Abstract
Introduction: Cognitive impairment (CI) is recognized as a very frequent feature of persons with multiple sclerosis (pwMSs). Multiple studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation (CR) in improving CI linked to cerebral functional connectivity facilitation and increased strategies to cope with daily living activities. Nevertheless, there is considerable heterogeneity in the methodologies and protocols proposed to pwMSs. Aim: This study aimed to establish a current state of CR for pwMSs, among different types of healthcare providers (HCPs) in France. Methods: A Web-based survey was conducted between March and September 2024 among HCPs involved in the care of pwMSs. Results: One hundred and one HCPs involved in the care of pwMSs participated in this survey. CR was considered efficient by 97% of HCPs, especially when multimodal. Based on the responses, CR is proposed mainly following cognitive complaints, for moderate or severe cognitive disorders, and at the onset of the disease (45%). HCPs mentioned several obstacles to the implementation of CR, notably the cost of remediation (37%), and the lack of availability of both professionals (58%) and patients (51%). Conclusions: This rehabilitation requires specific tools combined with psychoeducative advice provided by multidisciplinary HCPs.
1. Backgrounds
Cognitive impairment (CI) is recognized as a very frequent and disabling symptom of multiple sclerosis (MS) [1,2,3]. This is linked to a significant decrease in quality of life of patients with MS (pwMSs) as well as that of the caregiver [2,4]. CI, and more specifically slower information processing, which is the earliest and most severe CI in MS, is predictive not only of a higher disability score in the long term but also of the loss of employment [5,6]. As disease onset often occurs between ages 25 and 35, it affects people who have fully developed personal lives and work careers [7,8]. Indeed, MS is the most common neurological disorder causing disability in young and middle-aged adults [9]. CI is observed and may induce work difficulties even at an early stage of the disease [5,10]. A short cognitive battery specific to MS was developed and validated in many languages to harmonize cognitive evaluation internationally: the BICAMS [11]. It was validated into French [12]. As the BICAMS is mainly a screening tool, the procedure for a more complete neuropsychological evaluation in French for MS was described by a consensus produced by a group of experts [13]. The scientific community agrees on the necessity to manage CI in MS in order to prevent their repercussions on patients’ quality of life, as well as the burden and cost for pwMSs and society [14,15,16,17,18]. Pharmacological treatments show only a very limited therapeutic effect on CI in MS [19,20]. Cognitive remediation (CR) is thus the most widely recommended intervention to date, but which CR methodology is the best suited to target CI in MS remains unclear.
1.1. Fundamental Background of Cognitive Rehabilitation in pwMSs
For the cognitive management of pwMSs, three CR techniques are frequently combined [21]: (1) functional reorganization, defined as the use of procedures that the patient did not use before, or used too infrequently, such as the mental imagery strategy to reinforce memorization of a person’s name; (2) exploitation of intact functions, which involves the patient using preserved functions to compensate for impaired ones, such as using visual memory when verbal memory is impaired; and (3) adaptation of exercise conditions, which involves adapting the environment to minimize the impact of disorders on daily life, and proposing compensatory strategies such as external aids like diaries or calendars.
Depending on the type of CI and the patient’s preserved abilities, these different techniques could be combined. It has been shown that both stimulative and compensatory approaches may be efficient [19]. These techniques are developed on the hypothesis of an increase in brain plasticity capacities and the exploitation of cognitive reserve in these patients, to counter the long-term effects of the evolution of the pathophysiological process inherent in MS [22].
1.2. Proof of Concept
CR studies began in the 1990s and increased significantly in the 2010s. A large number of studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of certain techniques and methodologies, mainly in the field of episodic memory, where the implementation of strategies to reinforce encoding for better recall has shown significant results [23,24]. This approach is investigated in ongoing studies considering functional MRI to assess potential modifications and reorganization after CR [25]. About attention, the results are somewhat controversial, which does not seem surprising in this demyelinating pathology [26]. Nevertheless, some data are promising regarding improvements in the speed of information processing and attention through intensive computer-assisted cognitive rehabilitation [27]. Increased mental speed and working memory performances were also reported following two types of intervention, either intensive or distributed, over time [28]. Conversely, it appears that language is rarely assessed and does not seem to be the subject of targeted CR procedures, even though lexical access difficulties and word-finding issues were demonstrated and seem to be a major complaint in pwMSs [29,30].
Some studies have suggested an effect on perceived cognitive impairment rather than an improvement in cognitive performance [31]. Since then, numerous studies and more recent reviews of the literature have demonstrated its effectiveness not only on cognitive disorders measured on tests but also on more ecological tests, with a generalization to activities of daily living, as well as improved quality of life [19,32,33,34,35,36,37]. And, some studies have demonstrated the benefits of CR, with positive effects not only on behavior but also on post-remedial cerebral reorganization and at a distance from the end of CR [38,39].
Nevertheless, there is a degree of critical debate around the methodology used [33,40,41]. Significant heterogeneity of practices appears with computerized programs, single or multi-function programs, whether intensive or over several months. Guidance is needed to develop this practice, the benefits of which appear very promising for pwMSs. Is CR accessible to all MS patients, and which methods and materials are best suited? The aim of this study was to establish a current state of CR for pwMSs in France among different types of healthcare providers (HCPs). More specifically, the objective was to identify the potential barriers to the implementation of this type of rehabilitation.
2. Methods
A Web-based survey was conducted in France between March and September 2024 among HCPs involved in the care of pwMSs. The participants were invited to take the survey through a link on the French MS society (Société Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques: SFSEP) websites. The questionnaire was totally anonymous. General characteristics included profession, place of practice, and region to build up a representative panel of the different professions involved in supporting pwMSs and to identify any regional disparities.
Different subtypes of questions were proposed, such as open questions, multiple forced-choices, or one forced-choice. The first part of the questionnaire included questions on respondents’ socio-demographic characteristics (professional activity, type of practice center, and region), in order to describe the sample of respondents. The second part included questions on the representation of cognitive remediation (Do you think cognitive remediation is effective with pwMSs? How would you provide cognitive remediation support? Do you think that in MS, patients with cognitive complaints or disorders need cognitive remediation?). A third section explored the practice of CR in patients with different demographic and clinical characteristics, which guided the HCP in proposing CR to the patient (When do you propose cognitive remediation to your patient? On what socio-demographic criteria do you propose cognitive remediation to your patient? What clinical criteria do you use to suggest cognitive remediation?). The final section looked at the obstacles encountered by healthcare professionals in proposing cognitive remediation to their patients.
3. Results
A survey was conducted with 101 French HCPs involved in the care of pwMSs, mainly neurologists (45%), speech therapists (23%), neuropsychologists (20%), and physical medicine physicians (10%), practicing mainly in hospitals (56%) and in private practice (nearly 30%). CR in pwMSs is deemed effective by most of the sample (97%).
These HCPs consider that CR should be introduced mainly after the identification of cognitive complaints, for moderate or severe cognitive disorders, and at the onset of the disease (45%) and repeated on an episode-by-episode basis during the patient’s follow-up (66%). This remediation was considered better when multimodal, involving in particular, paper-and-pencil exercises, combined with computerized exercises and advice on learning strategies based on metacognition. Associated with these cognitive exercises, CR, according to this sample, must also be combined with psychoeducation (Figure 1). These results underline the highly multimodal perception of CR and the need to combine different methods in patient management. In addition, these results highlight the importance of metacognitive work with patients to encourage the transfer of acquired skills into activities of daily living.
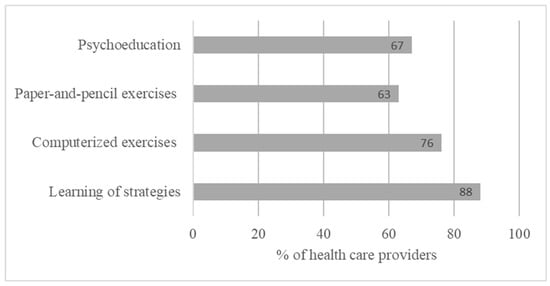
Figure 1.
Methods of cognitive rehabilitation among pwMSs with multiple-choice proposition.
HCPs refer patients for CR mainly based on the presence of a cognitive complaint expressed by the patient (82%), the presence of CI (47%), and the patient’s motivation (88%) and more rarely regarding the duration of the disease (3%) (Figure 2).
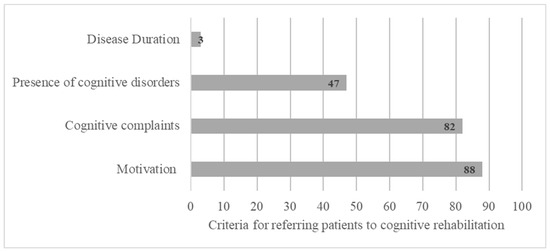
Figure 2.
Criteria for referring patients to cognitive rehabilitation based on open answers.
According to the interviewed participants, CR should be proposed mainly to young or middle-aged patients with an intermediate or higher socio-cultural level and engaged in professional activity (Figure 3).
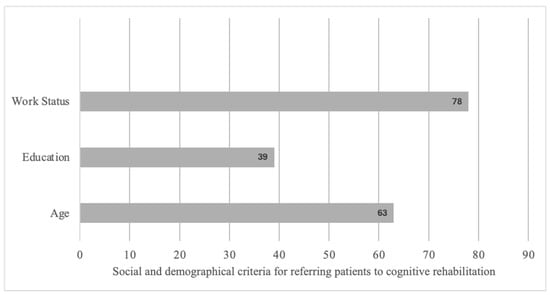
Figure 3.
Social and demographic criteria for referring patients to cognitive rehabilitation based on open answers.
In France, CR for pwMSs is mainly carried out by neuropsychologists in institutions (70%) or by speech therapists (72%), as well as by private neuropsychologists (30%). However, it should be noted that this type of remediation is costly and not well covered by the French healthcare system. Most of this rehabilitation is carried out during individual consultations (97%). However, in one-fifth of cases, rehabilitation is carried out remotely, using telerehabilitation tools.
Indeed, a final section of the questionnaire asking healthcare professionals about the obstacles to implementing CR with patients revealed several obstacles. Healthcare providers indicated several obstacles to the implementation of CR, notably the cost of remediation (37%), and the lack of availability of both professionals (58%) and patients (51%) (Figure 4). This result once again highlights the importance of developing tools that can be accessed remotely by patients, who are often young and working. Healthcare providers also highlighted certain obstacles specific to the patient, such as a lack of motivation (57%) or the severity of cognitive impairment (33%), which could represent an obstacle to the successful pursuit of remediation.
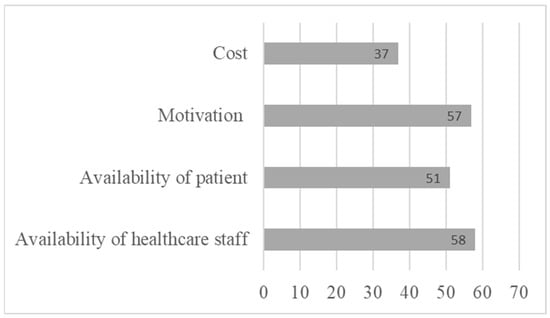
Figure 4.
Limitations to referring patients to cognitive rehabilitation.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to establish a current state of CR for pwMSs in France based on a survey among different types of HCPs. Our sample consisted mainly of hospital-based clinicians, particularly neurologists (45%). This involvement of neurologists in the front-line management of pwMSs confirms the need for these neurologists to be convinced of the effectiveness of CR, in the same way as physical rehabilitation for promoting exercise among pwMSs [42]. Similarly, it is important to be able to propose specific rehabilitation protocols and to suggest guidelines. Approximately 50% of the sample is made up of clinicians directly involved in the remediation of pwMSs, with as many speech therapists as neuropsychologists.
Most of the HCPs consider CR in pwMSs to be effective and necessary. It is perceived as multimodal, involving paper-and-pencil and/or computerized exercises and psychoeducational advice. Personalization of this approach allows for better compliance with CR treatments and encourages the transfer of acquired skills into activities of daily living. This transfer is fostered by metacognitive training. Metacognition was first described by Flavell in 1979 as “cognition about cognition”. In the field of MS neuropsychology and CR, it could be described as the ability to learn how cognition processes in general and more specifically its own cognition (in terms of preserved and impaired mechanisms) to improve this functioning [21,43,44]. The principle is that, by carrying out exercises, the patient gains a better understanding of his or her own functioning and how to adapt to it. CR is not just about performing exercises with a patient. This clinical, global and personalized approach contrasts with the standardized methodology used in clinical trials to assess the clinical efficacy of protocols.
HCPs refer pwMSs for CR mainly based on the presence of a cognitive complaint expressed by the patient (82%), the presence of CI (47%), and the patient’s motivation (88%) and more rarely the disease duration (3%) (Figure 2). Cognitive disorders can be found at disease onset, even at the preclinical stage of the disease [45,46]. However, duration and severity do not appear to be sufficiently reliable clinical factors to predict the presence of CI and the need for CR [47]. Finally, cognitive complaints alone are not predictive of the presence of CI. Hence, it should be considered with caution. Indeed, patients’ cognitive complaints might be associated with the presence of thymic disorders [48,49,50,51] or fatigue [52]. pwMSs with moderate to severe depression tend to underestimate their own cognitive performance, and those with severe cognitive deterioration may overestimate their cognitive functioning due to metacognitive disorders [53]. It is therefore important to reiterate the need for an exhaustive assessment of cognitive functioning to determine the presence of cognitive disorders, right from the initial stage of the disease [13]. Detecting cognitive disorders early and monitoring their development allows for the prescription of neuropsychological interventionist programs and psychological therapies [23,54]. This survey underscores the importance of early intervention with the patient at onset of the disease.
4.1. The Sooner the Better
Some authors highlight the pertinence of starting CR at an early stage of the disease, even before the identification of CI, as a preventive measure [55]. Their hypothesis was made on one hand to postpone the occurrence and increase in CI and on the other hand to intervene early to prevent job loss. Two theoretical concepts support this view and approach. First, it was suggested that objective CI occurs at a breaking point of network collapse as part of the evolution of the disease, particularly in a central brain region like the thalamus [56,57]. Thus, an adapted rehabilitation program like CR could postpone and prevent this collapse of network efficiency that induces CI emergence [58]. Second, the notion of cognitive reserve is now widely recognized to prevent the rise of CI in many degenerative diseases, including MS [22]. Thus, CR could be a way to prevent CI occurrence and worsening by stimulating and maintaining cognitive reserves [56,59]. Indeed, cognitive reserve is not only a predetermined status like educational level, but mainly a dynamic component that may be maintained and increased throughout life by practicing activities like leisure and different types of cognitive exercises. Moreover, psychoeducational advice provided by HCPs may include prompts to practice social and cultural activities that are known to be in favor of cognitive reserve preservation. In this perspective, not only should CR be proposed early but also CR could be pursued over a long period in the context of a chronic disease like MS as a protective measure. Further, when CIs are too severe, CR will mainly consist of proposing compensatory strategies like external aids and environmental adaptations.
4.2. Importance of Specific Tools and Their Accessibility
HCPs stress the importance of being able to rely on specific tools and on professionals specifically trained in the CR of pwMSs. Many tools are available in French such as paper–pen exercises either in group sessions or alone, like ProCog SEP [60], specifically developed for multidomain training specific to MS, or Manag’Mind [61], aimed at working memory training. This survey highlighted challenges in the accessibility of not only CR professionals specialized in MS in terms of time and cost but also the pwMSs themselves. Indeed, pwMSs are often young and professionally active. Furthermore, patients may be living in an isolated geographical region far from hospital or private resources. Many software and mobile apps for CR are accessible online in many languages including French, like Rehacom, Presco, Cognifit, etc. Some specific to MS showed promising results and are currently being tested [62,63,64,65]. Nevertheless, the use of software by the patient alone should be avoid, as psychoeducative and metacognitive advice are needed to foster cognitive improvement [66]. This supervision by HCPs may be provided distantly with tele-consultation.
In this context, the role of new technologies, such as Virtual Reality (VR), represent a promising and useful added value. VR could offer a real alternative for developing rehabilitative tools for pwMSs [67]. Many studies have confirmed the important role of VR in both motor and cognitive rehabilitation (see [68], for a review). A virtual interactive experience increases the self-efficacy, motivation, and interest of pwMSs. Moreover, VR facilitates the transfer of skills to everyday life in similar environments. Some studies have confirmed the important role of VR in CR in pwMSs [69]. Gaming through virtual scenarios is already being used in neurorehabilitation. Two distinctive approaches exist: (i) gaming through Serious Games (SG) or mobile apps, which refers to games that are designed and developed with the express purpose of being rehabilitative of a limited function; (ii) gaming through exergames, which refers to the use of games already available as entertainment for the general population applied in the context of rehabilitation. SG brings the playful and entertaining aspects typical of video games into a “serious” activity to promote notable health objectives [70]. The presence of a game challenge and of long-term goals in SG allow for sustaining the generalization of learnt activities to real life situations more effectively than classical computer-based training. Such devices specifically developed for pwMSs are still rare. However, some clinical trials have successfully tested devices developed in other disease settings on pwMSs [63,71]. New technologies are opening up interesting and motivating avenues for the development of devices to help patients adhere to their CR. Despite the advantages of these devices, they require supervision by a clinician, coupled with face-to-face sessions, to encourage patient compliance.
4.3. Importance of Assessing Intrinsic Motivation
HCPs stress the need to motivate patients to engage in this care, which requires their full participation. This result underscores the importance of working on the patient’s intrinsic motivation to engage in CR, but this is insufficiently assessed in clinical CR practice. Integrating Motivational Interviewing (MI) could be helpful in promoting engagement in CR, fostering adherence to the program, and increasing the effectiveness of cognitive interventions [72,73,74].
pwMSs are more likely to engage in CR with the aim of decreasing the repercussions of their CI on their daily life, while understanding the improvement it could bring to their quality of life. At the beginning of CR, MI encourages the building of therapeutic alliance by assessing pwMSs’ expectations, identifying perceived barriers to CR engagement (e.g., fatigue, stress, and organization), reducing ambivalence to change, and building intrinsic motivation. Then, MI helps to limit discouraged behaviors and promotes long-term adherence to CR. In evidence-based practice approaches [75,76,77], it is important to base CR on internal and external evidence by regularly reviewing the patient’s goals and motivation, considering it may evolve in conjunction with everyday external events. Sometimes, it may be necessary to strengthen the patient’s motivation with MI techniques before working concretely on cognitive exercises. Finally, the results of this survey highlight the importance of individualized CR and the need to adjust therapeutic objectives according to the patient’s progress and the evolution of their goals.
4.4. Limitations
There are some limitations to this survey, besides the size of our sample. It could be interesting to adapt this questionnaire to other languages to diffuse it in other countries, which could permit international comparisons. Also, it would be interesting to analyze whether there are differences in representation depending on profession. In addition, due to the anonymization of participants, we were unable to take into consideration the nature of the care center in which the respondent works or their level of expertise. In France, there are a number of reference centers for the care of MS patients. Clearly, these centers do not have the same resources for patient support. Nonetheless, one of the aims of these centers is to help spread and standardize best practice. Thus, even if there may be a “central” effect on the modality of responses to this questionnaire, this effect should remain negligible. Finally, this survey was broadcasted through the website of the French MS society (Société Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques: SFSEP), which is composed of expert HCPs in MS.
4.5. Perspectives for Cognitive Rehabilitation Among pwMSs
Also, pwMSs must be active participants in their own cognitive care. CR should not be limited to regular cognitive exercises. At the start of CR, patients must understand that they need to invest several months to obtain positive results. The frequency of sessions can be adapted to the patient’s pace of life, and changes will be necessary to reduce the nuisance of cognitive disorders in daily life [28]. Metacognition therefore takes place right at the start of treatment during explanations of how cerebral plasticity works, the cognitive disorders encountered in MS, and how they are dependent on the daily environment. Supports like the one produced in Figure 5 may be used for this purpose. Finally, pwMSs need to understand how the methods proposed by their therapist work, as well as the factors that influence cognitive disorders. In fact, there are other ways to improve cognitive disorders in their entirety: mood management, sleep, physical activity, food, etc. A combination of approaches has shown highly encouraging results, for example, using physical activity [78,79] and the practice of mindfulness in addition to CR, including metacognitive and psychoeducative advice [66]. This multi-dimensional approach is strongly supported by the innovative concept of brain healthcare.
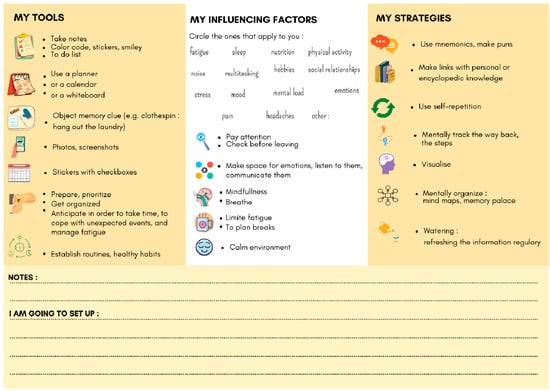
Figure 5.
Dashboard support for metacognitive advice as part of cognitive rehabilitation.
4.6. Guidelines for Cognitive Rehabilitation Among pwMSs Based on This Survey
This survey highlighted aspects that may support guidelines for future perspectives on CR in pwMSs. Initially, cognitive evaluation to identify cognitive impairment and preserved functions should be performed following international and native language specificity, as this survey was produced in French [13,80]. It is important to propose and develop CR tools specific to multiple sclerosis patients, accessible remotely for both patients and clinicians [62,63,64]. To consider and work on motivational aspects is essential because they have a significant impact on patient care and compliance. Holistic patient management is needed, not only focusing on cognitive symptomatology but including psychoeducational advice, taking in account the interactions between the multiple symptoms of MS (e.g., fatigue, sleep, and pain). The brain health concept is a perfect framework for these perspectives on MS CR [81,82,83].
5. Conclusions
The present survey highlights a consistent evolution in the perception of healthcare providers concerning the efficiency and usefulness of adapted cognitive rehabilitation for persons with MS. This rehabilitation requires specific tools combined with psychoeducative advice provided by multidisciplinary healthcare providers. The brain health concept is a promising framework for the future development of cognitive rehabilitation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: H.B., H.J., C.C. and B.L.; Methodology: H.B., C.C. and B.L.; Formal analysis: H.B. and B.L.; Writing—original draft: H.B., H.J., C.C. and B.L.; Writing—review & editing: H.B., H.J., C.C. and B.L.; Supervision: H.B. and B.L.; Project administration: H.B., H.J. and B.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were not applicable for this study, in accordance with French law.
Informed Consent Statement
Participants in this anonymous questionnaire completed a non-objection form co-informed to French law.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this article are available from the corresponding author upon request. The data contain sensitive information and are not publicly available for ethical reasons.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Brochet, B.; Ruet, A. Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis with Regards to Disease Duration and Clinical Phenotypes. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.M.; Leo, G.J.; Ellington, L.; Nauertz, T.; Bernardin, L.; Unverzagt, F. Cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. II. Impact on employment and social functioning. Neurology 1991, 41, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano, L.; Portaccio, E.; Goretti, B.; Niccolai, C.; Severo, M.; Patti, F.; Cilia, S.; Gallo, P.; Grossi, P.; Ghezzi, A.; et al. Age and disability drive cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis across disease subtypes. Mult. Scler. J. 2017, 23, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labiano-Fontcuberta, A.; Mitchell, A.J.; Moreno-García, S.; Benito-León, J. Cognitive impairment in patients with multiple sclerosis predicts worse caregiver’s health-related quality of life. Mult. Scler. J. 2014, 20, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloire, M.; Bonnet, M.; Salort, E.; Arimone, Y.; Boudineau, M.; Petry, K.; Brochet, B. How to detect cognitive dysfunction at early stages of multiple sclerosis? Mult. Scler. J. 2006, 12, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruet, A.; Deloire, M.; Hamel, D.; Ouallet, J.-C.; Petry, K.; Brochet, B. Cognitive impairment, health-related quality of life and vocational status at early stages of multiple sclerosis: A 7-year longitudinal study. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Dishon, S. Health-related quality of life in multiple sclerosis: The impact of disability, gender and employment status. Qual. Life Res. 2006, 15, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hiele, K.; van Gorp, D.A.M.; Heerings, M.A.P.; van Lieshout, I.; Jongen, P.J.; Reneman, M.F.; van der Klink, J.J.L.; Vosman, F.; Middelkoop, H.A.M.; Visser, L.H.; et al. The MS@Work study: A 3-year prospective observational study on factors involved with work participation in patients with relapsing-remitting Multiple Sclerosis. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krokavcova, M.; Nagyova, I.; Van Dijk, J.P.; Rosenberger, J.; Gavelova, M.; Middel, B.; Szilasiova, J.; Gdovinova, Z.; Groothoff, J.W. Self-rated health and employment status in patients with multiple sclerosis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2010, 32, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongen, P.J.; Wesnes, K.; van Geel, B.; Pop, P.; Sanders, E.; Schrijver, H.; Visser, L.H.; Gilhuis, H.J.; Sinnige, L.G.; Brands, A.M.; et al. Relationship between working hours and power of attention, memory, fatigue, depression and self-efficacy one year after diagnosis of clinically isolated syndrome and relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, D.W.; Amato, M.P.; Boringa, J.; Brochet, B.; Foley, F.; Fredrikson, S.; Hämäläinen, P.; Hartung, H.-P.; Krupp, L.; Penner, I.K.; et al. Recommendations for a Brief International Cognitive Assessment for Multiple Sclerosis (BICAMS). Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 18, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maubeuge, N.; Deloire, M.S.A.; Brochet, B.; Ehrlé, N.; Charré-Morin, J.; Saubusse, A.; Ruet, A. French validation of the Brief International Cognitive Assessment for Multiple Sclerosis. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 177, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jougleux, C.; Joly, H.; Brissard, H.; Lenne, B.; François, S.; Hamelin, F.; Derache, N.; Morin, J.; Reuter, F.; Colamarino, R.; et al. French consensus procedure for neuropsychological assessment in multiple sclerosis. Rev. Neurol. (Paris) 2025, 181, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, R.H.B.; Amato, M.P.; DeLuca, J.; Geurts, J.J.G. Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis: Clinical management, MRI, and therapeutic avenues. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaravalloti, N.D.; DeLuca, J. Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakimovski, D.; Bittner, S.; Zivadinov, R.; Morrow, S.A.; Benedict, R.H.; Zipp, F.; Weinstock-Guttman, B. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2024, 403, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobelt, G.; Thompson, A.; Berg, J.; Gannedahl, M.; Eriksson, J.; MSCOI Study Group; European Multiple Sclerosis Platform. New insights into the burden and costs of multiple sclerosis in Europe. Mult. Scler. J. 2017, 23, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meca-Lallana, V.; Gascón-Giménez, F.; Ginestal-López, R.C.; Higueras, Y.; Téllez-Lara, N.; Carreres-Polo, J.; Eichau-Madueño, S.; Romero-Imbroda, J.; Vidal-Jordana, Á.; Pérez-Miralles, F. Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis: Diagnosis and monitoring. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 5183–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Chiaravalloti, N.D.; DeLuca, J. Neurological update: Cognitive rehabilitation in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 4908–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmeyer, N.C.; Bürkner, P.-C.; Wiendl, H.; Ruck, T.; Hartung, H.-P.; Holling, H.; Meuth, S.G.; Johnen, A. Disease-modifying treatments and cognition in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: A meta-analysis. Neurology 2020, 94, e2373–e2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seron, X.; Linden, M.V.d. Traité de Neuropsychologie Clinique de L’adulte: Tome 2—Rééducation, 2nd ed.; DE BOECK SUP: Paris Louvain-la-Neuve (Belgique), France, 2016; 512p. [Google Scholar]
- Sumowski, J.F.; Leavitt, V.M. Cognitive reserve in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2013, 19, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissart, H.; Omorou, A.Y.; Forthoffer, N.; Berger, E.; Moreau, T.; De Seze, J.; Morele, E.; Debouverie, M. Memory improvement in multiple sclerosis after an extensive cognitive rehabilitation program in groups with a multicenter double-blind randomized trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2020, 34, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaravalloti, N.D.; Moore, N.B.; Weber, E.; DeLuca, J. The application of Strategy-based Training to Enhance Memory (STEM) in multiple sclerosis: A pilot RCT. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2021, 31, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaravalloti, N.D.; Weber, E.; Dobryakova, E.; Botticello, A.; Goverover, Y.; Moore, N.B.; DeLuca, J. Kessler Foundation Strategy-Based Training to Enhance Memory (KF-STEMTM): Study protocol for a single site double-blind randomized, clinical trial in Multiple Sclerosis. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2022, 30, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, M.; Goveas, D.; Safi, A.; Marshall, C.; Rosehart, H.; Orenczuk, S.; Morrow, S.A. Does cognitive training improve attention/working memory in persons with MS? A pilot study using the Cogmed Working Memory Training program. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 49, 102770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, F.; Flavia, M.; Stampatori, C.; Zanotti, D.; Parrinello, G.; Capra, R. Efficacy and specificity of intensive cognitive rehabilitation of attention and executive functions in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 288, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, A.; Kappos, L.; Calabrese, P.; Stöcklin, M.; Gschwind, L.; Opwis, K.; Penner, I.-K. Working memory training in patients with multiple sclerosis—comparison of two different training schedules. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2009, 27, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandstadter, R.; Fabian, M.; Leavitt, V.M.; Krieger, S.; Yeshokumar, A.; Katz Sand, I.; Klineova, S.; Riley, C.S.; Lewis, C.; Pelle, G.; et al. Word-finding difficulty is a prevalent disease-related deficit in early multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 1752–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, H.; Cohen, M.; Lebrun, C. Demonstration of a lexical access deficit in relapsing-remitting and secondary progressive forms of multiple sclerosis. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 170, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäntynen, A.; Rosti-Otajärvi, E.; Koivisto, K.; Lilja, A.; Huhtala, H.; Hämäläinen, P. Neuropsychological rehabilitation does not improve cognitive performance but reduces perceived cognitive deficits in patients with multiple sclerosis: A randomised, controlled, multi-centre trial. Mult. Scler. J. 2014, 20, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissart, H.; Leroy, M.; Morele, E.; Baumann, C.; Spitz, E.; Debouverie, M. Cognitive rehabilitation in multiple sclerosis. Neurocase 2013, 19, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brochet, B. Cognitive Rehabilitation in Multiple Sclerosis in the Period from 2013 and 2021: A Narrative Review. Brain Sci. 2021, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- das Nair, R.; Ferguson, H.; Stark, D.L.; Lincoln, N.B. Memory Rehabilitation for people with multiple sclerosis. In Cochrane Collaboration; das Nair, R., Ed.; Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews [Internet]; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lamargue, D.; Koubiyr, I.; Deloire, M.; Saubusse, A.; Charre-Morin, J.; Moroso, A.; Coupé, P.; Brochet, B.; Ruet, A. Effect of cognitive rehabilitation on neuropsychological and semiecological testing and on daily cognitive functioning in multiple sclerosis: The REACTIV randomized controlled study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 415, 116929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munger, K.C.; Martinez, A.P.; Hyland, M.H. The impact of cognitive rehabilitation on quality of life in multiple sclerosis: A pilot study. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2021, 7, 20552173211040239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.; Mhizha-Murira, J.; Law, G.; Evangelou, N.; Das Nair, R. Understanding who benefits most from cognitive rehabilitation for multiple sclerosis: A secondary data analysis. Mult. Scler. J. 2023, 29, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaravalloti, N.D.; Genova, H.M.; DeLuca, J. Cognitive Rehabilitation in Multiple Sclerosis: The Role of Plasticity. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobryakova, E.; Wylie, G.R.; DeLuca, J.; Chiaravalloti, N.D. A pilot study examining functional brain activity 6 months after memory retraining in MS: The MEMREHAB trial. Brain Imaging Behav. 2014, 8, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampit, A.; Heine, J.; Finke, C.; Barnett, M.H.; Valenzuela, M.; Wolf, A.; Leung, I.H.K.; Hill, N.T.M. Computerized Cognitive Training in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Neurorehabilit. Neural. Repair. 2019, 33, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosti-Otajärvi, E.M.; Hämäläinen, P.I. Neuropsychological rehabilitation for multiple sclerosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 2, CD009131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learmonth, Y.C.; Adamson, B.C.; Balto, J.M.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Molina-Guzman, I.M.; Finlayson, M.; Barstow, E.A.; Motl, R.W. Investigating the needs and wants of healthcare providers for promoting exercise in persons with multiple sclerosis: A qualitative study. Disabil. Rehabil. 2018, 40, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavell, J.H. Metacognition and cognitive monitoring: A new area of cognitive–developmental inquiry. Am. Psychol. 1979, 34, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazancieux, A.; Souchay, C.; Casez, O.; Moulin, C.J.A. Metacognition and self-awareness in Multiple Sclerosis. Cortex 2019, 111, 238–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, C.; Blanc, F.; Brassat, D.; Zephir, H.; de Seze, J. CFSEP Cognitive function in radiologically isolated syndrome. Mult. Scler. 2010, 16, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anhoque, C.F.; Domingues, S.C.A.; Teixeira, A.L.; Domingues, R.B. Cognitive impairment in clinically isolated syndrome: A systematic review. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2010, 4, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochet, B.; Clavelou, P.; Defer, G.; De Seze, J.; Louapre, C.; Magnin, E.; Ruet, A.; Thomas-Anterion, C.; Vermersch, P. Cognitive Impairment in Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: Effect of Disease Duration, Age, and Progressive Phenotype. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, R.H.B.; Munschauer, F.; Linn, R.; Miller, C.; Murphy, E.; Foley, F.; Jacobs, L. Screening for multiple sclerosis cognitive impairment using a self-administered 15-item questionnaire. Mult. Scler. J. 2003, 9, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, R.H.B.; Zivadinov, R. Predicting neuropsychological abnormalities in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 245, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, L.; Merluzzi, N.M.; Mohr, D.C. The relationship among depression, subjective cognitive impairment, and neuropsychological performance in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2007, 13, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maor, Y.; Olmer, L.; Mozes, B. The relation between objective and subjective impairment in cognitive function among multiple sclerosis patients-the role of depression. Mult. Scler. J. 2001, 7, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Jougleux-Vie, C.; Duhin, E.; Deken, V.; Outteryck, O.; Vermersch, P.; Zéphir, H. Does Fatigue Complaint Reflect Memory Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis? Mult. Scler. Int. 2014, 2014, 692468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carone, D.A.; Benedict, R.H.B.; Munschauer, F.E.; Fishman, I.; Weinstock-Guttman, B. Interpreting patient/informant discrepancies of reported cognitive symptoms in MS. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2005, 11, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weld-Blundell, I.V.; Grech, L.; Learmonth, Y.C.; Marck, C.H. Lifestyle and complementary therapies in multiple sclerosis guidelines: Systematic review. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2022, 145, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, J.; Saddal, S.R.D.; Bosmans, J.E.; de Groot, V.; de Jong, B.A.; Klein, M.; Ruitenberg, M.F.L.; Schaafsma, F.G.; Schippers, E.C.F.; Schoonheim, M.M.; et al. Don’t be late! Postponing cognitive decline and preventing early unemployment in people with multiple sclerosis: A study protocol. BMC Neurol. 2024, 24, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumowski, J.F.; Benedict, R.; Enzinger, C.; Filippi, M.; Geurts, J.J.; Hamalainen, P.; Hulst, H.; Inglese, M.; Leavitt, V.M.; Rocca, M.A.; et al. Cognition in multiple sclerosis: State of the field and priorities for the future. Neurology 2018, 90, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonheim, M.M.; Meijer, K.A.; Geurts, J.J.G. Network collapse and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoonheim, M.M.; Broeders, T.A.A.; Geurts, J.J.G. The network collapse in multiple sclerosis: An overview of novel concepts to address disease dynamics. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 35, 103108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumowski, J.F. Cognitive Reserve as a Useful Concept for Early Intervention Research in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissart, H.; Leroy, M. ProCog-SEP: Programme de Remédiation Cognitive Chez les Personnes Atteintes de Sclérose En Plaques et en Réduire L’impact au Quotidien; Independently Published: Chicago, IL, USA, 2020; 168p. [Google Scholar]
- Brissart, H.; Morèle, E.; Perf, M.L.; Leininger, M. Manag’mind: Un Matériel Modulable Pour la Prise en Charge Cognitive de la Mémoire de Travail, 1st ed.; DE BOECK SUP: Paris Louvain-la-Neuve (Belgique), France, 2018; 136 p. [Google Scholar]
- Gaspari, M.; Zini, F.; Stecchi, S. Enhancing cognitive rehabilitation in multiple sclerosis with a disease-specific tool. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2023, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, R.; Rowles, W.; Zhao, C.; Anderson, A.; Friedman, S.; Langdon, D.; Alexander, A.; Sacco, S.; Henry, R.; Gazzaley, A.; et al. A novel in-home digital treatment to improve processing speed in people with multiple sclerosis: A pilot study. Mult. Scler. J. 2021, 27, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, R.; Russo, M.; Gasparini, S.; Leonardi, S.; Foti Cuzzola, M.; Sciarrone, F.; Zichittella, C.; Sessa, E.; Maggio, M.G.; De Cola, M.C.; et al. Do people with multiple sclerosis benefit from PC-based neurorehabilitation? A pilot study. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 2021, 28, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harand, C.; Daniel, F.; Mondou, A.; Chevanne, D.; Creveuil, C.; Defer, G. Neuropsychological management of multiple sclerosis: Evaluation of a supervised and customized cognitive rehabilitation program for self-used at home (SEPIA): Protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2019, 20, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baetge, S.J.; Filser, M.; Renner, A.; Raithel, L.M.; Lau, S.; Pöttgen, J.; Penner, I.-K. Supporting brain health in multiple sclerosis: Exploring the potential of neuroeducation combined with practical mindfulness exercises in the management of neuropsychological symptoms. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 3058–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manera, V.; Ben-Sadoun, G.; Aalbers, T.; Agopyan, H.; Askenazy, F.; Benoit, M.; Bensamoun, D.; Bourgeois, J.; Bredin, J.; Bremond, F.; et al. Recommendations for the Use of Serious Games in Neurodegenerative Disorders: 2016 Delphi Panel. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, M.G.; Russo, M.; Cuzzola, M.F.; Destro, M.; La Rosa, G.; Molonia, F.; Bramanti, P.; Lombardo, G.; De Luca, R.; Calabrò, R.S. Virtual reality in multiple sclerosis rehabilitation: A review on cognitive and motor outcomes. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 65, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruet, A.; Brochet, B. Cognitive assessment in patients with multiple sclerosis: From neuropsychological batteries to ecological tools. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 63, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyda, M. From visual simulation to virtual reality to games. Computer 2005, 38, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, R.M.; Rush, G.; Zhao, C.; Rowles, W.; Garcha, P.; Morrissey, J.; Schembri, A.; Alailima, T.; Langdon, D.; Possin, K.; et al. A Videogame-Based Digital Therapeutic to Improve Processing Speed in People with Multiple Sclerosis: A Feasibility Study. Neurol. Ther. 2019, 8, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, R. Miller Motivational Interviewing, Fourth Edition: Helping People Change and Grow, 4th ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2023; 338p. [Google Scholar]
- Arkowitz, H.; Miller, W.R.; Rollnick, S. Motivational Interviewing in the Treatment of Psychological Problems, 2nd ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; 400p. [Google Scholar]
- Easthall, C.; Song, F.; Bhattacharya, D. A meta-analysis of cognitive-based behaviour change techniques as interventions to improve medication adherence. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e002749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norcross, J.C.; Wampold, B.E. A new therapy for each patient: Evidence-based relationships and responsiveness. J. Clin. Psychol. 2018, 74, 1889–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.B.; Devereaux, P.J.; Guyatt, G.H. Clinical expertise in the era of evidence-based medicine and patient choice. BMJ Evid. Based Med. 2002, 7, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.; Bennett, S.; Del Mar, C. Evidence-Based Practice Across the Health Professions, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Chatswood, NSW, Australia, 2017; 470p. [Google Scholar]
- Barbarulo, A.M.; Lus, G.; Signoriello, E.; Trojano, L.; Grossi, D.; Esposito, M.; Costabile, T.; Lanzillo, R.; Saccà, F.; Morra, V.B.; et al. Integrated Cognitive and Neuromotor Rehabilitation in Multiple Sclerosis: A Pragmatic Study. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On behalf of the CogEx Research Team; Feinstein, A.; Amato, M.P.; Brichetto, G.; Chataway, J.; Chiaravalloti, N.; Dalgas, U.; DeLuca, J.; Feys, P.; Filippi, M.; et al. Study protocol: Improving cognition in people with progressive multiple sclerosis: A multi-arm, randomized, blinded, sham-controlled trial of cognitive rehabilitation and aerobic exercise (COGEx). BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalb, R.; Beier, M.; Benedict, R.H.; Charvet, L.; Costello, K.; Feinstein, A.; Gingold, J.; Goverover, Y.; Halper, J.; Harris, C.; et al. Recommendations for cognitive screening and management in multiple sclerosis care. Mult. Scler. J. 2018, 24, 1665–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills, O.; Brischetto, D.; Zoszak, K.; Allogmanny, S.; McMahon, A.-T.; Haartsen, J.; Probst, Y. Establishing consensus on lifestyle recommendations and behaviour change strategies to promote brain health-focussed care for multiple sclerosis: A modified e-Delphi study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2024, 92, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, O.; Probst, Y. Towards new perspectives: A scoping review and meta-synthesis to redefine brain health for multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, C.L.A.; Endres, M.; Sander, A.; Crean, M.; Subramaniam, S.; Carvalho, V.; Di Liberto, G.; Franco, O.H.; Pijnenburg, Y.; Leonardi, M.; et al. The European Academy of Neurology Brain Health Strategy: One brain, one life, one approach. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 2559–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).