- Article
Shoulder Muscle Strength Assessment: A Comparative Study of Hand-Held Dynamometers and Load Cell Measurements
- Carla Antonacci,
- Arianna Carnevale and
- Letizia Mancini
- + 6 authors
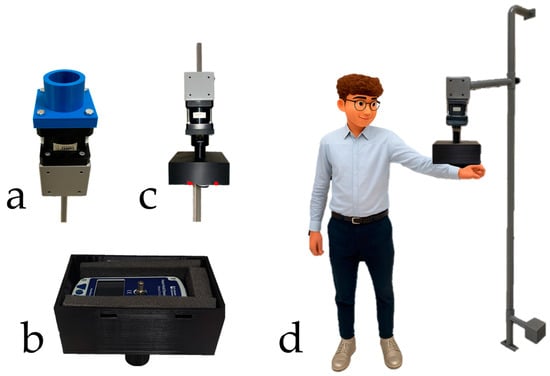
Accurate measurement of shoulder muscle strength is important for diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring recovery. Hand-held dynamometers (HHDs) are widely used in clinical practice but are affected by operator strength, patient positioning, and device stabilization, particularly under high-load conditions. No previous study has directly compared HHD measurements with a reference load cell in a rigid serial configuration or evaluated the effect of different load cell signal processing strategies on the final strength value. The aim of this study was to compare HHD measurements with those obtained from a reference load cell in a rigid serial configuration and to assess how different signal processing strategies applied to load cell data influence the final outcomes. A custom 3D-printed support was developed to align a commercial HHD and a load cell in series, ensuring identical loading conditions. Measurements were performed under two conditions: (i) application of known weights (9.81–98.10 N) and (ii) standardized strength tasks in five healthy volunteers. Agreement between instruments was evaluated using Bland–Altman analysis and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). In static validation (i.e., experiments applying know weights), the load cell demonstrated stable performance, with standard deviations below 1% of the applied load. HHD variability increased with load, with RMSE rising from 0.55 N at 9.81 N to 5.06 N at 98.10 N. In human testing, the HHD consistently underestimated muscle strength compared with the load cell, with mean differences ranging from −15 N to −19 N, over exerted force ranges of approximately 20–90 N. Overall, the load cell provided stable reference measurements, while the choice of signal processing strategy influenced the results: plateau-phase analysis tended to reduce systematic bias but did not consistently narrow the limits of agreement.
20 December 2025