Refractory Hypoxemia as a Trigger for Systemic Thrombolysis in Intermediate-High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction and Clinical Significance
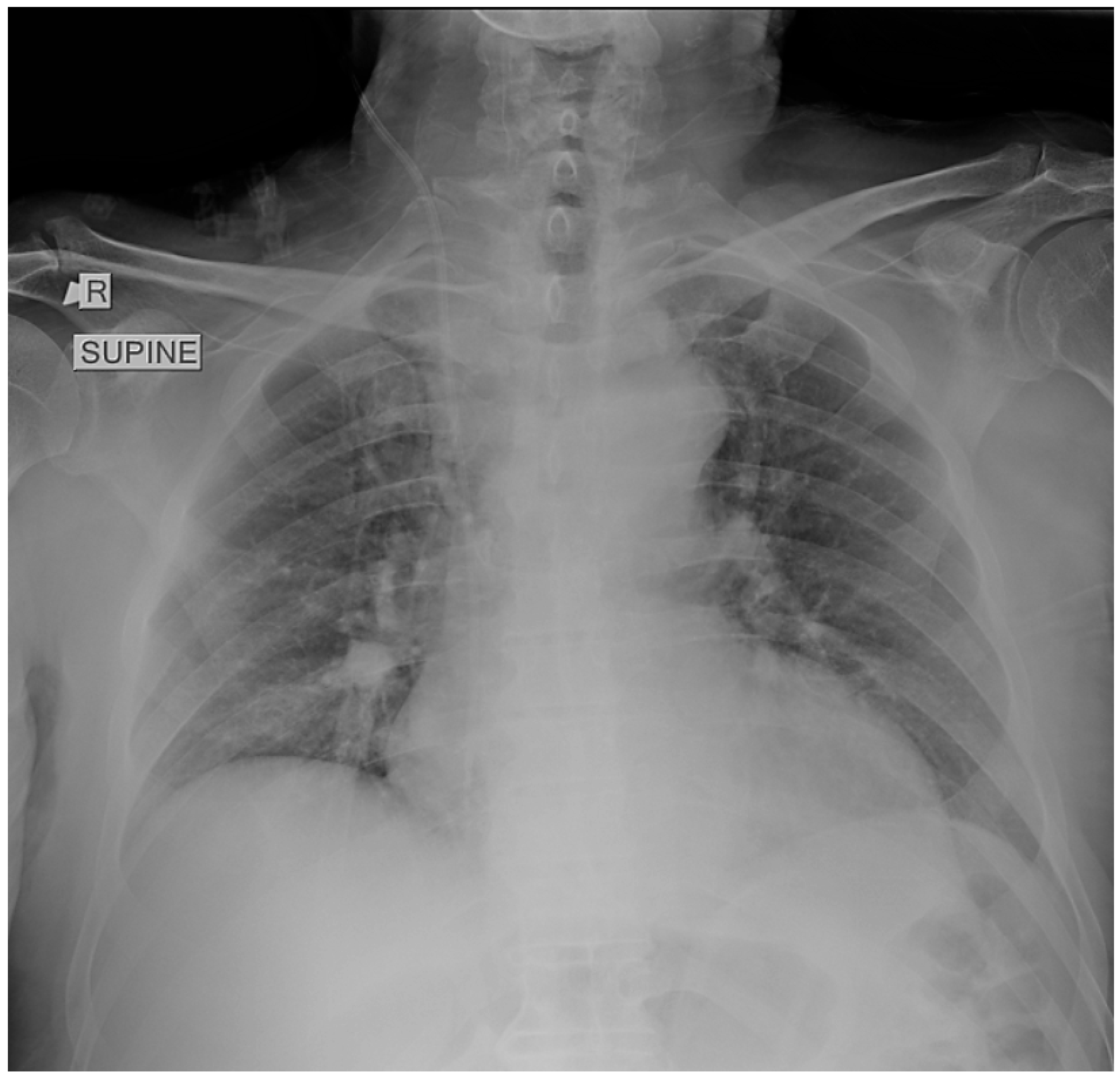
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BNP | B-type natriuretic peptide |
| CDT | catheter-directed therapy |
| ECMO | extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| FiO2 | fraction of inspired oxygen |
| PaCO2 | partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood |
| PaO2 | partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood |
| PE | pulmonary embolism |
| PFO | patent foramen ovale |
| RV | right ventricular |
| TAPSE | tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion |
References
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jiménez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, G.; Vicaut, E.; Danays, T.; Agnelli, G.; Becattini, C.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Bluhmki, E.; Bouvaist, H.; Brenner, B.; Couturaud, F.; et al. Fibrinolysis for patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, F.A.; Meyer, G.; Konstantinides, S. Management of intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism: Uncertainties and challenges. Eur. J. Haematol. 2015, 95, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, C.; Aissaoui, N.; Meneveau, N.; Bouvaist, H.; Rousseau, H.; Puymirat, E.; Sapoval, M.; Flecher, E.; Meyer, G.; Sanchez, O.; et al. Reperfusion therapies in pulmonary embolism-state of the art and expert opinion: A position paper from the “Unité de Soins Intensifs de Cardiologie” group of the French Society of Cardiology. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 113, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Barco, S. Systemic Thrombolytic Therapy for Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Who Is a Candidate? Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 38, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, G. Advanced Management of Intermediate- and High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: JACC Focus Seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuin, M.; Piazza, G.; Rigatelli, G.; Bongarzoni, A.; Enea, I.; Casazza, F.; Picariello, C.; Bilato, C.; Roncon, L. Clinical phenotypes and risk of early hemodynamic deterioration in intermediate-high-risk patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Thromb. Res. 2025, 252, 109380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Piedras, M.F.; Porres-Aguilar, M.; Mukherjee, D.; Cueto-Robledo, G.; Roldan-Valadez, E.; Tapia-Vargas, P.A. High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygenation Successfully Used as Bridge Therapy for Systemic Thrombolysis in COVID-19 Associated Intermediate-high Risk Pulmonary Embolism. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2022, 47, 101000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lacroix, G.; Pons, F.; D’Aranda, E.; Legodec, J.; Romanat, P.E.; Goutorbe, P. High-flow oxygen, a therapeutic bridge while awaiting thrombolysis in pulmonary embolism? Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 31, 463.e1–463.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malli, F.; Dimeas, I.E.; Sinis, S.I.; Karetsi, E.; Nana, P.; Kouvelos, G.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. Bilateral Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Due to Right Common Iliac Artery Aneurysm with a Contained Rupture. Medicina 2022, 58, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Moini, C.; Monchi, M.; Ramamourthy, U.; Awede, R.; Cabot, B.; Hraiech, K.; Jochmans, S. Effect of half-dose thrombolysis on hypoxemia duration in intermediate risk pulmonary embolism. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplovitch, E.; Shaw, J.R.; Douketis, J. Thrombolysis in Pulmonary Embolism: An Evidence-Based Approach to Treating Life-Threatening Pulmonary Emboli. Crit. Care Clin. 2020, 36, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, W.C.; Sullivan, L.; Odish, M.F.; Desai, B.; Morris, T.A.; Fernandes, T.M. Management Strategies for Acute Pulmonary Embolism in the ICU. Chest 2024, 166, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kültürsay, B.; Tanyeri, S.; Keskin, B.; Tokgöz, H.C.; Sırma, D.; Buluş, Ç.; Atıcı, Ş.Z.; Çiçek, Ş.N.; Erdoğan, F.B.; Sekban, A.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Reduced-Dose and Slow-Infusion Intravenous Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator Regimen in Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism at Intermediate-High Risk. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2025, 29, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.C.; Stevens, H.; Peter, K.; McFadyen, J.D. Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: Current Perspectives and Future Directions. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liew, J.; Stevens, J.; Slatore, C. Refractory Hypoxemia in a Patient with Submassive Pulmonary Embolism and an Intracardiac Shunt: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Perm. J. 2018, 22, 17–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, Y.; Du, X.; Zhou, L.; Guan, J.; Sun, Y.; Sun, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, D.; Ding, Y.; Shi, G. Use of the PaO2/FiO2 ratio in acute pulmonary embolism: A simple and reliable parameter to predict the risk stratification. J. Thorac. Dis. 2025, 17, 4681–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marti, C.; John, G.; Konstantinides, S.; Combescure, C.; Sanchez, O.; Lankeit, M.; Meyer, G.; Perrier, A. Systemic thrombolytic therapy for acute pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Becattini, C.; Agnelli, G.; Salvi, A.; Grifoni, S.; Pancaldi, L.G.; Enea, I.; Balsemin, F.; Campanini, M.; Ghirarduzzi, A.; Casazza, F.; et al. Bolus tenecteplase for right ventricle dysfunction in hemodynamically stable patients with pulmonary embolism. Thromb. Res. 2010, 125, e82–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boris, D.; Tamara, S.; Jovan, M.; Sandra, P.; Sonja, S.; Vladimir, M.; Tamara, K.P.; Ljiljana, K.; Irena, M.; Bojan, M.; et al. Comparing fibrinolytic strategies in intermediate-high-risk pulmonary embolism: Insights from a multicenter registry. Thromb. Res. 2025, 252, 109372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Weinberg, I.; Kadakia, M.; Wilensky, R.L.; Sardar, P.; Kumbhani, D.J.; Mukherjee, D.; Jaff, M.R.; Giri, J. Thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism and risk of all-cause mortality, major bleeding, and intracranial hemorrhage: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2014, 311, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellina, M.; Pavan, M.; Finardi, N.; Cicchetti, F.; Cè, M.; Biondetti, P.; Lanza, C.; Carriero, S.; Carrafiello, G. Advancements in Acute Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis and Treatment: A Narrative Review of Emerging Imaging Techniques and Intravascular Interventions. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Johnson, L.D.; Cole, J.C.; Erdman, M.J.; Boppana, L.K.T.; Najjar, N.; Shald, E.A.; Busey, K.V.; Stilley, K.L.; Ferreira, J.A. Safety and efficacy of thrombolytic interventions in the treatment of intermediate and high-risk pulmonary embolism. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2025, 36, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latsios, G.; Mantzouranis, E.; Kachrimanidis, I.; Theofilis, P.; Dardas, S.; Stroumpouli, E.; Aggeli, C.; Tsioufis, C. Recent advances in risk stratification and treatment of acute pulmonary embolism. World J. Cardiol. 2025, 17, 104983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimeas, I.E.; Vairami, P.; Zakynthinos, G.E.; McCarthy, C.; Daniil, Z. Refractory Hypoxemia as a Trigger for Systemic Thrombolysis in Intermediate-High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: A Case Report. Reports 2025, 8, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040253
Dimeas IE, Vairami P, Zakynthinos GE, McCarthy C, Daniil Z. Refractory Hypoxemia as a Trigger for Systemic Thrombolysis in Intermediate-High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: A Case Report. Reports. 2025; 8(4):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040253
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimeas, Ilias E., Panagiota Vairami, George E. Zakynthinos, Cormac McCarthy, and Zoe Daniil. 2025. "Refractory Hypoxemia as a Trigger for Systemic Thrombolysis in Intermediate-High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: A Case Report" Reports 8, no. 4: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040253
APA StyleDimeas, I. E., Vairami, P., Zakynthinos, G. E., McCarthy, C., & Daniil, Z. (2025). Refractory Hypoxemia as a Trigger for Systemic Thrombolysis in Intermediate-High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: A Case Report. Reports, 8(4), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8040253






