Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) Agonists and Protein Kinase Regulation in NAFLD and NASH: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of NAFLD/NASH
2.1. Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Dysfunction
2.2. Lipotoxicity and Hepatic Inflammation
2.3. Oxidative Stress in NAFLD/NASH
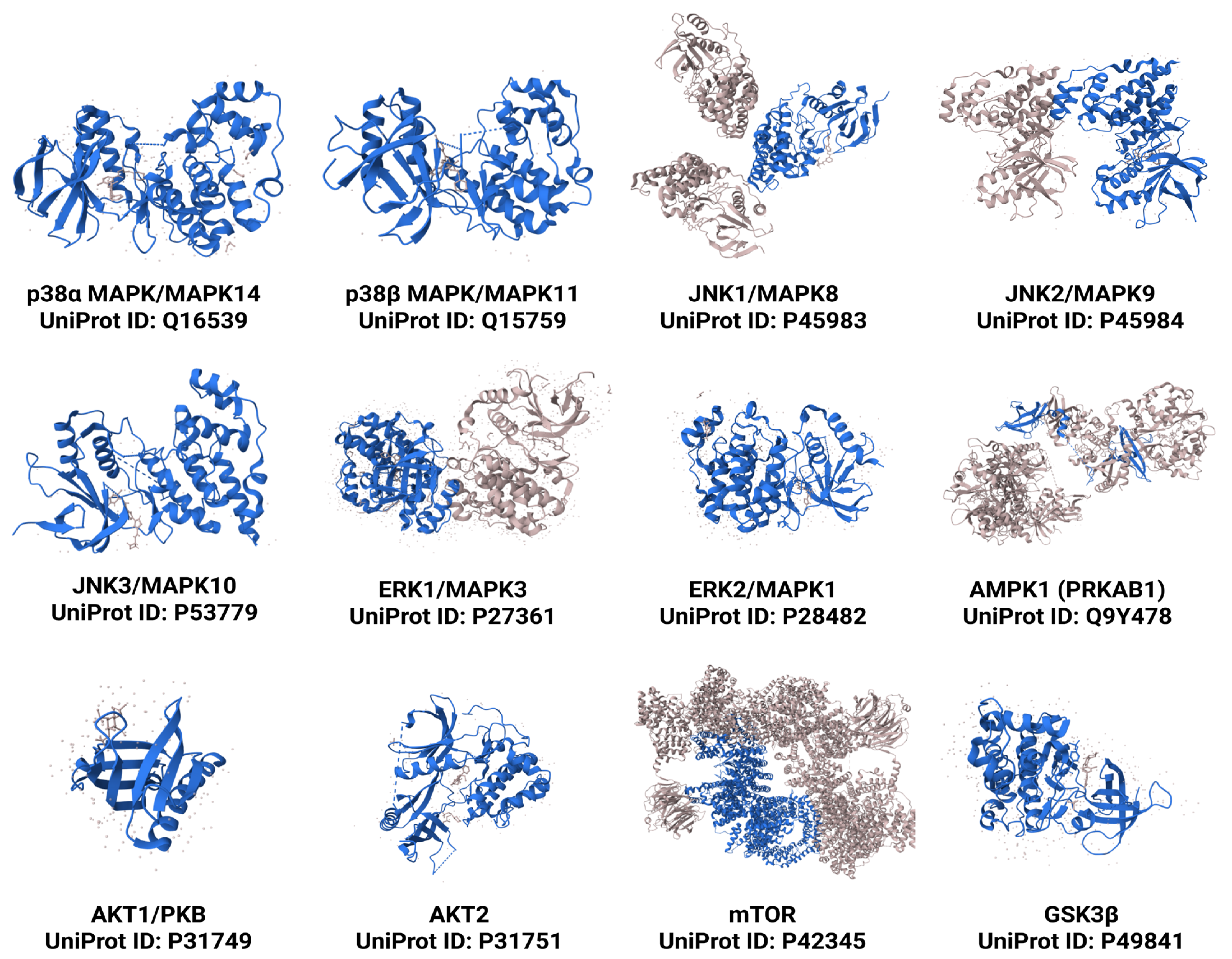
3. Key Protein Kinases in NAFLD and NASH Progression
3.1. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs)
3.2. Protein Kinase C (PKC)
3.3. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK)
3.4. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (PI3K)/AKT Pathway
3.5. Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR)
3.6. Other Kinases Involved in Hepatic Lipid Metabolism
4. FXR Agonists as Therapeutic Agents for NAFLD and NASH
4.1. Mechanism of Action of FXR Agonists
4.1.1. Activation of FXR
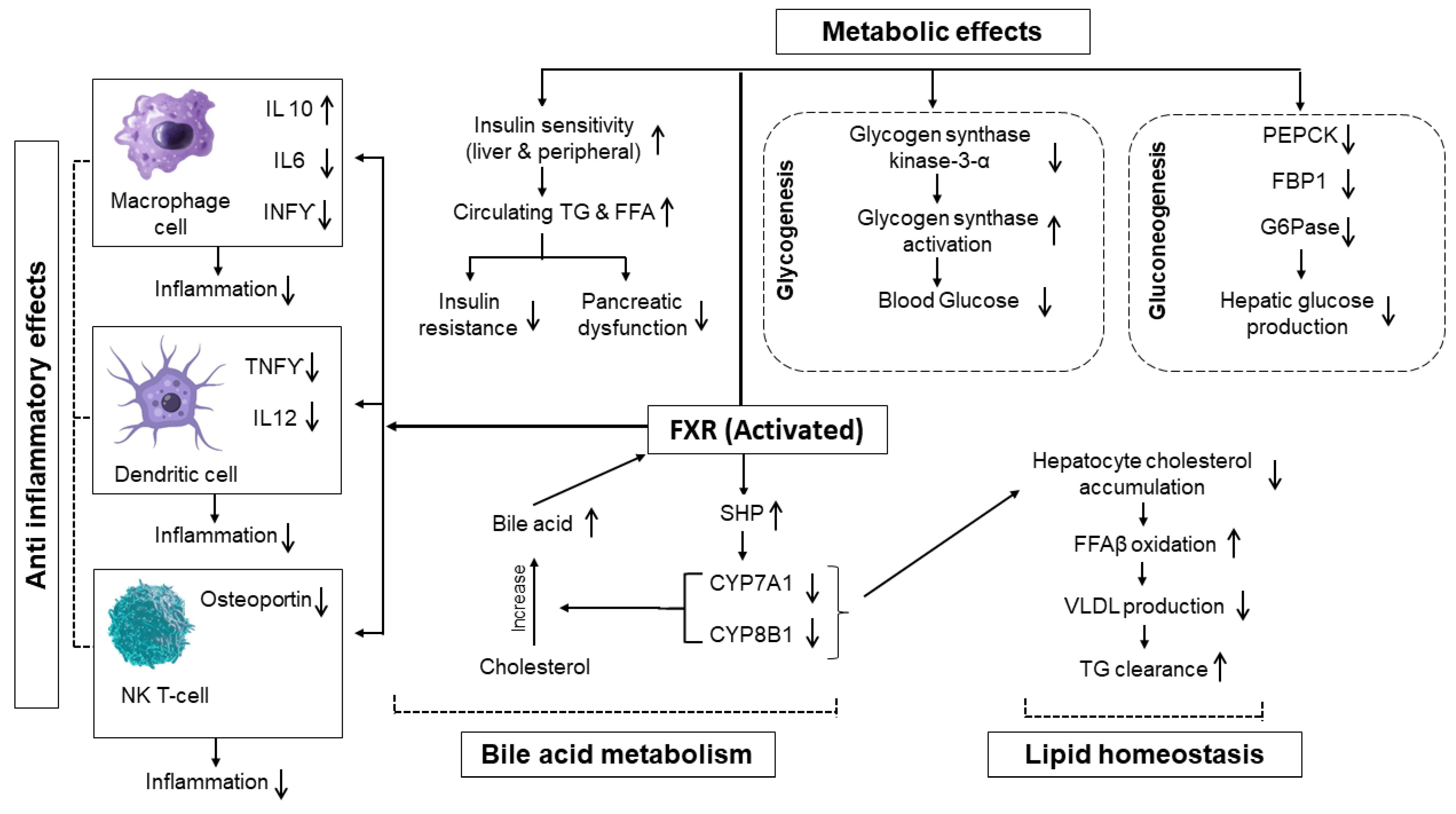
4.1.2. Regulation of Bile Acid Metabolism and Lipid Homeostasis
4.1.3. Anti-Inflammatory and Metabolic Effects
4.1.4. Interplay of FXR, PPARs, and LXRs in NAFLD/NASH Pathogenesis
4.2. Clinical Trials and Evidence Supporting Role of FXR Agonist in NAFLD/NASH
4.2.1. Summary of Key Clinical Trials and Their Outcomes
Obeticholic Acid (OCA)
Cilofexor
EDP305
Tropifexor
MET409 (EYP001)
Vonafexor
INT767
4.2.2. Comparison with Other Therapeutic Agents
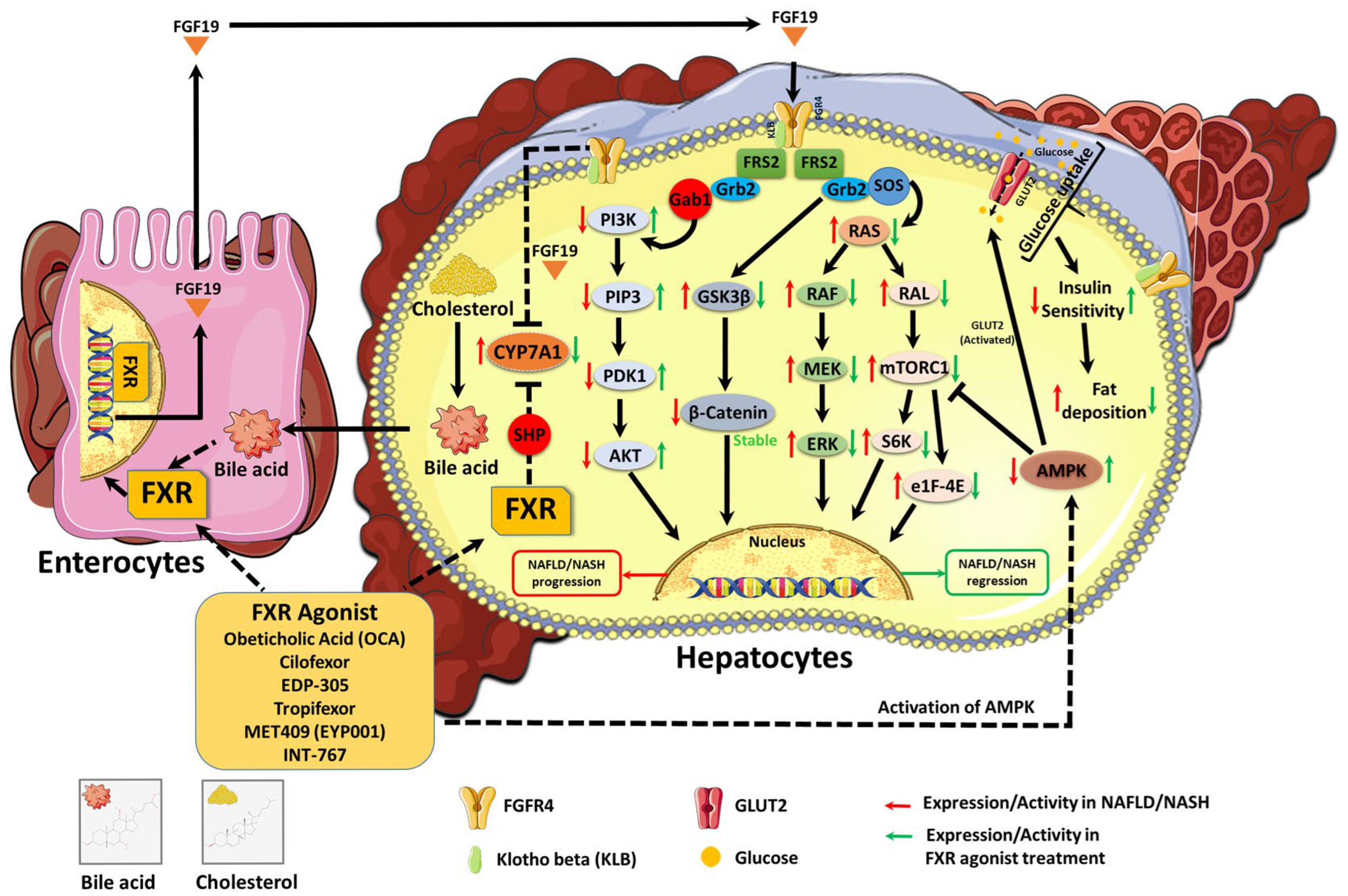
5. FXR Agonists and Protein Kinase Regulation in NAFLD and NASH
5.1. Effect of FXR Agonists on AMPK Activation and Lipid Metabolism
5.2. FXR Agonists’ Role in Modulating MAPK Signaling and Inflammation
5.3. FXR Agonists’ Influence on PI3K/AKT and Insulin Sensitivity
5.4. FXR Agonist and mTOR Pathway in NAFLD/NASH Progression
6. Potential of Combining FXR Agonist with Kinase-Targeting Drugs
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahlapuu, M.; Caputo, M.; Xia, Y.; Cansby, E. GCKIII kinases in lipotoxicity: Roles in NAFLD and beyond. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurice, J.; Manousou, P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanaka, M.; Nishino, K.; Morimoto, Y.; Ishii, K.; Tanikawa, T.; Urata, N.; Suehiro, M.; Sasai, T.; Haruma, K.; Kawamoto, H. Progression from nonalcoholic fatty liver to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis cirrhosis confirmed by liver histology after 14 years. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierantonelli, I.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Basic pathogenetic mechanisms in the progression from NAFLD to NASH. Transplantation 2019, 103, e1–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehade, S.; Alshawsh, M.A.; Murugaiyah, V.; Asif, M.; Alshehade, O.; Almoustafa, H.; Al Zarzour, R.H. The role of protein kinases as key drivers of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease progression: New insights and future directions. Life Sci. 2022, 305, 120732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Häring, H.U.; Cusi, K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecinski, M.; Noetel, A.; Elfimova, N.; Trebicka, J.; Schievenbusch, S.; Strack, I.; Molnar, L.; von Brandenstein, M.; Töx, U.; Nischt, R. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) inhibits collagen I and IV synthesis in hepatic stellate cells by miRNA-29 induction. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. Lipotoxicity and the gut-liver axis in NASH pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Sun, W.; Sun, F.; Yin, G.; Liang, P.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, F. Biological mechanisms and related natural inhibitors of CD36 in nonalcoholic fatty liver. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 3829–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Jin, Z.; Qian, T.; Xu, X.; Zhu, X.; Fei, Q.; Yang, J.; Sui, C.; Xu, M. Falcarindiol enhances cisplatin chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma via down-regulating the STAT3-modulated PTTG1 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 656697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tian, R.; She, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, N.U.; Sheikh, T.A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitase, A.; Hino, K.; Furutani, T.; Okuda, M.; Gondo, T.; Hidaka, I.; Hara, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y. In situ detection of oxidized n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in chronic hepatitis C: Correlation with hepatic steatosis. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 40, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J. Mammalian MAPK signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation: A 10-year update. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 689–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Karin, M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 2001, 410, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirosumi, J.; Tuncman, G.; Chang, L.; Görgün, C.Z.; Uysal, K.T.; Maeda, K.; Karin, M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 2002, 420, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Konstantopoulos, N.; Lee, J.; Hansen, L.; Li, Z.-W.; Karin, M.; Shoelson, S.E. Reversal of obesity-and diet-induced insulin resistance with salicylates or targeted disruption of Ikkβ. Science 2001, 293, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.C. Protein kinase C: Perfectly balanced. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 53, 208–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms for insulin resistance: Common threads and missing links. Cell 2012, 148, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Madiraju, A.K.; Gassaway, B.M.; Marcel, M.; Nasiri, A.R.; Butrico, G.; Marcucci, M.J.; Zhang, D.; Abulizi, A.; Zhang, X.-M. Insulin receptor Thr 1160 phosphorylation mediates lipid-induced hepatic insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 4361–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Qian, M.P.; Cui, Y.Y. Protein kinases: The key contributors in pathogenesis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-derived hepatocellular carcinoma. Metabolism 2023, 147, 155665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Sun, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Luo, W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. AMPK regulates autophagy by phosphorylating BECN1 at threonine 388. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Fang, L.; Chen, F.; Zhong, P.; Zheng, X.; Xing, H.; Fan, R.; Yuan, L.; Peng, W.; Li, X. Targeting AMPK related signaling pathways: A feasible approach for natural herbal medicines to intervene non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 15, 101052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaywitz, A.J.; Courtney, K.D.; Patnaik, A.; Cantley, L.C. PI3K enters beta-testing. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsan, E.; Almezgagi, M.; Gamah, M.; Khan, N.; Qasem, A.; Chuanchuan, L.; Haining, F. The role of PI3k/AKT signaling pathway in attenuating liver fibrosis: A comprehensive review. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1389329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, M.P. Insulin action and resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Bertrand, L.; Pollak, M.; Viollet, B. Metformin: From mechanisms of action to therapies. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Leavens, K.F.; Saleh, D.; Easton, R.M.; Guertin, D.A.; Peterson, T.R.; Kaestner, K.H.; Sabatini, D.M.; Birnbaum, M.J. Postprandial hepatic lipid metabolism requires signaling through Akt2 independent of the transcription factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yecies, J.L.; Zhang, H.H.; Menon, S.; Liu, S.; Yecies, D.; Lipovsky, A.I.; Gorgun, C.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Lee, C.H.; et al. Akt stimulates hepatic SREBP1c and lipogenesis through parallel mTORC1-dependent and independent pathways. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götting, I.; Jendrossek, V.; Matschke, J. A New Twist in Protein Kinase B/AKT Signaling: Role of Altered Cancer Cell Metabolism in AKT-Mediated Therapy Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, W.J.; Jacinto, E. mTOR complex 2 signaling and functions. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 2305–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, K.; Sostre-Colón, J.; Gavin, M.; Santoleri, D.; Leonard, K.-A.; Jacobs, R.L.; Titchenell, P.M. Activation of liver mTORC1 protects against NASH via dual regulation of VLDL-TAG secretion and de novo lipogenesis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 13, 1625–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F.; Hu, F. mTOR signaling in Brown and Beige adipocytes: Implications for thermogenesis and obesity. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphrey, M.B.; Quaim, L.; Rahimi, N.; Varacallo, M. Biochemistry, epidermal growth factor receptor. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Galve-Roperh, I.; Chiurchiù, V.; Díaz-Alonso, J.; Bari, M.; Guzmán, M.; Maccarrone, M. Cannabinoid receptor signaling in progenitor/stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Cai, L.; Jia, X.; Xia, M.; Bian, H.; Gao, X.; Pan, C.; Li, X.; Xia, P. IGFBP2 functions as an endogenous protector against hepatic steatosis via suppression of the EGFR-STAT3 pathway. Mol. Metab. 2024, 89, 102026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, C.; Bedi, O. Proposed hypothesis of GSK-3 β inhibition for stimulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway which triggers liver regeneration process. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2022, 395, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farage, A.E.; Abdo, W.; Osman, A.; Abdel-Kareem, M.A.; Hakami, Z.H.; Alsulimani, A.; Bin-Ammar, A.; Alanazi, A.S.; Alsuwayt, B.; Alanazi, M.M.; et al. Betulin prevents high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by mitigating oxidative stress and upregulating Nrf2 and SIRT1 in rats. Life Sci. 2023, 322, 121688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendel, C.; Schoonjans, K.; Botrugno, O.A.; Treuter, E.; Auwerx, J. The small heterodimer partner interacts with the liver X receptor α and represses its transcriptional activity. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 2065–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Kagal, U. Gene Expression of Cyp7a1 in Liver Tissue of Type 2 Diabetic Rats Treated with Fenugreek and/or Metformin. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2025, 15, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeqdadi, M.; Gordon, F.D. Farnesoid X receptor agonists: A promising therapeutic strategy for gastrointestinal diseases. Gastro Hep Adv. 2024, 3, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, J.Y. Negative feedback regulation of bile acid metabolism: Impact on liver metabolism and diseases. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroonwitchawan, T.; Arimochi, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Ishifune, C.; Kondo, H.; Otsuka, K.; Tsukumo, S.-I.; Yasutomo, K. Stimulation of the farnesoid X receptor promotes M2 macrophage polarization. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1065790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, S.; Gadaleta, R.M.; Moschetta, A. Deciphering the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR paradigm. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2010, 8, e005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braissant, O.; Foufelle, F.; Scotto, C.; Dauca, M.; Wahli, W. Differential expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs): Tissue distribution of PPAR-alpha, -beta, and -gamma in the adult rat. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandard, S.; Muller, M.; Kersten, S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha target genes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girroir, E.E.; Hollingshead, H.E.; He, P.; Zhu, B.; Perdew, G.H.; Peters, J.M. Quantitative expression patterns of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-beta/delta (PPARβ/δ) protein in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 371, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariello, M.; Piccinin, E.; Moschetta, A. Transcriptional regulation of metabolic pathways via lipid-sensing nuclear receptors PPARs, FXR, and LXR in NASH. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 1519–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Han, X.; Bian, Z.; Peng, Y.; You, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Qiu, D.; Ma, X. Activation of liver X receptors attenuates endotoxin-induced liver injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo-Umeda, K.; Makishima, M. Liver X receptors regulate cholesterol metabolism and immunity in hepatic non-parenchymal cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Lavine, J.E.; Van Natta, M.L.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Chalasani, N.; Dasarathy, S.; Diehl, A.M.; Hameed, B. Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pate, J.; Gutierrez, J.A.; Frenette, C.T.; Goel, A.; Kumar, S.; Manch, R.A.; Mena, E.A.; Pockros, P.J.; Satapathy, S.K.; Yimam, K.K.; et al. Practical strategies for pruritus management in the obeticholic acid-treated patient with PBC: Proceedings from the 2018 expert panel. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2019, 6, e000256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Harrison, S.A.; Elkhashab, M.; Trotter, J.F.; Herring, R.; Rojter, S.E.; Kayali, Z.; Wong, V.W.S.; Greenbloom, S.; Jayakumar, S. Cilofexor, a nonsteroidal FXR agonist, in patients with noncirrhotic NASH: A phase 2 randomized controlled trial. Hepatology 2020, 72, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratziu, V.; Rinella, M.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Lawitz, E.; Denham, D.; Kayali, Z.; Sheikh, A.; Kowdley, K.V.; Desta, T.; Elkhashab, M. EDP-305 in patients with NASH: A phase II double-blind placebo-controlled dose-ranging study. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Lopez, P.; Lawitz, E.J.; Lucas, K.J.; Loeffler, J.; Kim, W.; Goh, G.B.; Huang, J.-F.; Serra, C.; Andreone, P. Tropifexor for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: An adaptive, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2a/b trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Harrison, S.A.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Bureau, C.; Lawitz, E.; Abdelmalek, M.; Alkhouri, N.; Francque, S.; Girma, H.; Darteil, R. Hepatic and renal improvements with FXR agonist vonafexor in individuals with suspected fibrotic NASH. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bashir, M.R.; Lee, K.-J.; Shim-Lopez, J.; Lee, J.; Wagner, B.; Smith, N.D.; Chen, H.C.; Lawitz, E.J. A structurally optimized FXR agonist, MET409, reduced liver fat content over 12 weeks in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, D.C.; Rucker, P.V.; Chianelli, D.; Williams, J.; Vidal, A.; Alper, P.B.; Mutnick, D.; Bursulaya, B.; Schmeits, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Discovery of Tropifexor (LJN452), a Highly Potent Non-bile Acid FXR Agonist for the Treatment of Cholestatic Liver Diseases and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 9960–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Z.; Visentin, M.; Gui, T.; Zhao, L.; Thasler, W.E.; Häusler, S.; Hartling, I.; Cremonesi, A.; Hiller, C.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A. Effects of farnesoid X receptor activation on arachidonic acid metabolism, NF-kB signaling, and hepatic inflammation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 94, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorucci, S.; Biagioli, M.; Zampella, A.; Distrutti, E. Bile acids activated receptors regulate innate immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pols, T.W.; Noriega, L.G.; Nomura, M.; Auwerx, J.; Schoonjans, K. The bile acid membrane receptor TGR5 as an emerging target in metabolism and inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Chen, W.D.; Yu, D.; Forman, B.M.; Huang, W. The G-Protein-coupled bile acid receptor, Gpbar1 (TGR5), negatively regulates hepatic inflammatory response through antagonizing nuclear factor kappa light-chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) in mice. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, Q.; Chen, T.; Cao, X.; Wen, C.; Shen, X.; Li, J. A Current Understanding of FXR in NAFLD: The multifaceted regulatory role of FXR and novel lead discovery for drug development. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, B.L.; Sedgeman, L.R.; Williams, K.J.; Morand, P.; Cheng, A.; Jarrett, K.E.; Chan, A.P.; Brearley-Sholto, M.C.; Wahlström, A.; Ashby, J.W. FXR activation protects against NAFLD via bile-acid-dependent reductions in lipid absorption. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1671–1684.e1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.-Y.; Li, Z.-P.; Zhang, L.; Ji, G. Recent insights into farnesoid X receptor in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 13493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Yu, B.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, W.; Zhong, H.; Bai, W.; Yang, Y.; Nie, B. Obeticholic acid induces hepatoxicity via FXR in the NAFLD mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 880508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Poulsen, K.L.; Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Miyata, T.; Song, Q.; Wei, Q.; Zhao, C.; Lin, C.; Yang, J. Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH). Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Kemper, J.K. MicroRNA regulation of AMPK in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1974–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, A.; Yang, X.; Zhen, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Ma, H. Farnesoid X receptor agonist decreases lipid accumulation by promoting hepatic fatty acid oxidation in db/db mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y.; Ferrell, J.M. Bile acid receptors FXR and TGR5 signaling in fatty liver diseases and therapy. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G554–G573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitulo, M.; Gnodi, E.; Rosini, G.; Meneveri, R.; Giovannoni, R.; Barisani, D. Current therapeutical approaches targeting lipid metabolism in NAFLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.A.; Friedman, S.L. Inflammatory and fibrotic mechanisms in NAFLD—Implications for new treatment strategies. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, M.; Samodelov, S.L.; Visentin, M.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A. The farnesoid X receptor as a master regulator of hepatotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Fan, C.; Zhu, C.; Fu, R.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rh4 improves hepatic lipid metabolism and inflammation in a model of NAFLD by targeting the gut liver axis and modulating the FXR signaling pathway. Foods 2023, 12, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Hou, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Cao, H. Microbial Metabolites: Critical Regulators in NAFLD. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 567654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidou, A.I.; Dedoussis, G.V. Construction and analysis of protein-protein interaction network of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 131, 104243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, L. Gene expression profiling reveals key genes and pathways related to the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2016, 15, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.H.; Carey, E.J.; Lindor, K.D. Recent advances in the development of farnesoid X receptor agonists. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y.; Dong, R.; Yang, Y.; Lv, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. The Upstream Pathway of mTOR-Mediated Autophagy in Liver Diseases. Cells 2019, 8, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.Y. Farnesoid X receptor: A master regulator of hepatic triglyceride and glucose homeostasis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Park, C.-Y. Implications for Farnesoid X Receptor Signaling on Bile Acid Metabolism as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Korean J. Obes. 2016, 25, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Butler, A.E.; De Vincentis, A.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Microarray-based Detection of Critical Overexpressed Genes in the Progression of Hepatic Fibrosis in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Protein-protein Interaction Network Analysis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024, 31, 3631–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, M. Current options and future directions for NAFLD and NASH treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, W.; Li, Y.; Xin, Y.; Alsareii, S.A.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D. A synthetic peptide AWRK6 ameliorates metabolic associated fatty liver disease: Involvement of lipid and glucose homeostasis. Peptides 2021, 143, 170597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Light, P.E.; Manning Fox, J.E.; Riedel, M.J.; Wheeler, M.B. Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits pancreatic ATP-sensitive potassium channels via a protein kinase A-and ADP-dependent mechanism. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Dong, Z.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Atorvastatin promotes AMPK signaling to protect against high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver in golden hamsters. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gineste, R.; Sirvent, A.; Paumelle, R.; Helleboid, S.; Aquilina, A.; Darteil, R.; Hum, D.W.; Fruchart, J.-C.; Staels, B. Phosphorylation of farnesoid X receptor by protein kinase C promotes its transcriptional activity. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 2433–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Feng, Q.; Amazit, L.; Lonard, D.M.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.-J.; O’Malley, B.W. Atypical protein kinase C regulates dual pathways for degradation of the oncogenic coactivator SRC-3/AIB1. Mol. Cell 2008, 29, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.-Y.; Lin, H.-Y.; Zhang, S.; Davis, F.B.; Davis, P.J. Thyroid hormone causes mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent phosphorylation of the nuclear estrogen receptor. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 3265–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.; Horan, G.; Bennett, B.; Blease, K.; Ye, Y.; Azaryan, A.; Ramirez-Valle, F.; Ceres, R.; Schafer, P. Late breaking abstract-evaluation of the JNK inhibitor, CC-90001, in a phase 1b pulmonary fibrosis trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50 (Suppl. S61), OA474. [Google Scholar]
- Pockros, P.J.; Fuchs, M.; Freilich, B.; Schiff, E.; Kohli, A.; Lawitz, E.J.; Hellstern, P.A.; Owens-Grillo, J.; Van Biene, C.; Shringarpure, R. CONTROL: A randomized phase 2 study of obeticholic acid and atorvastatin on lipoproteins in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 2082–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Kota, V.G.; Venkat, K.M.; Tasnim, F.; Yu, H. Characteristics of contemporary drug clinical trials regarding the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2024, 18, 102921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Xu, H.; Wu, F.; Tu, Q.; Dong, X.; Xie, H.; Cao, Z. Empagliflozin inhibits macrophage inflammation through AMPK signaling pathway and plays an anti-atherosclerosis role. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 367, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, M. Treatment of liver fibrosis: Past, current, and future. World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.L.; Haynes, W.; Meyers, C.D.; Amer, A.; Zhang, Y.; Mahling, P.; Mendonza, A.E.; Ma, S.; Chutkow, W.; Bachman, E. The effects of licogliflozin, a dual SGLT1/2 inhibitor, on body weight in obese patients with or without diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhouri, N.; Herring, R.; Kabler, H.; Kayali, Z.; Hassanein, T.; Kohli, A.; Huss, R.S.; Zhu, Y.; Billin, A.N.; Damgaard, L.H. Safety and efficacy of combination therapy with semaglutide, cilofexor and firsocostat in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomised, open-label phase II trial. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| FXR Agonist and Structure | Trial Name/Phase/Approval | Mechanism of Action | Adverse Effects | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Obeticholic Acid (OCA) | FLINT Trial (Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled) Accelerated approval (2016) for primary biliary cholangitis, full approval pending |
| Pruritus, ↑ LDL, ↓ HDL cholesterol | [53,54] |
 Cilofexor | Phase II, Randomized Controlled Trial |
| Mild-to-moderate pruritus, GI disturbances | [55] |
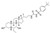 EDP305 EDP305 | Phase II, Dose-Ranging Study |
| Pruritus (dose-dependent) | [56] |
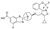 Tropifexor | FLIGHT-FXR, Phase II |
| Pruritus, GI upset, transient ↑ LDL | [57] |
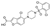 Vonafexor | Phase IIa, Proof-of-Concept Study |
| Mild pruritus, fatigue | [58] |
 MET409 | Phase I/II, Dose-Escalation Study |
| Mild pruritus, headache | [59] |
| Name | FXR Agonist | 2nd Drug | Impact of 2nd Drug on Protein Kinases | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CONTROL Phase 2 (NCT02633956) | Obeticholic Acid (OCA) | Atorvastatin | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor that activates AKT pathway | [93] |
| ELIVATE Phase 2 (NCT04065841) | Tropifexor | Licoglifozin | Indirectly targets multiple kinases | [96] |
| ATLAS Phase 2 (NCT03449446) | Cilofexor | Firsocostat, Selonsertib | Selonsertib inhibiting apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) | [98] |
| Phase 2 (NCT04702490) | MET409 | Empagliflozin | Activates AMPK | [94] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saha, A.; Wood, E.; Omeragic, L.; Minkara, M.; Marma, K.; Gupta, S.D.; Ferdoush, J. Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) Agonists and Protein Kinase Regulation in NAFLD and NASH: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3030016
Saha A, Wood E, Omeragic L, Minkara M, Marma K, Gupta SD, Ferdoush J. Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) Agonists and Protein Kinase Regulation in NAFLD and NASH: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Kinases and Phosphatases. 2025; 3(3):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3030016
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaha, Ayan, Emily Wood, Luna Omeragic, Maya Minkara, Kethain Marma, Shipan Das Gupta, and Jannatul Ferdoush. 2025. "Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) Agonists and Protein Kinase Regulation in NAFLD and NASH: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential" Kinases and Phosphatases 3, no. 3: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3030016
APA StyleSaha, A., Wood, E., Omeragic, L., Minkara, M., Marma, K., Gupta, S. D., & Ferdoush, J. (2025). Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) Agonists and Protein Kinase Regulation in NAFLD and NASH: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Kinases and Phosphatases, 3(3), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3030016






