Journal Description
Current Oncology
Current Oncology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal published online by MDPI (from Volume 28 Issue 1-2021). Established in 1994, the journal represents a multidisciplinary medium for clinical oncologists to report and review progress in the management of this disease. The Canadian Association of Medical Oncologists (CAMO), the Canadian Association of Psychosocial Oncology (CAPO), the Canadian Association of General Practitioners in Oncology (CAGPO), the Cell Therapy Transplant Canada (CTTC), the Canadian Leukemia Study Group (CLSG) and others are affiliated with the journal and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Oncology)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Clusters of Oncology: Cancers, Current Oncology, Onco and Targets.
Impact Factor:
3.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
Docetaxel and Ramucirumab as Subsequent Treatment After First-Line Immunotherapy-Based Treatment for Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Study and Literature Review
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 612; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110612 (registering DOI) - 1 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: A combination of docetaxel and ramucirumab represents a standard of care in second-line treatment for patients with advanced NSCLC. Evidence of the regimen’s efficacy is based on the results of the REVEL trial conducted in the pre-immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitors–ICIs) era.
[...] Read more.
Background: A combination of docetaxel and ramucirumab represents a standard of care in second-line treatment for patients with advanced NSCLC. Evidence of the regimen’s efficacy is based on the results of the REVEL trial conducted in the pre-immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitors–ICIs) era. Given the lack of randomized trials after the use of ICIs in front-line therapy, a question remains regarding the impact of the combination when disease progresses after ICI-based therapy. Methods: From 1 January 2018 to 31 December 2024, 55 patients from three oncology centers who had documented progression on ICI-based therapy subsequently received docetaxel/ramucirumab, and we reviewed their outcomes. Results: The studied group’s median progression-free survival (PFS) was 5.8 months, while the median overall survival (OS) was 11.1 months. The objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR) were 42% and 76%, respectively. Patients who had received ICI-based therapy for ≥6 months had a numerically better median PFS and statistically significant OS compared to those who had experienced progression on ICI-based therapy in <6 months. Regarding adverse events (AEs), 92.7% of patients experienced Grade 1–2 AEs, whereas 54.5% experienced Grade ≥ 3 AEs. One death due to GI bleeding was also recorded. Conclusion: Docetaxel/ramucirumab is an acceptable regimen for patients progressing on first-line ICI-based therapies. Our results are in concordance with the REVEL study and other retrospective studies of this combination after ICIs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hype or Hope—Combination Therapies for Lung Cancer)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Neurocognitive and Emotional Outcomes in Childhood Cancer: A Developmental Perspective
by
Antonios I. Christou, Georgia Kalfadeli, Stella Tsermentseli and Flora Bacopoulou
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 611; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110611 (registering DOI) - 1 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Childhood cancer survivors (CCSs) are at heightened risk of long-term neurocognitive and emotional difficulties that can affect educational attainment, social participation, and overall quality of life. These outcomes vary across developmental stages and are influenced by treatment modality, age at diagnosis, and
[...] Read more.
Background: Childhood cancer survivors (CCSs) are at heightened risk of long-term neurocognitive and emotional difficulties that can affect educational attainment, social participation, and overall quality of life. These outcomes vary across developmental stages and are influenced by treatment modality, age at diagnosis, and central nervous system (CNS) involvement. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus, PsycINFO, and Web of Science for articles published between January 2000 and June 2024. Search terms included combinations of “childhood cancer survivors,” “neurocognitive outcomes,” “executive function,” “emotional regulation,” and related MeSH terms. Inclusion criteria required peer-reviewed studies assessing CCS using standardized neuropsychological or emotional measures. Results: Evidence indicates persistent deficits in processing speed, working memory, and higher-order executive functions, with additional challenges in attention and memory. Emotional difficulties, including anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal, were prevalent and often co-occurred with cognitive impairments. Developmental timing of cancer and treatment was a key determinant of outcome. Family functioning, school reintegration support, and broader social environments emerged as important moderators of resilience. Conclusions: CCSs face complex, interrelated cognitive and emotional challenges that warrant early identification and ongoing, developmentally tailored intervention. Integrated approaches combining cognitive remediation and psychosocial support appear most effective. Future research should prioritize longitudinal designs, multi-informant assessments, and culturally sensitive frameworks to inform targeted prevention and rehabilitation strategies. Our synthesis highlights that deficits in processing speed and working memory are most pronounced following CNS-directed therapies during early developmental stages, whereas emotional vulnerabilities such as anxiety and social withdrawal often emerge later in adolescence. Interventions combining cognitive remediation, targeted psychosocial support, and structured school reintegration show the strongest evidence for improving adaptive outcomes. Coordinated survivorship care across healthcare, educational, and family systems is essential to sustain developmental recovery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Quality of Life and Management of Pediatric Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessConference Report
Bridging Gaps in Cancer Pain Care: Barriers, Solutions, and a Path Forward for Integrated Management
by
Marta Gentili, Francesco Cellini, Leonardo Consoletti, Massimo Di Maio, Diego M. M. Fornasari, Gianpaolo Fortini, Marco Krengli, Ernesto Maranzano, Silvia Natoli, Stefano Pergolizzi, Rodolfo Sacco and Luca Giacomelli
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 610; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110610 (registering DOI) - 1 Nov 2025
Abstract
Cancer-related pain remains one of the most frequent and burdensome symptoms in oncology, significantly impairing patients’ quality of life and functional status. Despite advances in treatment and the availability of evidence-based guidelines, pain continues to be undertreated worldwide. In Italy, legislative efforts such
[...] Read more.
Cancer-related pain remains one of the most frequent and burdensome symptoms in oncology, significantly impairing patients’ quality of life and functional status. Despite advances in treatment and the availability of evidence-based guidelines, pain continues to be undertreated worldwide. In Italy, legislative efforts such as Law 38/2010 have not fully translated into consistent clinical practice. On 28 March 2025, a national roundtable held in Rome, Italy, brought together experts from medical oncology, radiation oncology, palliative care, anesthesiology, and pain medicine, representing the main Italian scientific societies involved in oncology and supportive care, to examine the current status of cancer pain management and develop a consensus on actionable priorities. Four key gaps were identified: insufficient education and training of healthcare providers in pain management; fragmented care pathways and limited interdisciplinary integration; lack of clarity regarding professional roles; and challenges in implementing shared diagnostic and therapeutic care pathways (Percorsi Diagnostico Terapeutici Assistenziali). The roundtable proposed coordinated strategies to address these gaps, including expanding interdisciplinary educational initiatives and integrating pain management into undergraduate and specialty curricula; establishing local oncology orientation centers to provide joint, patient-centered assessments; promoting cross-specialty collaboration through congress sessions, educational activities, and practical workshops; and developing adaptable therapeutic frameworks to ensure standardized yet context-sensitive care delivery. This congress report formalizes a joint framework aimed at embedding pain management within comprehensive cancer care. Its implementation will require sustained advocacy, structured education, and alignment of clinical practice with policy support. By addressing these barriers through pragmatic, evidence-informed actions, the proposed strategies aim to optimize timely, integrated, and effective pain care, ultimately improving outcomes for patients with cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Palliative and Supportive Care)
Open AccessArticle
The Relevance of Lymphadenectomy Extension to the Right Paratracheal Space in the Treatment of Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma: A Retrospective Bicentric Study
by
Dina Yazidi, Maarten Vander Kuylen, Meriem Ennaji, Fadi Charara, Issam El Nakadi, Michel Moreau, Maria Galdon Gomez, Laurine Verset and Gabriel Liberale
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 609; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110609 (registering DOI) - 31 Oct 2025
Abstract
The benefit of extensive lymphadenectomy including the right paratracheal station (RPTS) in the upper mediastinum for esophagogastric junction (EGJ) adenocarcinoma remains controversial. Upper mediastinal lymph node (LN) involvement has been associated with esophageal invasion length, representing a potential research area. This study aimed
[...] Read more.
The benefit of extensive lymphadenectomy including the right paratracheal station (RPTS) in the upper mediastinum for esophagogastric junction (EGJ) adenocarcinoma remains controversial. Upper mediastinal lymph node (LN) involvement has been associated with esophageal invasion length, representing a potential research area. This study aimed to assess the rate of RPTS LN involvement in EGJ adenocarcinoma and its correlation with esophageal invasion length, as well as potential impacts on survival and postoperative complications. Patients undergoing two- or three-field esophagectomy with lymphadenectomy extended to the RPTS between 2006 and 2023 were retrospectively included. Patient, tumor, operative, and postoperative data were collected. Among 321 esophagectomies, 147 met inclusion criteria. Median esophageal invasion length was 3 cm. No patients (0%) had LN metastasis in the RPTS, regardless of invasion length (>4 cm or ≤4 cm). Postoperative complications occurred in 41.5% of patients, most commonly weight loss > 10% (29.2%), pleural effusion (21.1%), and infectious pneumonitis (19.7%). Five-year overall and disease-free survival rates were 44% and 29%, respectively. Our findings suggest that extending lymphadenectomy to the right paratracheal space fails to detect lymph node invasion in patients with esophageal invasion greater than or less than 4 cm in patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastrointestinal Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures
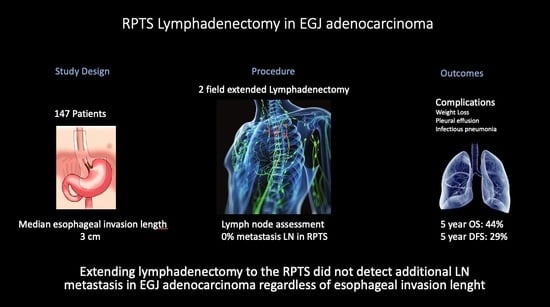
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Endoscopic Stenting for Unresectable Malignant Hilar Biliary Obstruction: Where Do We Stand Today? A Narrative Review
by
Tadahisa Inoue, Itaru Naitoh, Michihiro Yoshida and Fumihiro Okumura
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 608; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110608 (registering DOI) - 31 Oct 2025
Abstract
Malignant hilar biliary obstruction (MHBO) is a complex clinical condition commonly observed in individuals with advanced cholangiocarcinoma and other hepatobiliary malignancies. Endoscopic stenting remains the primary palliative intervention for unresectable cases; however, the optimal strategy has not been clearly defined owing to the
[...] Read more.
Malignant hilar biliary obstruction (MHBO) is a complex clinical condition commonly observed in individuals with advanced cholangiocarcinoma and other hepatobiliary malignancies. Endoscopic stenting remains the primary palliative intervention for unresectable cases; however, the optimal strategy has not been clearly defined owing to the anatomical intricacies of the hilar region and the heterogeneity of disease presentation. This narrative review summarizes current evidence and ongoing debates on functional liver volume-based drainage, unilateral versus bilateral stenting, stent type selection, and above-the-papilla approaches. In addition, we highlight recent progress in endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage as a promising alternative or complementary approach when conventional transpapillary drainage proves inadequate. With recent advances in systemic therapies, including immunotherapy, patient survival has improved, underscoring the need for durable, reintervention-friendly stent strategies. Although uncovered metal stents have long been regarded as the standard for unresectable cases, their limitations in reintervention have prompted renewed consideration of both stent type and drainage technique. Robust prospective studies remain essential to establish standardized, evidence-based guidelines that optimize patient benefit and improve long-term outcomes in unresectable MHBO.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastrointestinal Oncology)
Open AccessArticle
Cytotoxic Effects of Sorafenib, Lapatinib, and Bevacizumab, Alone and in Combination, on Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells
by
Gülşah Altun and Özlem Yönem
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 607; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110607 (registering DOI) - 31 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Medullary thyroid carcinoma is a rare neuroendocrine tumor with limited therapeutic options, as current kinase inhibitors are often associated with significant toxicity and drug resistance. This study aimed to explore novel treatment strategies by testing targeted agents alone and in combination. Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background: Medullary thyroid carcinoma is a rare neuroendocrine tumor with limited therapeutic options, as current kinase inhibitors are often associated with significant toxicity and drug resistance. This study aimed to explore novel treatment strategies by testing targeted agents alone and in combination. Methods: Human medullary thyroid carcinoma TT cells with RET mutations were treated with Sorafenib, Lapatinib, and Bevacizumab. Cell proliferation was monitored in real time using the xCELLigence system, and apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry. Results: Sorafenib and Lapatinib each showed strong, dose-dependent cytotoxic effects, with Lapatinib demonstrating the greatest potency. Bevacizumab alone exhibited minimal cytotoxic activity, but when combined with Sorafenib or Lapatinib it significantly enhanced their effects, even at concentrations that were only partially effective individually. The Lapatinib–Bevacizumab combination produced the most potent inhibition of cell viability, comparable to high-dose monotherapy. Conclusions: These findings suggest that combining kinase inhibitors with Bevacizumab may enhance antitumor activity, allow the use of lower drug doses, and overcome resistance, representing a promising therapeutic strategy for medullary thyroid carcinoma that warrants further investigation in clinical settings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancements in Thyroid Cancer Management)
►▼
Show Figures
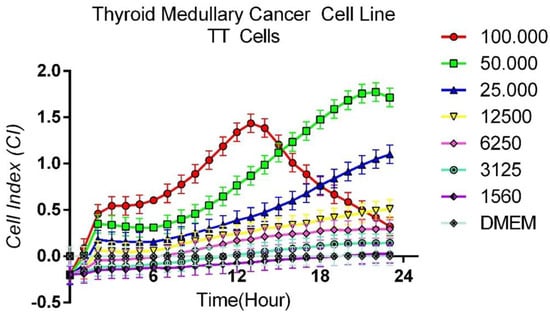
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury and Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Breast Cancer: A Case Report
by
Camilla Lisanti, Serena Della Rossa, Emma Zottarelli, Riccardo Vida, Silvia Bolzonello, Lucia Da Ros, Adrian Zdjelar, Erika Cecchin, Tiziana Perin and Fabio Puglisi
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 606; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110606 (registering DOI) - 31 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) has demonstrated efficacy in HER2-positive and HER2-low breast cancer. Its main safety concern is interstitial lung disease, while clinically relevant hepatotoxicity is rarely reported. In our case report we describe a 49-year-old woman with HER2-positive advanced breast cancer that developed
[...] Read more.
Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) has demonstrated efficacy in HER2-positive and HER2-low breast cancer. Its main safety concern is interstitial lung disease, while clinically relevant hepatotoxicity is rarely reported. In our case report we describe a 49-year-old woman with HER2-positive advanced breast cancer that developed persistent grade 3 transaminase elevations after 2 cycles of T-DXd, refractory to corticosteroid treatment and requiring treatment discontinuation. This case underlines the unpredictable and idiosyncratic nature of T-DXd associated hepatotoxicity and the importance of liver function monitoring. Clinicians should consider DILI in patients with unexplained liver enzyme elevations during therapy. Further studies are needed to clarify mechanisms and risk factors.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Unveiling the Genetic Mosaic of Pediatric AML: Insights from Southwest China
by
Lan Huang, Xingyu Peng, Wenjing Shu, Hui Shi, Li Xiao, Tao Liu, Yan Xiang, Yuxia Guo, Xianmin Guan, Jiacheng Li and Jie Yu
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 605; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110605 - 30 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (pAML) is the second most common type of childhood leukemia, behind acute lymphoblastic leukemia. High-throughput technologies have enabled the identification of increasing molecular alterations linked to AML prognosis, revealing genomic heterogeneity among individual patients and providing clinically valuable
[...] Read more.
Background: Pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (pAML) is the second most common type of childhood leukemia, behind acute lymphoblastic leukemia. High-throughput technologies have enabled the identification of increasing molecular alterations linked to AML prognosis, revealing genomic heterogeneity among individual patients and providing clinically valuable diagnostic and prognostic information. This study systematically analyzed the correlation between high-frequency mutated genes and prognosis in pAML by performing whole-transcriptome sequencing (WTS) of bone marrow samples from newly diagnosed AML children in Southwest China and mapping their genetic profiles. Methods: pAML patients treated at the Department of Hematology and Oncology, Children’s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, from January 2015 to October 2024, were enrolled, and WTS was performed. The study described the frequency, pathogenicity classification, and risk stratification of mutation genes and fusion genes, and constructed a genetic landscape. For high-frequency pAML mutations, the impact on early induction remission rate (CR) and long-term event-free survival (EFS) was evaluated. Results: A total of 134 pediatric AML patients from Southwest China were included, with a male-to-female ratio of 74:60 and a median diagnosis age of 5.96 years. Based on pathogenicity classification using WTS, fusion genes were categorized into level 1, level 2, and level 3 genes, as well as mutation genes. The study identified five fusion genes of level 1, the most frequent being RUNX1::RUNX1T1 (32/134, 23.88%), KMT2A rearrangements (29/134, 21.64%), and CBFB::MYH11 (13/134, 9.7%). Sixteen mutation genes of level 1 were detected, seven of which recurred in over 5% of patients, including NRAS (31/134, 23.13%), FLT3 (25/134, 18.66%), KIT (24/134, 17.91%), CEBPA (14/134, 10.45%), WT1 (13/134, 9.7%), KRAS (11/134, 8.2%), and PTPN11 (7/134, 5.22%). Sex-based analysis revealed that PTPN11 mutations were significantly more frequent in males (9.45% vs. 0%, p = 0.023), as were KIT mutations (24.32% vs. 10.00%, p = 0.044). Risk-stratified analysis showed that WT1 mutations (14.13% vs. 0%, p = 0.031) and FLT3-ITD mutations (13.19% vs. 0%, p = 0.042) were enriched in intermediate- and high-risk groups, whereas CEBPA (25.64% vs. 5.43%, p = 0.012), KIT (35.90% vs. 10.87%, p = 0.003), and KIT-E8 (20.51% vs. 1.10%, p < 0.001) mutations were more prevalent in low-risk groups. Prognostic analysis indicated that PTPN11 and KIT mutations did not affect CR or EFS across sexes, nor did WT1, CEBPA, or KIT mutations influence outcomes by risk stratification. However, FLT3-ITD-positive patients had significantly lower CRs (χ2 value = 11.965, p = 0.007), although EFS differences were nonsignificant. In contrast, WT1 mutations were associated with inferior EFS compared to wild-type (p = 0.036). Furthermore, the univariate and multivariate Cox regression revealed consistent results with the above findings, indicating that WT1 mutation was an independent adverse prognostic factor for EFS (HR = 2.400, 95% CI: 1.101–5.233, p = 0.028). The results of univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses also confirmed that FLT3-ITD mutation was an independent predictor of initial treatment response in our cohort (OR = 10.699, 95% CI: 2.108–54.302, p = 0.004). Conclusions: This study delineated the genetic landscape of pAML in Southwest China and explored the prognostic value of gene fusions and mutations in early and long-term outcomes. These findings provide a foundation for understanding the genetic heterogeneity of pAML and offer evidence for the development of precision medicine approaches.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Hematology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
New Horizons with Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Oncology: From Cancer Cachexia and Tumour Immunity to Novel Therapeutic Strategies
by
Keiji Sugiyama, Naureen Starling and Ian Chau
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 604; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110604 - 29 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) is a stress-induced cytokine produced by tumour cells and peripheral cells. It is implicated in the development of cancer cachexia, a debilitating condition for which no effective pharmacological therapy currently exists. GDF-15 regulates appetite and metabolic processes through
[...] Read more.
Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) is a stress-induced cytokine produced by tumour cells and peripheral cells. It is implicated in the development of cancer cachexia, a debilitating condition for which no effective pharmacological therapy currently exists. GDF-15 regulates appetite and metabolic processes through complex neural and hormonal networks. Furthermore, it has been implicated in chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, representing a potential therapeutic target. GDF-15 negatively affects tumour immunity, suggesting that anti-GDF-15 therapy could potentially enhance immune responses and help overcome resistance to immunotherapy. Recently, early clinical trials have reported preliminary results of GDF-15-targeted therapies in alleviating cancer cachexia and potentially enhancing the efficacy of immunotherapy. This review aims to provide an overview of the role of GDF-15 in cancer cachexia, including the underlying neural mechanisms and their involvement in tumour immunity. This review also summarises recent clinical trial findings and discusses future perspectives on GDF-15-targeted therapy in oncology, offering important insights for future research.
Full article
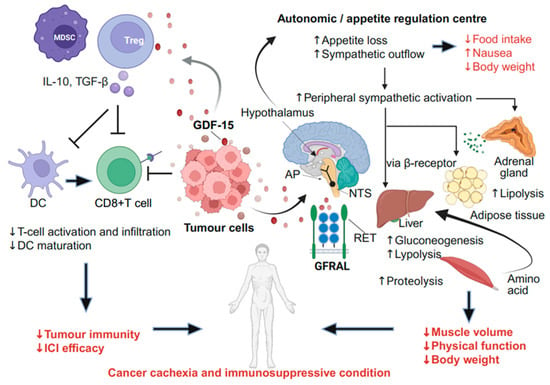
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Predictors of Pathologic Complete Response and Its Prognostic Value in Early Breast Cancer: A Real-World Cohort Study
by
Selami Bayram, Ali Murat Tatli, Muharrem Okan Cakir and Mustafa Ozdogan
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 603; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110603 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Pathologic complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant systemic therapy (NAST) is a key prognostic marker in early breast cancer (EBC), particularly in triple-negative (TNBC) and HER2-positive subtypes. However, real-world data on predictors of pCR and their impact on survival remain limited. Methods: We
[...] Read more.
Background: Pathologic complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant systemic therapy (NAST) is a key prognostic marker in early breast cancer (EBC), particularly in triple-negative (TNBC) and HER2-positive subtypes. However, real-world data on predictors of pCR and their impact on survival remain limited. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 200 patients with stage II–III EBC treated with NAST at a single institution (2015–2023). Clinicopathologic variables and treatment characteristics were evaluated for association with pCR (ypT0/is ypN0), and histological regression was additionally assessed using the Miller–Payne scoring system. Multivariable logistic regression identified independent predictors. Disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were estimated using Kaplan–Meier methods. Results: Overall, 36.0% achieved pCR, with the highest rates in HER2-positive (65%) and TNBC (56%) subtypes. Independent predictors of pCR included HER2 positivity (OR 4.21, 95% CI 1.83–9.67, p < 0.001), high Ki-67 > 47.5% (OR 3.62, 95% CI 1.68–7.80, p = 0.001), ER < 10% (OR 2.77, 95% CI 1.18–6.50, p = 0.019), and radiologic complete response (OR 10.03, 95% CI 2.91–34.60, p < 0.001). At a median follow-up of 75 months, compared with non-pCR, patients achieving pCR had a significantly lower risk of recurrence (HR 0.16, 95% CI 0.04–0.70, p = 0.014) with 5-year DFS rates of 91.5% vs. 72.8%. For OS, pCR patients showed a lower risk of death (HR 0.33, 95% CI 0.07–1.49, p = 0.150), corresponding to 5-year OS of 92.2% vs. 87.0%, although this difference was not statistically significant. Conclusions: HER2 positivity, high Ki-67, low ER expression, and radiologic complete response are independent predictors of pCR. Achieving pCR strongly correlates with improved DFS but not OS, likely due to limited sample size and event number. These findings reinforce pCR as a surrogate endpoint in TNBC and HER2-positive disease and highlight the need for post-neoadjuvant escalation in non-pCR patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Breast Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures
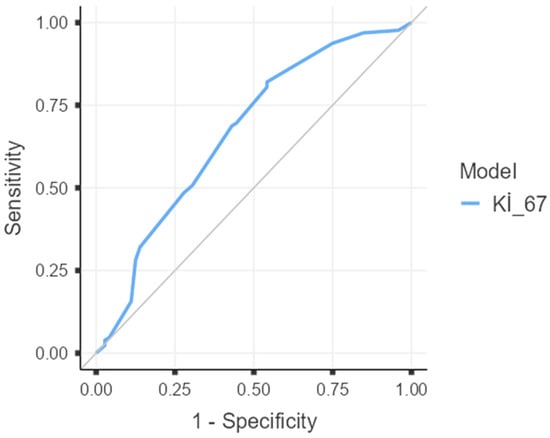
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Machine Learning-Based Prognostic Modelling Using MRI Radiomic Data in Cervical Cancer Treated with Definitive Chemoradiotherapy and Brachytherapy
by
Kamuran Ibis, Mustafa Durmaz, Deniz Yanik, Irem Bunul, Mustafa Denizli, Erkin Akyuz, Bayarmaa Khishigsuren, Ayca Iribas Celik, Merve Gulbiz Dagoglu Kartal, Nezihe Seden Kucucuk, Inci Kizildag Yirgin and Murat Emec
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 602; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110602 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: This study aims to evaluate the contribution of clinical and radiomic features to machine learning-based models for survival prediction in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer. Methods: Clinical and radiomic data from 161 patients were retrospectively collected from a single center. Radiomic
[...] Read more.
Background: This study aims to evaluate the contribution of clinical and radiomic features to machine learning-based models for survival prediction in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer. Methods: Clinical and radiomic data from 161 patients were retrospectively collected from a single center. Radiomic features were obtained from contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T1-weighted (T1W), T2-weighted (T2W), and diffusion-weighted (DWI) sequences. After data cleaning, feature engineering, and scaling, survival prediction models were created using the CatBoost algorithm with different data combinations (clinical, clinical + T1W, clinical + T2W, clinical + DWI). The performance of the models was evaluated using test accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, ROC curve, and Bland–Altman analysis. Results: Models using both clinical and radiomic features showed significant improvements in accuracy and F1-score compared to models based solely on clinical data. In particular, the CatBoost_CLI + T2W_DMFS model achieved the best performance, with a test accuracy of 92.31% and an F1-score of 88.62 for distant metastasis-free survival prediction. ROC and Bland–Altman analyses further demonstrated that this model has high discriminative power and prediction consistency. Conclusions: The CatBoost algorithm shows high accuracy and reliability for survival prediction in locally advanced cervical cancer when clinical and radiomic features are combined. The addition of radiomics data significantly improves model performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Clinical Management of Cervical Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures
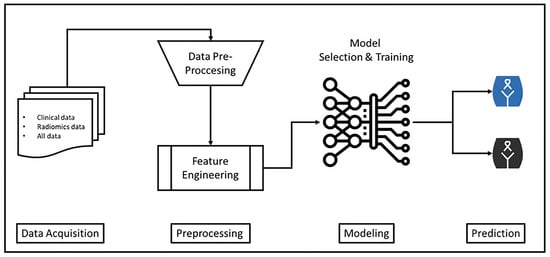
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Retrospective Analysis of Endovascular Stent Insertion for Malignant Superior Vena Cava Obstruction, Focusing on Anticoagulation Practices
by
Joshua Walker, Amsajini Ravinthiranathan, Athanasios Diamantopoulos, Spyridon Gennatas and Alexandros Georgiou
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 601; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110601 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: A knowledge gap persists regarding anticoagulation therapy after endovascular stent insertion for malignant superior vena cava obstruction (mSVCO). Guidelines are supported by retrospective studies with a radiological focus and lack specific drug recommendations. No studies to date have captured the multi-disciplinary nature
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: A knowledge gap persists regarding anticoagulation therapy after endovascular stent insertion for malignant superior vena cava obstruction (mSVCO). Guidelines are supported by retrospective studies with a radiological focus and lack specific drug recommendations. No studies to date have captured the multi-disciplinary nature of decision-making over time. Methods: This single-center retrospective service evaluation includes patients with solid organ malignancy who received a stent for mSVCO between July 2016 and May 2022. Patient and treatment characteristics, clinical outcomes and prescribing decisions were collected from medical records and analyzed. Results: Of 49 patients (55% female, mean age 59), 73% had metastatic extra-thoracic disease at stent insertion. Technical success was achieved in 98% of cases and 92% survived to discharge. Forty-eight patients were followed until death. Median survival was 2.4 months. Post-procedure imaging (performed in 55% of patients) revealed 10 (21%) cases of systemic venous thromboembolism and 7 cases of stent thrombosis. Forty-four (91%) patients received anticoagulation therapy (62% therapeutic dose low molecular weight heparin). Those with thrombotic complications were fitter pre-procedurally than the rest of the cohort. There was one case of major bleeding. Twenty-two instances of therapy modification occurred following the initial plan, including nine changes due to a patient preference for oral therapy. Conclusion: Patients undergoing stenting for mSVCO demonstrate high thrombotic risk and a poor prognosis. Anticoagulation plans are frequently modified post discharge due to changing risk profiles and patient preferences. Multi-disciplinary collaboration is essential to support patient-centered and individualized management. Future research should investigate direct oral anticoagulants and anti-platelet therapy and develop risk assessment tools for this population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Role of Real-World Evidence (RWE) in Thoracic Malignancies)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Advances in Therapeutic Vaccines Against HPV: A Review of Human Clinical Trials
by
Elena Martín, Gabriel Reina and Silvia Carlos
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 600; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110600 - 25 Oct 2025
Abstract
Cervical cancer remains a major public health concern, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) where access to preventive measures is limited. Persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) types, mainly HPV16 and HPV18, is the key cause of cervical cancer. While prophylactic
[...] Read more.
Cervical cancer remains a major public health concern, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) where access to preventive measures is limited. Persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) types, mainly HPV16 and HPV18, is the key cause of cervical cancer. While prophylactic HPV vaccines effectively prevent new infections, they offer no therapeutic benefit for individuals with established lesions. This review evaluates the clinical evidence on therapeutic HPV vaccines, focusing on their ability to promote viral clearance. A bibliographic search was conducted in PubMed, selecting human studies reporting outcomes on HPV clearance. Seventeen clinical trials were identified, including DNA-based (VGX-3100, GX-188E), viral-vector (MVA E2, TG4001), peptide-based (Pepcan), and bacterial-vector (GLT 001) vaccines. Among them, DNA-based vaccines, particularly VGX-3100, showed the most consistent results, whereas several protein- or vector-based approaches demonstrated variable outcomes. Early therapeutic HPV vaccine trials faced setbacks due to limited efficacy, delivery approaches, and study design challenges, preventing progression to late-phase development. Recent DNA-based candidates, however, are advancing through phase II/III trials. While none have yet to be approved for commercial use, these vaccines elicit virus-specific T-cell responses and can induce regression of precancerous lesions, offering a promising addition to prophylactic vaccination and screening. Variability in study designs and endpoints underlines the need for standardized protocols and further phase III trials. Overall, therapeutic HPV vaccines represent a rapidly advancing field with the potential to complement prophylactic vaccination and screening, thereby strengthening global cervical cancer control efforts, particularly in LMICs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gynecologic Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Symptom Reporting Behaviors, Symptom Burden, and Quality of Life in Patients with Hormone Receptor–Positive Breast Cancer Undergoing Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy
by
Ece Ulukal Karanci, Halil Göksel Güzel and Banu Öztürk
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 599; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110599 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Adjuvant endocrine therapy (AET) enhances survival outcomes in hormone receptor–positive (HR+) breast cancer. However, this treatment is associated with toxicities that may adversely affect the quality of life (QoL) and impact patient–physician communication. A thorough understanding of symptom-reporting behaviors is essential
[...] Read more.
Background: Adjuvant endocrine therapy (AET) enhances survival outcomes in hormone receptor–positive (HR+) breast cancer. However, this treatment is associated with toxicities that may adversely affect the quality of life (QoL) and impact patient–physician communication. A thorough understanding of symptom-reporting behaviors is essential for optimizing survivorship care. Methods: This cross-sectional study surveyed 191 female patients with HR+ breast cancer undergoing adjuvant AET (tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors ± ovarian function suppression [OFS]) at Antalya Training and Research Hospital between July and August 2025. QoL, symptom burden, and adverse event (AE) reporting behaviors were assessed using validated instruments (European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire C30 [EORTC QLQ-C30], adapted Patient-Reported Outcomes version of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events [PRO-CTCAE]). Categorical variables were compared using chi-square tests, and multivariate analyses were performed using logistic regression. Results: The median age was 54 years (interquartile range [IQR]: 46–61 years). The following independent variables were identified as predictors of a higher symptom burden: prior chemotherapy (odds ratio [OR]: 3.75; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.46–9.69; p = 0.006), OFS use (OR: 3.29; 95% CI: 1.51–7.15; p = 0.003), AE reporting to physicians (OR: 3.52; 95% CI: 1.80–6.88; p < 0.001), and complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) use (OR: 7.27; 95% CI: 1.57–33.63; p = 0.011). Independent predictors of poor QoL included receiving psychological support (OR: 0.36; 95% CI: 0.19–0.67; p = 0.002) and AE reporting (OR: 0.28; 95% CI: 0.13–0.64; p = 0.001). Conclusions: Symptom burden and QoL in patients with HR+ breast cancer receiving AET are influenced by clinical history, including chemotherapy and OFS; behavioral factors, such as reporting behaviors; and supportive care, including CAM and psychological support. The routine integration of patient-reported outcomes and proactive symptom monitoring is crucial for delivering personalized and effective survivorship care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Breast Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Using the Edmonton Symptom Assessment System (ESAS) to Describe Symptom Burden Associated with Breast Cancer and Related Treatments: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Sofia Torres, Maureen Trudeau, Geoffrey Liu, Nicholas Mitsakakis and Ahmed M. Bayoumi
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 598; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110598 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Symptom burden and functional impairment are common in women with breast cancer, yet their prevalence and clinical significance across the disease spectrum remain underexplored. We sought to describe symptom burden and performance status using patient-reported outcome measures and to identify patient characteristics
[...] Read more.
Background: Symptom burden and functional impairment are common in women with breast cancer, yet their prevalence and clinical significance across the disease spectrum remain underexplored. We sought to describe symptom burden and performance status using patient-reported outcome measures and to identify patient characteristics associated with symptoms requiring clinical intervention. Methods: In this cross-sectional study, women with stage I–IV breast cancer completed the Edmonton Symptom Assessment System (ESAS) and the Patient-Reported Functional Status tool. We assessed the prevalence and severity of symptoms and calculated summary distress scores. Multivariable logistic regression was used to identify patient characteristics associated with clinically significant symptoms (ESAS ≥ 4). Results: Among 381 women (mean age 56.8 years; 27% metastatic; 72% with no comorbidities), 70% reported at least one moderate to severe symptom. The most common were tiredness (31%), lack of well-being (30%), and anxiety (21%). Mean summary distress scores were low overall. Most patients reported functional status scores of 0 or 1, and 43% of those with scores ≥2 had metastatic disease. Compared with metastatic patients, women within the first year after diagnosis were less likely to report a symptom requiring intervention (OR 0.49, 95% CI 0.24–0.90). Conclusions: Clinically significant symptoms are common among women with breast cancer, including those with potentially curable disease. Threshold-based use of ESAS, rather than reliance on mean scores, provides a more accurate assessment of patient needs. These findings support the routine integration of patient-reported outcomes into oncology care and underscore the importance of targeted multidisciplinary interventions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Breast Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Metabolic Imaging as Future Technology and Innovation in Brain-Tumour Surgery: A Systematic Review
by
Thomas Kapapa, Ralph König, Jan Coburger, Benjamin Mayer, Kornelia Kreiser and Volker Rasche
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 597; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110597 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Standard imaging in neurosurgery often fails to visualize infiltrative tumor regions that extend beyond contrast enhancement. Metabolic imaging using hyperpolarized 13C-MRI may offer new intraoperative insights into tumor biology. Objective: To systematically assess the clinical and technical evidence on hyperpolarized MRI for
[...] Read more.
Background: Standard imaging in neurosurgery often fails to visualize infiltrative tumor regions that extend beyond contrast enhancement. Metabolic imaging using hyperpolarized 13C-MRI may offer new intraoperative insights into tumor biology. Objective: To systematically assess the clinical and technical evidence on hyperpolarized MRI for metabolic tumour characterization in patients with malignant brain tumors. Eligibility criteria: We included original human studies reporting on hyperpolarized 13C-MRI for perioperative and diagnostic use in brain tumor patients. Reviews, animal studies, and technical-only reports were excluded. Information sources: Searches were conducted in PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science on 26 December 2024. Risk of bias: Methodological quality was assessed using the QUADAS-2 tool. Synthesis of results: A qualitative synthesis was performed, and where feasible, random-effects meta-analysis was used to calculate standardized mean differences (SMDs) and heterogeneity statistics. Results: Three studies (n = 15 patients) met inclusion criteria. The bicarbonate-to-pyruvate ratio showed a significant difference between tumor and non-tumour brain (SMD = 1.34, p = 0.002), whereas pyruvate-to-lactate ratio (kPL) values showed minimal difference (SMD = 0.06, p = 0.730). Asmall effect was observed for kPL between tumor and normal-appearing white matter (SMD = –0.33). One study provided qualitative data only. Overall heterogeneity was high (I2 = 69.4%). Limitations: Limitations include small sample sizes, heterogeneous methodologies, and limited availability of patient-level data. Interpretation: Hyperpolarized 13C-MRI shows metabolic differentiation between tumor and healthy tissue in certain parameters, especially bicarbonate metabolism. While promising, the technology requires further clinical validation before routine intraoperative application.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Innovations in Brain Tumor Surgery: Techniques and Outcomes)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Exceptional Response to Trastuzumab Deruxtecan (T-DXd) in HER2-Positive Metastatic Endometrial Cancer
by
Riccardo Vida, Michele Bartoletti, Lucia Lerda, Serena Corsetti, Simona Scalone, Anna Calabrò, Angela Caroli, Monica Rizzetto, Giulia Zapelloni, Elisabetta Caccin, Stefano Fucina, Giorgia Bortolin, Sara Cecco, Paolo Baldo, Sandro Pignata, Daniela Califano, Vincenzo Canzonieri, Antonino Ditto and Fabio Puglisi
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 596; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110596 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
Objectives: Endometrial cancer is the most common gynaecologic malignancy, and its mortality rate is rising. Advanced or recurrent disease remains challenging because historically there have been limited therapeutic options. We aim to describe a complete and durable response to the HER2-directed antibody–drug conjugate
[...] Read more.
Objectives: Endometrial cancer is the most common gynaecologic malignancy, and its mortality rate is rising. Advanced or recurrent disease remains challenging because historically there have been limited therapeutic options. We aim to describe a complete and durable response to the HER2-directed antibody–drug conjugate trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) in a heavily pretreated patient with HER2-positive, mismatch-repair-deficient metastatic serous endometrial cancer. Methods: A 72-year-old woman underwent hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and staging procedures for FIGO stage IIIA, high-grade serous papillary endometrial carcinoma. Tumour profiling revealed dMMR, a p53 abnormal pattern, and HER2 overexpression (IHC 3+). She received carboplatin/paclitaxel plus avelumab, followed by pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and weekly paclitaxel. After progression on paclitaxel, off-label T-DXd was initiated. Molecular data (FoundationOne CDx) were collected, along with and serial imaging and CA125 assessments. Results: The patient developed cough after two cycles of T-DXd; interstitial lung disease was excluded, and treatment resumed with steroid cover. By December 2024, PET/CT demonstrated complete metabolic response, with resolution of vaginal-vault and para-aortic lesions and normalisation of CA125. Real-world progression-free survival exceeded eight months, with ongoing symptom improvement. Treatment was generally well tolerated; the principal adverse event was grade 3 neutropenia requiring dose reduction. No cardiotoxicity or interstitial lung disease occurred. Conclusions: This case illustrates that T-DXd can induce deep and durable remission in HER2-positive, dMMR metastatic serous endometrial cancer after multiple lines of therapy. It adds real-world evidence supporting further investigation of HER2-directed antibody–drug conjugates in gynaecologic malignancies, and underscores the need for confirmatory trials and refined biomarker-driven patient selection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gynecologic Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Primary Intracranial Meningeal Melanocytoma with Malignant Transformation: A Case Report and Comparison of Early Versus Late Immunotherapy Interventions
by
Yi-Qi Zhang, Kun-Ming Rau, Cheng-Loong Liang, Yu-Duan Tsai, He-Tai Jheng and Kuo-Wei Wang
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 595; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110595 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
Primary meningeal melanocytoma is an uncommon, pigmented neoplasm that rarely undergoes malignant transformation, and therapeutic guidelines remain undefined. We report a 43-year-old woman who initially presented with a sudden headache and a right temporal intraparenchymal mass. Subtotal resection revealed a melanocytoma (WHO grade
[...] Read more.
Primary meningeal melanocytoma is an uncommon, pigmented neoplasm that rarely undergoes malignant transformation, and therapeutic guidelines remain undefined. We report a 43-year-old woman who initially presented with a sudden headache and a right temporal intraparenchymal mass. Subtotal resection revealed a melanocytoma (WHO grade I); residual tumor was treated with Gamma Knife. About 15 months later, she deteriorated rapidly due to malignant transformation with cerebral hemorrhage and spinal leptomeningeal metastasis. Pembrolizumab was initiated within four weeks of the malignant diagnosis and produced transient neurological improvement. Due to symptomatic progression, ipilimumab plus nivolumab was commenced and achieved temporary radiographic stabilization, but the patient succumbed to diffuse progression later. Including this case, only five intracranial melanocytomas with malignant transformation treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors have been reported. Our experience supports initiating immunotherapy promptly after malignant transformation and suggests that sequential dual-agent blockade may modestly extend disease control.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neuro-Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
HPV Testing, Self-Collection, and Vaccination: A Comprehensive Approach to Cervical Cancer Prevention
by
Shannon Salvador
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 594; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110594 - 23 Oct 2025
Abstract
This white paper, prepared by a consortium of Canadian national and provincial organizations and experts, outlines urgent strategies to curb the rising incidence of HPV-related cancers, of which, cervical cancer is currently the fastest-growing cancer in Canada. Despite school-based vaccination programs, the national
[...] Read more.
This white paper, prepared by a consortium of Canadian national and provincial organizations and experts, outlines urgent strategies to curb the rising incidence of HPV-related cancers, of which, cervical cancer is currently the fastest-growing cancer in Canada. Despite school-based vaccination programs, the national HPV vaccine uptake remains suboptimal at about 64%, far below the 90% coverage target by 2025 necessary to eliminate cervical cancer by 2040. The report emphasizes a multi-pronged approach: support access to HPV vaccination with expanded funding policies and education around school-based programs while addressing inequities in underserved populations. HPV testing is highlighted as the preferred method for cervical cancer screening, offering higher sensitivity than Pap smears. Self-collection is presented as an innovative strategy to reduce barriers, particularly for marginalized groups, with promising evidence from Canadian pilots and international models. Crucially, we call for investment in comprehensive, population-based databases to track vaccination, screening participation, and follow-up care. Robust registries would allow targeted outreach to under- or never-screened individuals, ensure timely follow-up of abnormal results, and measure the impact of prevention programs across Canada. With vaccination, equitable access to HPV testing, integration of self-collection, and strong data systems, Canada can achieve its goal of eliminating cervical cancer within two decades.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Action and Impact: Prevention and Screening Strategies Contributing to the Elimination of Cervical Cancer)
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Hydrocodone Rescheduling on Pain Management Practices Among Older Breast Cancer Patients
by
Chan Shen, Mohammad Ikram, Shouhao Zhou, Roger Klein, Douglas Leslie and James Douglas Thornton
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(11), 593; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110593 - 23 Oct 2025
Abstract
Hydrocodone, a commonly prescribed opioid, was rescheduled from Schedule III to Schedule II in October 2014, imposing stricter prescribing regulations. While prior studies have examined its effects in general populations, its impact on breast cancer patients remains unclear. We evaluated changes in pain
[...] Read more.
Hydrocodone, a commonly prescribed opioid, was rescheduled from Schedule III to Schedule II in October 2014, imposing stricter prescribing regulations. While prior studies have examined its effects in general populations, its impact on breast cancer patients remains unclear. We evaluated changes in pain management among older women with early-stage breast cancer following this policy change. Using SEER-Medicare data from 2011–2019, we identified a retrospective cohort of 52,792 women aged ≥66 years. We assessed trends in the use of hydrocodone, non-hydrocodone opioids, NSAIDs, and antidepressants before and after rescheduling. Hydrocodone use declined from 55% to 40%, while non-hydrocodone opioid use increased from 43% to 50%. Multivariable logistic regression adjusted for demographic and clinical factors confirmed a significant decrease in hydrocodone use (AOR: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.75–0.86) and an increase in non-hydrocodone opioid use (AOR: 1.25, 95% CI: 1.21–1.30). Hydrocodone dosage also declined, while non-hydrocodone opioid dosages remained stable. No significant changes were observed in NSAID or antidepressant use. These findings suggest that hydrocodone rescheduling significantly altered opioid prescribing patterns, reducing hydrocodone use and prompting a shift toward alternative opioids. Further research is warranted to evaluate the appropriateness and outcomes of such shifts in cancer pain management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Breast Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Current Oncology Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Volumes not published by MDPI
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Cancers, IJMS, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Sci. Pharm., Current Oncology, Molecules
Recent Advances in Anticancer Strategies, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Hassan Bousbaa, Zhiwei HuDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Brain Sciences, Cancers, JCM, Neurology International, Diagnostics, Therapeutics, Current Oncology
Innovations in Brain Tumor Surgery: Techniques and Outcomes
Topic Editors: Maria Caffo, Teresa SommaDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Cancers, Current Oncology, JCM, Medicina, Onco
Cancer Biology and Radiation Therapy: 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Chang Ming Charlie Ma, Ka Yu Tse, Ming-Yii Huang, Mukund SeshadriDeadline: 25 July 2026
Topic in
Cancers, Diagnostics, Gastrointestinal Disorders, JCM, Current Oncology
Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: From Laboratory to Clinical Studies, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Ioannis Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, Diamantis I. TsilimigrasDeadline: 20 August 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
Advances in Melanoma: From Pathogenesis to Personalized Therapy
Guest Editor: Patricia TaiDeadline: 14 November 2025
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
Combined Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Guest Editor: Hooman YarmohammadiDeadline: 15 November 2025
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
Therapeutic Studies from Pre-Clinical to Clinical (Phase I–IV) for Gastrointestinal Cancers
Guest Editor: Erica TsangDeadline: 30 November 2025
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
Innovative Therapeutic Strategies, Biomarkers, and Molecular Pathways in Gastrointestinal and Hepatobiliary Cancers
Guest Editors: Anwaar Saeed, Azhar SaeedDeadline: 30 November 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
New Insights into Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Collection Editor: Sazan Rasul
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
New Insights into Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Collection Editors: Filippo Pesapane, Matteo Suter
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series in "Exercise and Cancer Management"
Collection Editors: Linda Denehy, Ravi Mehrotra, Nicole Culos-Reed
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Contemporary Perioperative Concepts in Cancer Surgery
Collection Editors: Vijaya Gottumukkala, Jörg Kleeff











