Topic in
Antioxidants, IJPB, Molecules, Pharmaceuticals, Plants
Plants Volatile Compounds
Topic Editors: Dario Kremer, Igor Jerković, Valerija DunkićDeadline: 30 April 2024
Topic in
Energies, Molecules, Nanomaterials, Separations, Sustainability
Carbon Capture Science & Technology (CCST)
Topic Editors: Zilong Liu, Meixia Shan, Yakang JinDeadline: 15 May 2024
Topic in
Beverages, Fermentation, Foods, Molecules, Separations
Advances in Analysis of Flavors and Fragrances: Chemistry, Properties and Applications in Food Quality Improvement
Topic Editors: Ana Leahu, Marìa Soledad Prats Moya, Cristina GhineaDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
BioChem, Biomedicines, Biomolecules, IJMS, Metabolites, Molecules
Natural Products in Prevention and Therapy of Metabolic Syndrome
Topic Editors: Jianbo Wan, Ligen LinDeadline: 30 June 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Molecules
Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Halogens
Guest Editors: Grzegorz Mlostoń, Józef Drabowicz, Piotr KiełbasińskiDeadline: 20 April 2024
Special Issue in
Molecules
Modulation and Determination of Lipases Activity
Guest Editor: Silvana CasatiDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
Molecules
Advances in Computational Chemistry for Drug Design, Discovery and Screening
Guest Editors: Shuguang Yuan, Sławomir Filipek, Hideya NakamuraDeadline: 15 May 2024
Special Issue in
Molecules
Plant Secondary Metabolites with Health Effects: Discovery and Engineering
Guest Editors: Giuseppe Dionisio, Vittorio CalabreseDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Ultrasound- and Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Compounds
Collection Editors: Stela Jokić, Jelena Vladić
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Novel Approache of Anticancer Therapy
Collection Editor: Isabelle Mus-Veteau