Comparative Accuracy of the ECORE-BF Index Versus Non-Insulin-Based Insulin Resistance Markers in over 400,000 Spanish Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Variables and Measurements
- TyG = Ln [fasting triglycerides (mg/dL) × fasting glucose (mg/dL)/2]
- TyG-BMI = TyG × BMI
- METS-IR = Ln [(2 × fasting glucose) + triglycerides] × BMI/[Ln(HDL-C)]
- SPISE = 600 × HDL-C^0.185/(Triglycerides^0.2 × BMI^1.338)
2.3. Classification of Insulin Resistance Risk
2.4. Sociodemographic Data and Social Class
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Strengths and Limitations
4.2. Contributions
4.3. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CCC | Concordance Correlation Coefficient (Lin’s) |
| CNAE-11 | National Classification of Economic Activities 2011 (Spain) |
| CUN-BAE | Clínica Universidad de Navarra Body Adiposity Estimator |
| DBP | Diastolic Blood Pressure |
| ECORE-BF | Córdoba Equation for Estimation of Body Fat |
| FSIGT | Frequently Sampled Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Test |
| GLUT4 | Glucose Transporter Type 4 |
| HDL-C | High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance |
| IDISBA | Health Research Institute of the Balearic Islands (Institut d’Investigació Sanitària de les Illes Balears) |
| IR | Insulin Resistance |
| IUNICS | University Institute for Research in Health Sciences (Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Ciencias de la Salud) |
| LDL-C | Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| MASLD | Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease |
| METS-IR | Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance |
| NAFLD | Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| PMCID | PubMed Central Identifier |
| PMID | PubMed Identifier |
| QUICKI | Quantitative Insulin Sensitivity Check Index |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SBP | Systolic Blood Pressure |
| SEE | Spanish Society of Epidemiology (Sociedad Española de Epidemiología) |
| SPISE | Single-Point Insulin Sensitivity Estimator |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| TLA | Three-Letter Acronym |
| TyG | Triglyceride–Glucose Index |
| TyG-BMI | Triglyceride–Glucose Index adjusted for BMI |
| WHtR | Waist-to-Height Ratio |
References
- Merz, K.E.; Thurmond, D.C. Role of Skeletal Muscle in Insulin Resistance and Glucose Uptake. Compr. Physiol. 2020, 10, 785–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahmed, B.; Sultana, R.; Greene, M.W. Adipose tissue and insulin resistance in obese. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasubbu, K.; Devi Rajeswari, V. Impairment of insulin signaling pathway PI3K/Akt/mTOR and insulin resistance induced AGEs on diabetes mellitus and neurodegenerative diseases: A perspective review. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2023, 478, 1307–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gerwen, J.; Shun-Shion, A.S.; Fazakerley, D.J. Insulin signalling and GLUT4 trafficking in insulin resistance. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2023, 51, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sangwung, P.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I.; Knowles, J.W. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Insulin Resistance, and Potential Genetic Implications. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Bousvarou, M.D.; Kostara, C.E.; Papakonstantinou, E.J.; Salamou, E.; Guzman, E. Insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 3000605231164548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, Z. Biological aging mediates the associations of metabolic score for insulin resistance with all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality among US adults: A nationwide cohort study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 3552–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianopoulos, I.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Daskalopoulou, S.S. Adiponectin and Adiponectin Receptors in Atherosclerosis. Endocr. Rev. 2025, 46, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mir, S.A.; Narasimhan, K.; Annadurai, J.K.; Vaitheeswari Ji, S.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Eriksson, J.G.; Leow, M.K.; Wenk, M.R.; Torta, F.; Khoo, C.M. Lipidomic Signatures of Insulin Resistance Identified from Hyperinsulinemic-Euglycemic Clamp Studies in Asian Men. Diabetes 2025, 11, db250010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongwananuruk, T.; Prasongvej, P.; Chantrapanichkul, P.; Indhavivadhana, S.; Tanmahasamut, P.; Rattanachaiyanont, M.; Techatraisak, K.; Angsuwathana, S. Measures of Serum Markers HbA1c, HOMA-IR, HOMA-β, QUICKI and G/I Ratio as Predictors of Abnormal Glucose Tolerance Among Thai Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tosoratto, J.; Carriedo, B.; Cantón, C. Cardiometabolic risk level in 43074 Spanish office workers: Associated variables. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Hu, P.; Hou, X.; Sun, Y.; Jiao, M.; Peng, L.; Dai, Z.; Yin, X.; Liu, R.; Li, Y. Association between triglyceride-glucose related indices and mortality among individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Duan, M.; Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Miao, G.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhao, X. Metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the general population: Evidence from NHANES 2001–2018. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cederholm, J.; Zethelius, B. SPISE and other fasting indexes of insulin resistance: Risks of coronary heart disease or type 2 diabetes. Comparative cross-sectional and longitudinal aspects. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 124, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Molina-Luque, R.; Romero-Saldaña, M.; Álvarez-Fernández, C.; Bennasar-Veny, M.; Álvarez-López, Á.; Molina-Recio, G. Equation Córdoba: A Simplified Method for Estimation of Body Fat (ECORE-BF). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 16, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marina Arroyo, M.; Ramírez Gallegos, I.; López-González, A.A.; Vicente-Herrero, M.T.; Vallejos, D.; Tárraga López, P.J.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I. Equation Córdoba body fat values according to sociodemographic variables and healthy habits in 386924 Spanish workers. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marina Arroyo, M.; Ramírez Gallegos, I.; Paublini, H.; López-González, Á.A.; Tárraga López, P.J.; Martorell Sánchez, C.; Sastre-Alzamora, T.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I. Usefulness of the Córdoba Equation for Estimating Body Fat When Determining the Level of Risk of Developing Diabetes Type 2 or Prediabetes. Medicina 2025, 61, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sastre-Alzamora, T.; Tomás-Gil, P.; Paublini, H.; Pallarés, L.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I.; López-González, A.A. Relationship between heart age and insulin resistance risk scales in 139634 Spanish workers. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Lu, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhou, X. Association between non-insulin-based insulin resistance indices and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: A retrospective study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Domingo-Salvany, A.; Bacigalupe, A.; Carrasco, J.M.; Espelt, A.; Ferrando, J.; Borrell, C.; del Grupo de Determinantes Sociales de la Sociedad Española de Epidemiología. Propuestas de clase social neoweberiana y neomarxista a partir de la Clasificación Nacional de Ocupaciones 2011. Gac. Sanit. 2013, 27, 263–272. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiló Juanola, M.C.; López-González, A.A.; Tomás-Gil, P.; Paublini, H.; Tárraga-López, P.J.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I. Influence of tobacco consumption on the values of different insulin resistance risk scales and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatic fibrosis scales in 418,343 spanish people. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 29.0; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Marina Arroyo, M.; Ramírez Gallegos, I.; López-González, Á.A.; Vicente-Herrero, M.T.; Vallejos, D.; Sastre-Alzamora, T.; Ramírez Manent, J.I. Usefulness of the ECORE-BF Scale to Determine Atherogenic Risk in 386,924 Spanish Workers. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Muhammad, I.F.; Bao, X.; Nilsson, P.M.; Zaigham, S. Triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index is a predictor of arterial stiffness, incidence of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A longitudinal two-cohort analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 9, 1035105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Contreras-Hernández, I.F.; Vargas-De-León, C.; García-Cortes, L.R.; Flores-Miranda, A.; Romero-Nava, R.; Ocharán-Hernández, M.E. Comparison of Ten Surrogate Insulin Resistance and Obesity Markers to Identify Metabolic Syndrome in Mexican Adults. Metabolites 2024, 14, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Molina-Luque, R.; Yañez, A.M.; Bennasar-Veny, M.; Romero-Saldaña, M.; Molina-Recio, G.; López-González, Á.A. A Comparison of Equation Córdoba for Estimation of Body Fat (ECORE-BF) with Other Prediction Equations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hoddy, K.K.; Axelrod, C.L.; Mey, J.T.; Hari, A.; Beyl, R.A.; Blair, J.B.; Dantas, W.S.; Kirwan, J.P. Insulin resistance persists despite a metabolically healthy obesity phenotype. Obesity 2022, 30, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Imerb, N.; Thonusin, C.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Aging, obese-insulin resistance, and bone remodeling. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020, 191, 111335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayyaz, K.; Bataineh, M.F.; Ali, H.I.; Al-Nawaiseh, A.M.; Al-Rifai’, R.H.; Shahbaz, H.M. Validity of Measured vs. Self-Reported Weight and Height and Practical Considerations for Enhancing Reliability in Clinical and Epidemiological Studies: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Krijnen, H.K.; Hoveling, L.A.; Liefbroer, A.C.; Bültmann, U.; Smidt, N. Socioeconomic differences in metabolic syndrome development among males and females, and the mediating role of health literacy and self-management skills. Prev. Med. 2022, 161, 107140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Herrero, M.T.; Egea-Sancho, M.; Ramírez Iñiguez de la Torre, M.V.; López-González, A.A. Relación de los índices de adiposidad visceral (VAI) y adiposidad disfuncional (DAI) con las escalas de riesgo de resistencia a la insulina y prediabetes. Acad. J. Health Sci. 2024, 39, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, E.; Zhang, C. Estimated glucose disposal rate outperforms other insulin resistance surrogates in predicting incident cardiovascular diseases in cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome stages 0–3 and the development of a machine learning prediction model: A nationwide prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lambert, D.C.; Kane, J.; Newberry, C. Lifestyle Therapy for Obesity. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 34, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaskolka Meir, A.; Tsaban, G.; Rinott, E.; Zelicha, H.; Schwarzfuchs, D.; Gepner, Y.; Rudich, A.; Shelef, I.; Blüher, M.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Individual response to lifestyle interventions: A pooled analysis of three long-term weight loss trials. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2025, zwaf308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
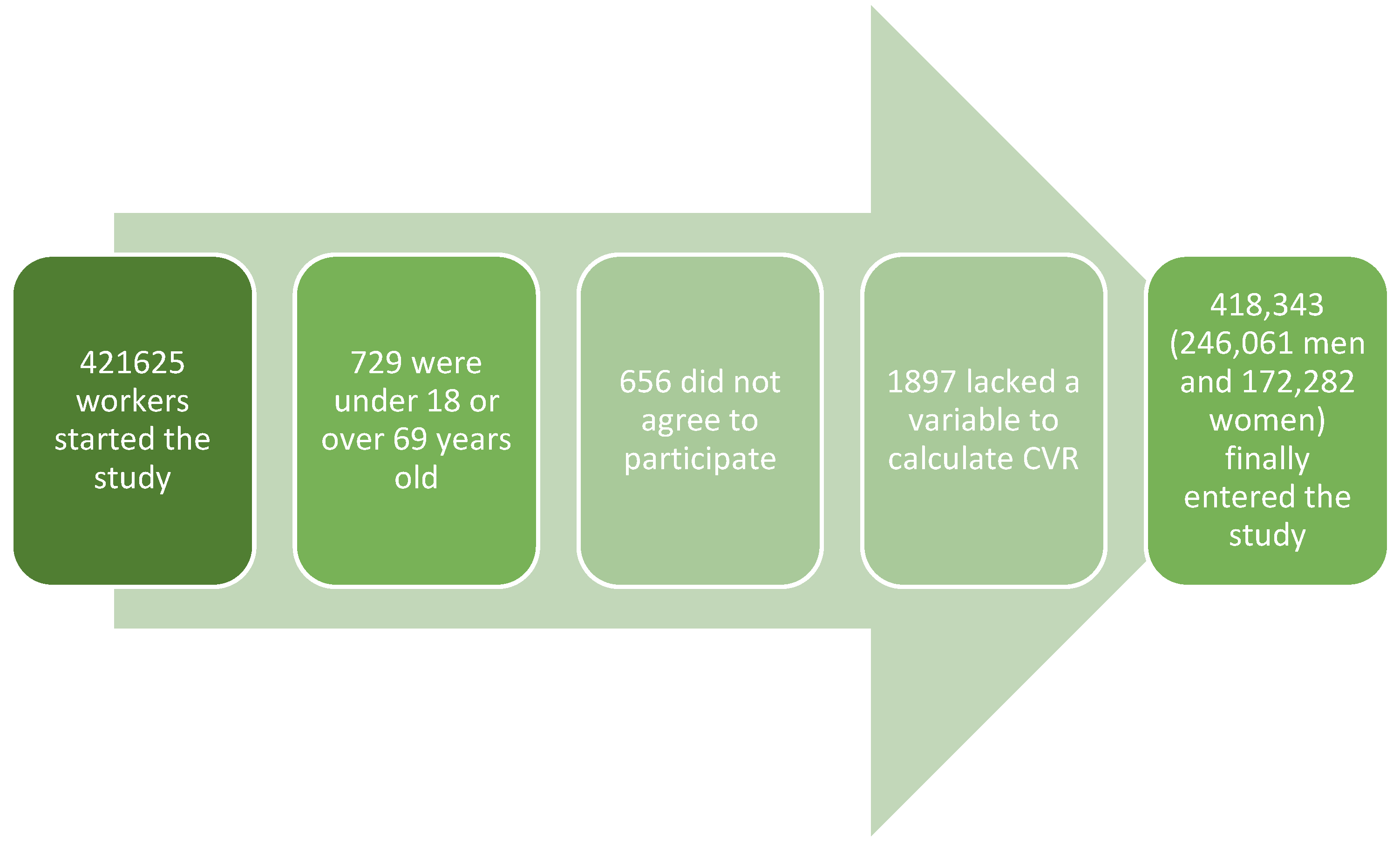

| Women | Men | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 172.282 | n = 246.061 | n = 418.343 | ||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p-value | |
| Age | 39.6 (10.8) | 40.6 (11.1) | 40.2 (11.0) | <0.0001 |
| Height | 161.8 (6.5) | 174.6 (7.0) | 169.4 (9.3) | <0.0001 |
| Weight | 66.2 (14.0) | 81.4 (14.7) | 75.1 (16.2) | <0.0001 |
| Waist | 74.8 (10.6) | 86.2 (11.1) | 81.5 (12.2) | <0.0001 |
| SBP | 117.4 (15.7) | 128.2 (15.5) | 123.7 (16.5) | <0.0001 |
| DBP | 72.6 (10.4) | 77.8 (11.0) | 75.6 (11.0) | <0.0001 |
| Cholesterol | 190.6 (35.8) | 192.6 (38.9) | 191.8 (37.7) | <0.0001 |
| HDL-c | 56.8 (8.7) | 50.3 (8.5) | 53.0 (9.1) | <0.0001 |
| LDL-c | 116.1 (34.8) | 118.0 (36.7) | 117.2 (35.9) | <0.0001 |
| Triglycerides | 89.1 (46.2) | 123.7 (86.4) | 109.5 (74.6) | <0.0001 |
| Glycemia | 87.8 (15.1) | 93.3 (21.3) | 91.0 (19.2) | <0.0001 |
| % | % | % | p-value | |
| 18–29 years | 20.7 | 18.8 | 19.6 | <0.0001 |
| 30–39 years | 29.7 | 27.6 | 28.4 | |
| 40–49 years | 29.6 | 30.0 | 29.9 | |
| 50–59 years | 16.8 | 19.7 | 18.5 | |
| ≥60 years | 3.2 | 3.9 | 3.6 | |
| Social class I | 6.9 | 4.9 | 5.7 | <0.0001 |
| Social class II | 23.4 | 14.9 | 18.4 | |
| Social class III | 69.7 | 80.3 | 75.9 | |
| Non-smokers | 67.2 | 66.6 | 66.9 | <0.0001 |
| Smokers | 32.8 | 33.4 | 33.2 |
| Men | Women | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean (SD) | p-Value | n | Mean (SD) | p-Value | |
| TyG index normal | 178,806 | 24.2 (6.0) | <0.001 | 150,798 | 34.4 (6.9) | <0.001 |
| TyG index high | 67,255 | 28.9 (5.8) | 21,484 | 40.6 (7.4) | ||
| TyG-BMI normal | 179,496 | 23.4 (4.4) | <0.001 | 133,436 | 33.1 (5.3) | <0.001 |
| TyG-BMI high | 53,318 | 33.0 (3.8) | 20,674 | 47.0 (4.1) | ||
| METS-IR normal | 218,013 | 24.1 (5.2) | <0.001 | 161,225 | 34.1 (6.2) | <0.001 |
| METS-IR high | 28,048 | 36.0 (3.8) | 11,057 | 50.5 (3.8) | ||
| SPISE normal | 208,871 | 23.8 (5.1) | <0.001 | 157,570 | 33.8 (6.0) | <0.001 |
| SPISE high | 37,190 | 34.8 (4.1) | 14,712 | 49.2 (4.1) |
| Men | Women | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECORE-BF Obesity | n | % | p-Value | n | % | p-Value |
| TyG index normal | 178,806 | 42.8 | <0.001 | 150,798 | 42.5 | <0.001 |
| TyG index high | 67,255 | 75.7 | 21,484 | 77.7 | ||
| TyG-BMI normal | 179,496 | 45.6 | <0.001 | 133,436 | 41.3 | <0.001 |
| TyG-BMI high | 53,318 | 74.8 | 20,674 | 75.8 | ||
| METS-IR normal | 218,013 | 45.5 | <0.001 | 161,225 | 43.2 | <0.001 |
| METS-IR high | 28,048 | 99.8 | 11,057 | 99.9 | ||
| SPISE normal | 208,871 | 43.3 | <0.001 | 157,570 | 41.9 | <0.001 |
| SPISE high | 37,190 | 99.9 | 14,712 | 99.9 |
| Men n = 246,061 | AUC (95% CI) | Cutoff-Sens-Specif-Youden |
| TyG index high | 0.698 (0.695–0.700) | 26.5-65.0-64.8-0.298 |
| TyG-BMI high | 0.966 (0.965–0.966) | 28.7-90.0-89.4-0.794 |
| SPISE-IR high | 0.952 (0.951–0.954) | 29.9-87.8-88.7-0.757 |
| METS-IR high | 0.968 (0.967–0.967) | 31.1-90.1-89.8-0.799 |
| Women n = 172,282 | AUC (95% CI) | Cutoff-Sens-Specif-Youden |
| TyG index high | 0.726 (0.722–0.730) | 36.8-67.8-67.8-0.356 |
| TyG-BMI high | 0.987 (0.987–0.988) | 41.4-94.0-93.7-0.877 |
| SPISE-IR high | 0.987 (0.986–0.987) | 43.3-94.3-94.0-0.883 |
| METS-IR high | 0.992 (0.992–0.993) | 44.7-95.6-95.3-0.909 |
| Men | ECORE-BF | TyG | TyG-BMI | METS-IR | SPISE-IR | BMI | WHtR |
| ECORE-BF | 1 | 0.65 | 0.83 | 0.8 | 0.72 | 0.87 | 0.85 |
| TyG | 0.65 | 1 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.6 | 0.58 |
| TyG-BMI | 0.83 | 0.78 | 1 | 0.88 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.8 |
| METS-IR | 0.8 | 0.74 | 0.88 | 1 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.78 |
| SPISE-IR | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.68 |
| BMI | 0.87 | 0.6 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.86 |
| WHtR | 0.85 | 0.58 | 0.8 | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.86 | 1 |
| Women | ECORE-BF | TyG | TyG-BMI | METS-IR | SPISE-IR | BMI | WHtR |
| ECORE-BF | 1 | 0.68 | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.74 | 0.89 | 0.87 |
| TyG | 0.68 | 1 | 0.8 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.6 |
| TyG-BMI | 0.86 | 0.8 | 1 | 0.9 | 0.76 | 0.85 | 0.83 |
| METS-IR | 0.83 | 0.77 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.81 |
| SPISE-IR | 0.74 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.78 | 1 | 0.72 | 0.7 |
| BMI | 0.89 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.72 | 1 | 0.88 |
| WHtR | 0.87 | 0.6 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.7 | 0.88 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marina Arroyo, M.; Obrador de Hevia, J.; López-González, Á.A.; Tárraga López, P.J.; Busquets-Cortés, C.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I. Comparative Accuracy of the ECORE-BF Index Versus Non-Insulin-Based Insulin Resistance Markers in over 400,000 Spanish Adults. Diabetology 2025, 6, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110130
Marina Arroyo M, Obrador de Hevia J, López-González ÁA, Tárraga López PJ, Busquets-Cortés C, Ramírez-Manent JI. Comparative Accuracy of the ECORE-BF Index Versus Non-Insulin-Based Insulin Resistance Markers in over 400,000 Spanish Adults. Diabetology. 2025; 6(11):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110130
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarina Arroyo, Marta, Joan Obrador de Hevia, Ángel Arturo López-González, Pedro J. Tárraga López, Carla Busquets-Cortés, and José Ignacio Ramírez-Manent. 2025. "Comparative Accuracy of the ECORE-BF Index Versus Non-Insulin-Based Insulin Resistance Markers in over 400,000 Spanish Adults" Diabetology 6, no. 11: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110130
APA StyleMarina Arroyo, M., Obrador de Hevia, J., López-González, Á. A., Tárraga López, P. J., Busquets-Cortés, C., & Ramírez-Manent, J. I. (2025). Comparative Accuracy of the ECORE-BF Index Versus Non-Insulin-Based Insulin Resistance Markers in over 400,000 Spanish Adults. Diabetology, 6(11), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110130







